Basic Concepts
1. System Life Cycle
대규모 SW 시스템을 어떻게 개발하고 관리할지
- Requirements
- 프로젝트의 기본 사양을 정의
- Analysys
- 요구사항을 바탕으로 문제를 관리 가능한 부분으로 분해
- Design
- 시스템 상세 설계
- Refinement and coding
- 디자인된 것을 기반으로 실제로 코딩하는 것
- Verification
- 시스템의 정확성, 효율성, 오류 제거 보장
- Error removal
Abstract Data Type
- 데이터 구조의 인터페이스
- 오브젝트와 오퍼레이션들을 합쳐놓은 것
- 안의 구체적인 구현 내용을 모르더라도 그 자료구조를 사용할 수 있도록 정의하는 것
ADT Natural Number

- ADT 활용의 예시
- 주어진 함수들로 자연수를 다루는 방식과 연산들을 정의
Pointers
- & the address operator 주소 연산자
- the dereferencing (indirection) operator 역참조 연산자
- int i, *pi
- pi = &i
- 포인터 pi 에 변수 i의 주소를 저장
- i = 10; or *pi = 10;
- 둘은 같은 결과임
- 얘네 둘은 하나의 메모리 스페이스를 사용함
- 하나가 바뀌면 같이 바뀐다는 것
Dynamic Memory Allocation
int i, *pi;
float f, *pf;
// 메모리를 따로 할당해줘야함
pi = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
pf = (float *) malloc(sizeof(float));
*pi = 1024;
*pf= 3.14;
printf(“an integer = %d, a float = %f\n”, *pi, *pf);
free(pi);
free(pf);Quiz 1
- Write a simple C code for 2 dimensional array with dynamic memory allocation
-답은,,, 미공개 ^_^2. Algorithm Specification
- Definition : 어떤 문제를 해결하기 위한 instruction set
- 구성 요소
- Input
- Output
- Definiteness : 각 instruction은 명확하고 모호하지 않아야함
- Finiteness : 정해진 시간 안에 끝나야함 ↔ infinite
- Effectiveness : 효율적으로
Example: Selection Sort
// Selection Sort Suedo code
for (i=0;i<n;i++) {
Examine list[i] to list[n-1] and suppose that
the smallest integer is at list[min];
Interchange list[i] and list[min];
}
// swap function
void swap(int *x, int *y) {
int temp *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
#define SWAP(x,y,t) ((t)=(x),(x)=(y),(y)=(t))Selection Sort
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 101
#define SWAP(x, y, t) ((t) = (x), (x) = (y), (y) = (t))
// Selection Sort
void sort(int [], int);
void main(void)
{
int i, n;
int list[MAX_SIZE];
printf(“Enter the number of numbers to generate: ”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
if(n<1 || n> MAX_SIZE) {
fprintf(stderr, “Improper value of n\n”);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
/* randomly generate numbers*/
list[i] = rand() % 1000;
printf(“%d”, list[i]);
}
sort(list, n);
printf(“\n Sorted array:\n”);
for(i=0; i<n; i++) /*print out sorted numbers */
printf(“%d”, list[i]);
printf(“\n”);
}
void sort(int list[], int n)
{
int i, j, min, temp;
for(i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
min = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if(list[j] < list[min])
min = j;
SWAP(list[i], list[min], temp);
}
}Example : Binary Search
while (there are more integers to check) {
middle = (left + right) / 2;
if(searchnum < list[middle])
right = middle-1;
else if (searchnum == list[middle])
return middle;
else
left = middle + 1;
}int compare(int x, int y)
{
/* compare x and y, return -1 for less than,
0 for equal, 1 for greater */
if (x<y)
return -1;
else if (x == y)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}Binary Search
#define COMPARE(x,y) (((x)<(y))?-1:((x)==(y))?0:1) // 삼항연산자
int binsearch(int list[], int searchnum, int left, int right)
{
/* search list [0] <= list[1] <= … <= list[n-1] for searchnum.
Return its position if found. otherwise return -1 */
int middle;
while (left <= right) {
middle = (left + right) / 2;
switch (COMPARE(list[middle], searchnum)) {
case -1: left = middle + 1
break;
case 0 : return middle;
case 1 : right = middle -1;
}
}
return -1;
}Recursive Algorithm (Binary Search)
int binsearch(int list[], int searchnum, int left, int right)
{
/* search list [0] <= list[1] <= … <= list[n-1] for searchnum.
Return its position if found. Otherwise return -1 */
int middle;
if (left <=right) {
middle = (left + right) / 2;
switch (COMPARE(list[middle], searchnum)) {
case -1:
return binsearch(list, searchnum, middle+1, right);
case 0 :
return middle;
case 1 :
return binsearch(list, searchnum,left, middle-1);
}
}
return -1;
}Quiz 2
- Write a C program that prints out the integer values of x, y, z in ascending order.
-답은,,, 미공개 ^_^
3. Performance Analysis
- Space Complexity 공간 복잡도
- Time Complexity 시간 복잡도
이제는 메모리가 충분해져서 Space 보다는 Time에 비중을 두고 개발하는 추세
Time Complexity
- T(P) = Compile time + run time
| Method 1 | Method 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Start timing | start = clock(); | start = time(NULL); |
| Stop timing | stop = clock(); | stop = time(NULL); |
| Type returned | clock_t | time_t |
| Results in second | Duration = ((double)(stop-start))/CLOCKS_PER_SEC | duration = (double) difftime(stop,start); |
- 직접 시간을 재서 하는 것은 컴퓨터 사양 따라 달라짐
- 프로그램 스텝을 카운팅해서 시간 복잡도를 계산함
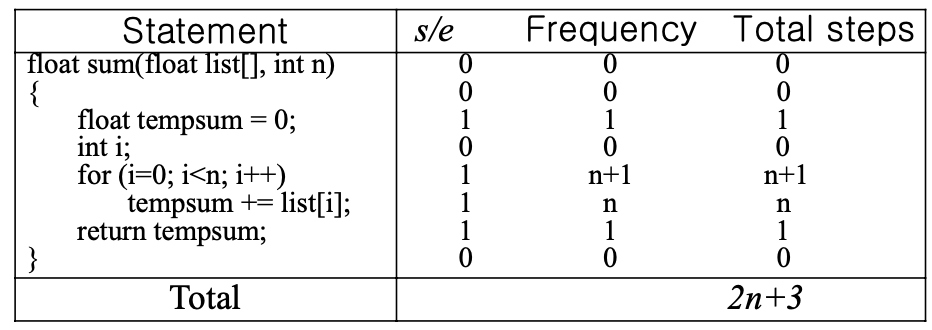
Counting the Steps
float sum(float list[], int n)
{
float tempsum = 0;
count++; /*for assignment */
int i;
for(i=0; i<n; i++) {
count++; /*for the for loop */
tempsum += list[i];
count++; /*for assignment */
}
count++; /* last execution of for */
count++; /* for return */
return tempsum;
}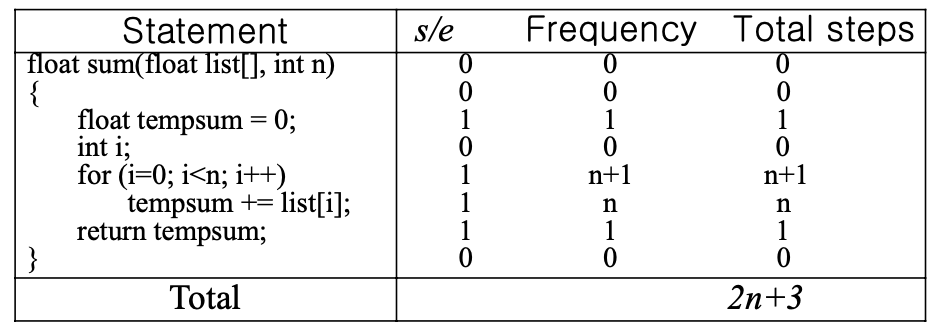
- 얘는 너무 디테일함
Asymptotic Notation - O
- Big O 표기법 - 알고리즘의 성능을 입력 크기에 따라 최악의 경우 시간 또는 공간 복잡도로 표현하는 표기법
- O(1)< O(log n)< O(n)< O(n logn)< O(n^2)< O(n^3)< O(2^n)
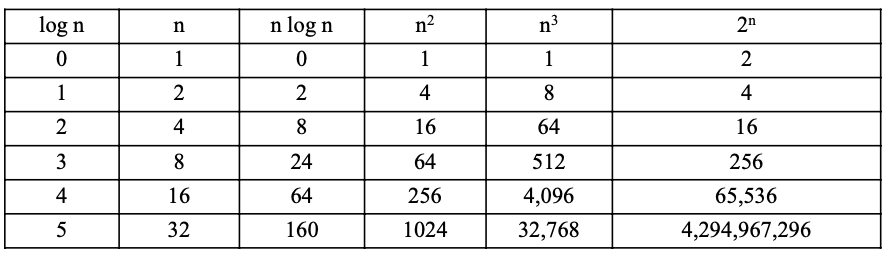
- 그래서 우리는 O 표기법을 사용
Quiz 3
- Show that the following statements are correct.
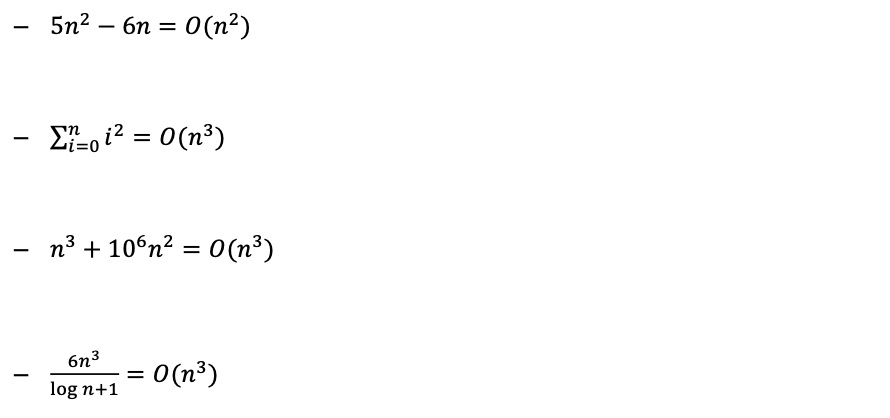
-답은,,, 미공개 ^_^
