1. Array
Definition of Array
- a set of consecutive memory locations 연속된 메모리 위치들의 집합
- a collection of data of the same type 동일한 타입의 데이터 모음
- a set of pairs, <index, value>, such that each index that is defined has a value associated with it
각 인덱스가 정의되어 있고 그에 연관된 값을 가지는 <인덱스, 값> 쌍의 집합
Array as an ADT
ADT Array is
objects :
A set of pairs <index, value> where for each value of index there is a value from the set item.
index is a finite ordered set of one or more dimensions
functions:
for all A Array, i index, x item, j, size integer
Array Create(j,list) ::= return… // j 는 array의 size
item Retrieve(A,i) ::= if () return … else return … // 검색
Array Store(A,i,x) ::= if () return … else return … // 저장
end Array
Array Representation in C
Data structure for one dimensional Array
- int list[5] == int* list;
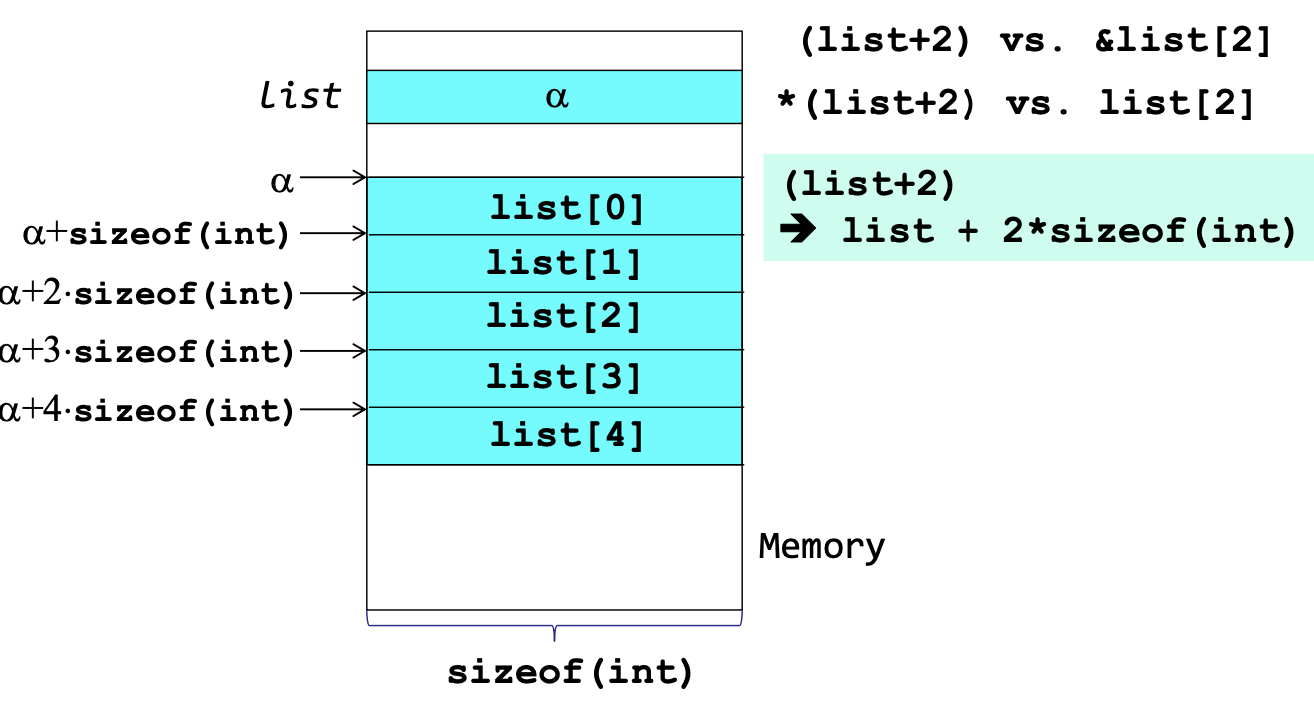
int 는 보통 4바이트임, 그래서 list+2는 사실 list + 2*sizeof(int) , 8임!
Example Array Program
#define MAX_SIZE 100
float sum(float [], int);
float input[MAX_SIZE], answer;
int i;
void main(void)
{
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++)
input[i] = i;
answer = sum(input, MAX_SIZE);
printf("The sum is: %f\n", answer);
}
float sum(float list[], int n) // *list 도 가능
{
int i;
float tempsum = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
tempsum += list[i];
return tempsum;
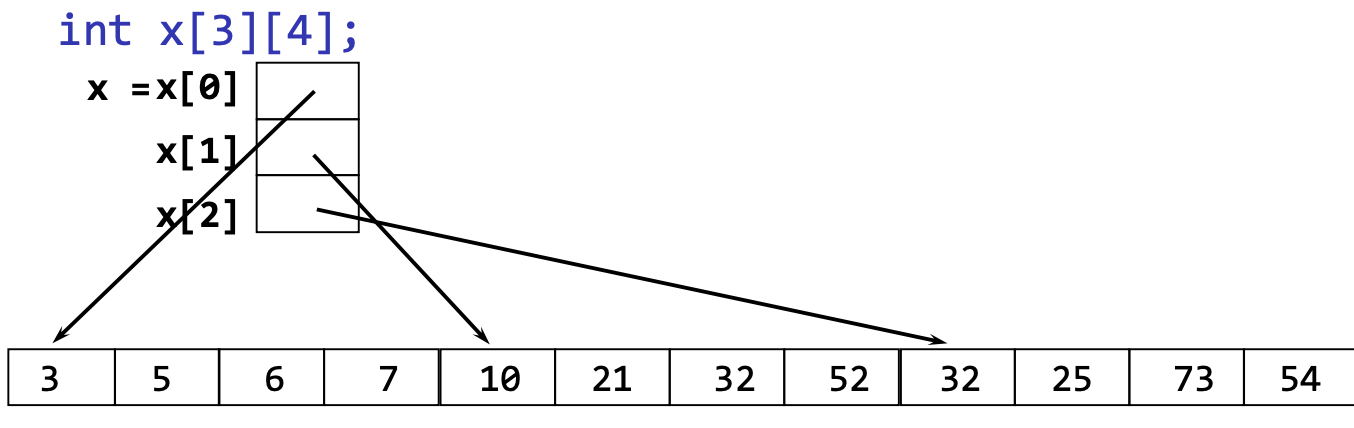
}2D Array Representation in C
int x[3][4]
첫 번째가 세로, 두 번째가 가로
array 속 array
첫 번째 array는 실제 int 값을 가지고 있는게 아니라 int 값을 가지고 있는 1d array들의 첫 번째 주소를 가지고 있는 array로 구성되어있음
Dynamically Allocated Arrays - One Dimension (1)
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 101
main()
{
int i, n, list[MAX_SIZE];
printf(“Enter the number of number to generate: ”);
scanf(“%d”, &n”); // n이 MAX_SIZE를 넘게되면 segmentation falut가 남
for (i=0;i<n;i++){
list[i]=rand()%1000;
printf (“%d\n”, list[i]);
}
}- n이 MAX_SIZE를 넘게되면 segmentation falut가 남
- 메모리 부족으로 프로그램이 컴파일 타임에서 에러날 수 있음
Dynamically Allocated Arrays - One Dimension (2)
int i, n, *list;
printf(“Enter the number of number to generate: ”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
if (n < 1) {
fprintf(stderr, “Improper value of n \n”);
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
list=malloc(n * sizeof(int));
if (list==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, “lack of memory\n”);
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}- 다른 건 *list
- n을 입력받고 n*sizeof(int) 만큼 동적할당 해줌
- N이 미리 정해져있으면 굳이 malloc 할 필요는 없지만 n이 runtime에 정해진다면 동적할당 방식이 효율적임
Dynamically Allocated Arrays - Two Dimension
int** make2dArray(int rows, int cols)
{
/* create a two dimensional rows cols array */
int** x, i;
/* get memory for row pointers */
MALLOC(x, rows * sizeof(*x));
/* get memory for each row */
for (i = 0; i < rows; i++)
MALLOC(x[i], cols * sizeof(**x);
return x;
}
void main()
{
int** myArray;
myArray=make2dArray(5,10);
myArray[2][4]=6;
}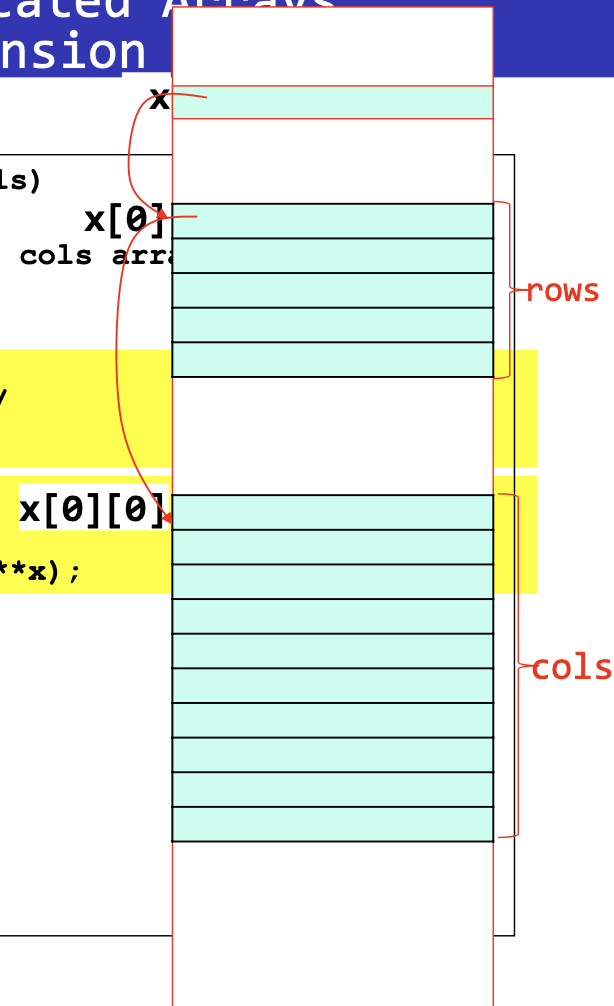
- 이중 포인터에 주의
- x는 각 행에 대한 포인터를 가리키는 포인터
- x에 rows sizeof(x) 바이트만큼 메모리를 할당
- x[i]는 각 행을 가리키는 1차원 배열에 대한 포인터
- x[i]는 행을 가리키고, 이 행에 cols 개의 int를 위한 메모리를 할당
Quiz 4
- Let length[i] be the desired length of row i of a two dimensional array.
Write a function similar to make2dArray() to create a two dimensional array such that row i has length[i] elements. - length[i]는 2차원 배열의 i번째 행의 원하는 길이
make2dArray() 함수와 유사하게, i번째 행이 length[i]개의 요소를 갖도록 2차원 배열을 생성하는 함수를 작성
정답은,, 안대영,,힌트
pi:
┌───┬───┬───┬───┬───┐
│ * │ * │ * │ * │ * │ ← 각 포인터는 각기 다른 행을 가리킴
└───┴───┴───┴───┴───┘
pi[0]: [int, int, int] (3개)
pi[1]: [int, int, int, int, int] (5개)
pi[2]: [int, int] (2개)
pi[3]: [int, int, int, int] (4개)
pi[4]: [int, int, int, int, int, int] (6개)2. Structures
Structures (1)
- A collection of data items, where each item is identified as to its type and name 데이터 아이템들의 집합
- array는 빠른 엑세스가 가능하지만, 모든 데이터가 같은 타입이어야함
- structure 구조체는 다른 타입도 하나로 묶을 수 있음
struct {
char name[10];
int age;
float salary;
} person;
strcpy(person.name, “korykang”);
person.age=34;
person.salary=35000;- 나만의 own structure data type 만들 수 있음
typedef struct humanBeing {
char name[10];
int age;
float salary;
};
typedef struct {
char name[10];
int age;
float salary;
} humanBeing;
둘이 동일함- 값이 같은지 확인할 때에
if (person1 == person2) {}
=> 가능?얘네 둘이가 같으려면 둘이 같은 object를 포인팅, 즉 가리키고 있어야함
단순히 value만 같아서는 안됨
- to embed a structure within a structure
typedef struct {
int month;
int day;
int year;
} date;
typedef struct humanBeing{
char name[10];
int age;
float salary;
date dob;
} humanBeing;
person1.dob.month=12; person1.dob.day=3;
person1.dob.year=1969;하나의 스트럭쳐가 다른 스트럭쳐 안에 임베딩, 즉 속할 수 있음
구조체 안 구조체가 멤버로 가능하다는 뜻
Quiz 5
- Develop a structure to represent each of the following geometric
objects: rectangle, triangle, and circle.
- 사각형, 삼각형, 원을 모두 표현할 수 있는 하나의 구조체를 구현
- 어떤 멤버를 넣을 것인지정답은,, 시크릿,,
3. Applications of Array
Ordered List
- 1d array
- numeric non-numeric 모두 가능
- example
- Days of a week (sun, mon, tues,,,)
- values in a deck of cards (1,2,3,4…)
- Operations
- Finding length n
- Reading the item
- Retrieving
- Replacing
- Inserting
- Deleting
Polynomial ADT
다항식
exponent, 지수 기준으로 ordered list 만들기

/* d = a + b, where a, b, and d are polynomials */
d = Zero();
while (! IsZero(a) && ! IsZero(b)) do {
switch COMPARE(LeadExp(a), LeadExp(b)) {
case -1: /* if LeadExp(a) < LeadExp(b) */
d = Attach (d, Coef(b, LeadExp(b)), LeadExp(b));
b = Remove(b, LeadExp(b));
break;
case 0: /* if LeadExp(a) == LeadExp(b) */
sum = Coef(a, LeadExp(a)) + Coef(b, LeadExp(b));
if (sum) {
d = Attach(d, sum, LeadExp(a));
a = Remove(a, LeadExp(a));
b = Remove(b, LeadExp(b));
}
break;
case 1: /* if LeadExp(a) > LeadExp(b) */
d = Attach(d, Coef(a, LeadExp(a)), LeadExp(a));
a = Remove(a, LeadExp(a));
}
}
- expo 기준으로 제일 큰 것부터 비교하며 최종 다항식에 반영하는 역할
Polynomial Representation (1)
#define MAX_DEGREE 101
typedef struct {
int degree;
float coef[MAX_DEGREE];
} polynomial;n < MAX_DEGREE
`a.degree = n, a.coef[i] = An-1`
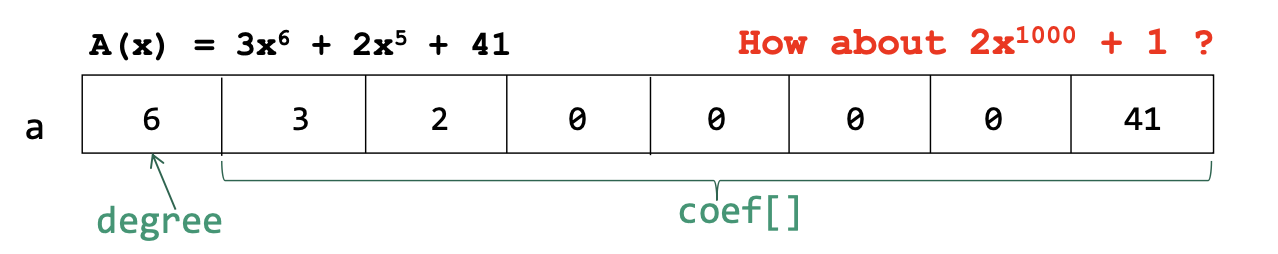
- Problem : 그렇다면 2x^1000 은???
Polynomial Representation (2)
#define MAX_TERMS 100
typedef struct {
float coef;
int expon;
} polynomial;
polynomial terms[MAX_TERMS];
int starta, finisha, startb, finishb, avail;
starta=0; finisha=1; startb=2; finishb=5; avail=6;
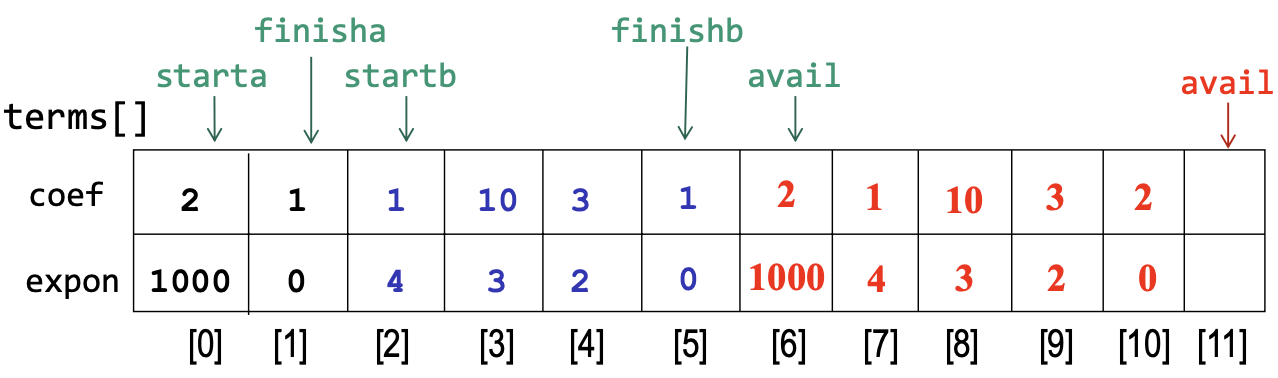
- 기존 1d array 방식보다 조금 더 효율적임
- 하나의 terms에 여러개의 poly를 넣기 때문에 시작, 끝을 표시할 수 있는 인덱스 변수를 넣어야함
Quiz 6
- Implement Remove() and Attach() in slide 21 using polynomial
representation in slide 22.
정답은 안돼~
그런데 이 문제 좀 어렵당,,