1. HRNet의 필요성
HRNet의 경우 cityscapes의 paper with codes를 보면 2019, 2020년에 높은 성능을 보인 것을 볼 수 있다. 그리고 HRNet을 바탕으로한 OCR, Multi scale attention, self attention등 다양한 연구가 계속 되고 있다.

Image Classification
이미지 분류를 위한 CNN구조는 아래 그림과 같이 고해상도 입력을 점차 저해상도로 줄여나가는 설계방식을 사용한다.
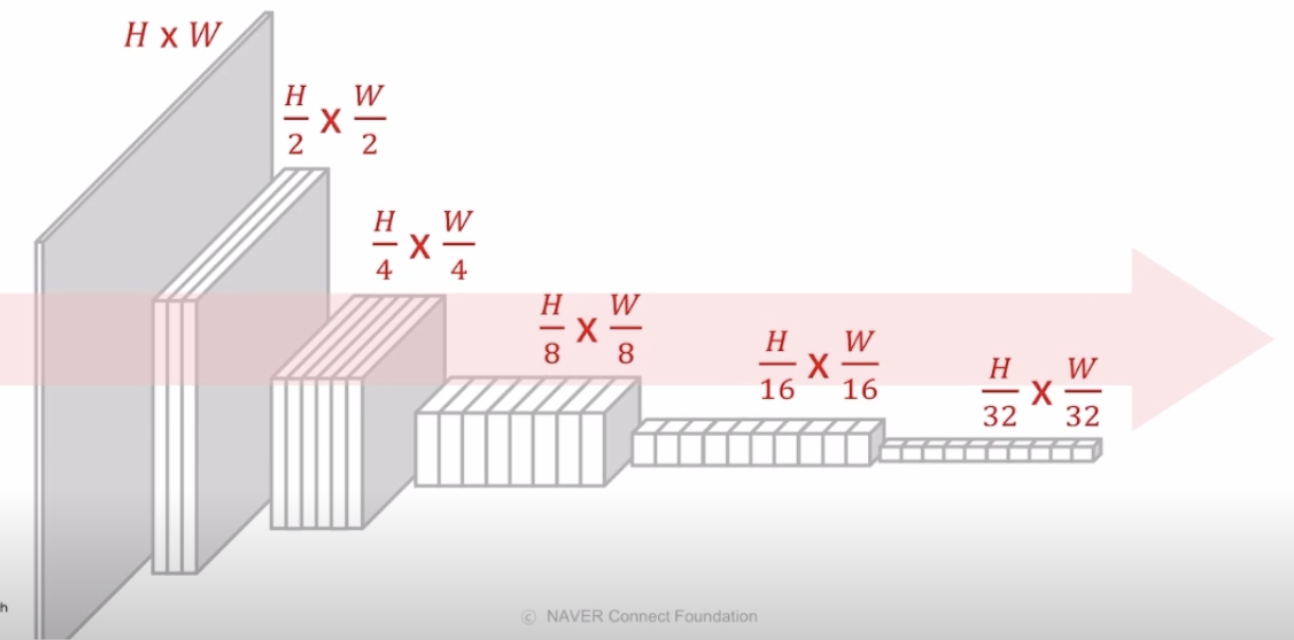
Image Classification task에서 해상도를 줄이는 이유
- 특정 물체를 분류하는데 이미지 내 모든 특징이 필요하지 않다.
- 해상도가 줄어들어 효율적인 연산이 가능하며, 각 pixel이 넓은 Receptive fiedl를 갖게 된다.
- 중요한 특징만을 추출하여 과적합을 방지할 수 있다.
Sementic Segmentation VS Image Classification
- 이미지 분류 모델은 공간적(spatial) 정보를 고려하지 않지만 Segmentation의 경우 예측하려는 Pixel 주변의 context를 잘 파악하기 위해 공간 상의 위치 정보가 중요하다.
- 중요 특징을 추출하기 위해 수행하는 pooling 등의 연산은, 모든 픽셀에 대해 정확히 분류하기에 자세한 정보를 유지하지 못한다.
Image class 모델을 그대로 사용하여 얻은 저해상도 특징은 모든 픽셀에 대해 정확한 분류를 수행하기엔 부족한 정보를 가짐
즉 segmentation에서는 더 많고 자세한 정보가 필요하기 때문에, 높은 해상도를 유지하는 것이 중요함
HRNet 등장배경텍스트
기존 segmetation 모델들은 image classification 모델들을 backbone으로 사용하기 때문에. 저해상도/중해상도의 feature map을 고상도로 복원하는 과정에서 sparse한 map이 만들어질 수 있다.
HRNet은 고해상도의 정보를 계속 유지하여 segmentation에 사용할 수 있는 새로운 backbone network다.
2. HRNet의 구조 살펴보기
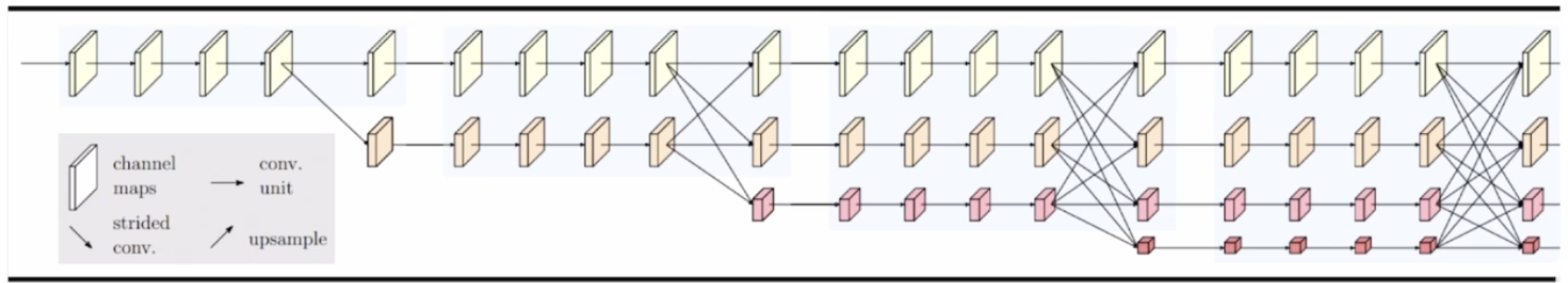
2.1 HRNet의 구성요소
- [구성요소 1]: 전체 과정에서 고해상도(high resolution) 특징을 유지
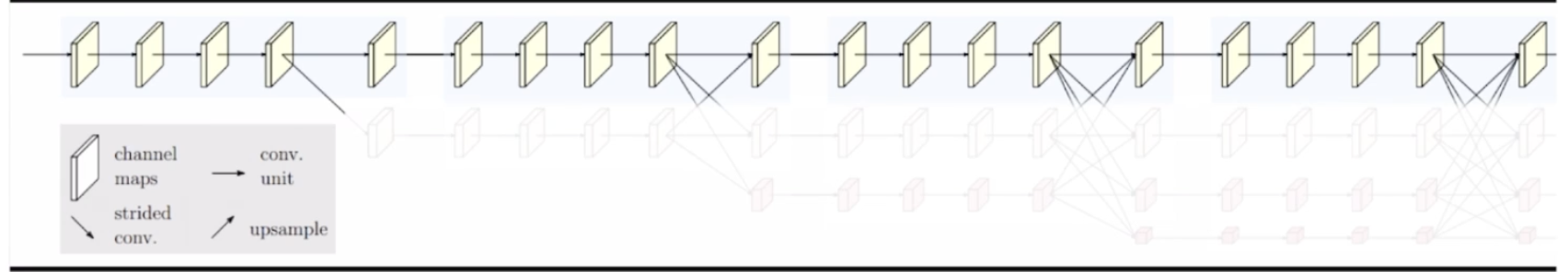
위에서 말하는 high resolution 특징은 입력 이미지의 해상도를 그대로 유지하는 것이 아닌, stride conv을 두번 거쳐 해상도를 1/4로 줄인 feature를 유지하는 것을 의미기존 segmentation 모델인 Unet, DeepLabv3+는 입력해상도를 각각 1/20, 1/16으로 줄이는 것을 볼때 1/4은 충분히 고해상도라 볼수 있음
- [구성요소 2]: 고해상도부터 저해상도까지 다양한 해상도를 갖는 특징을 병렬적으로 연산
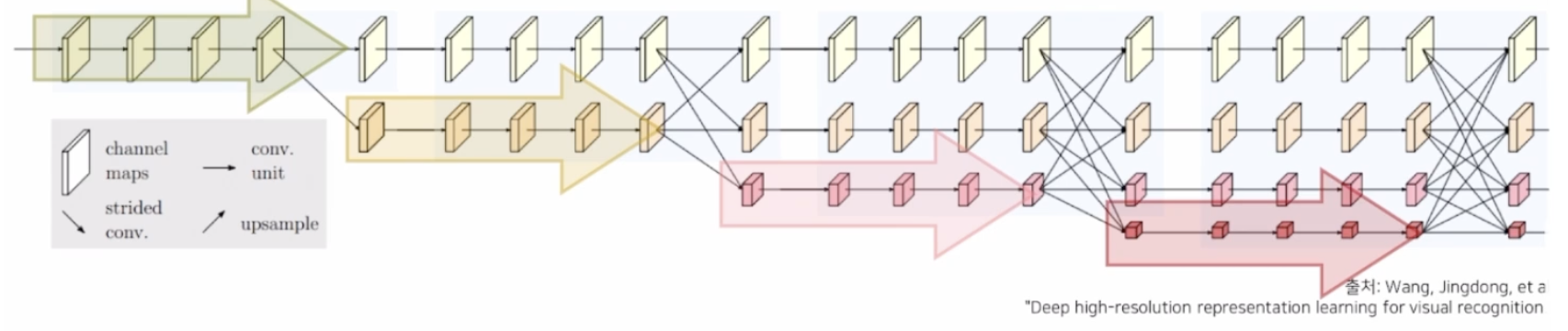
- [구성요소 3]: 다중 해상도 정보를 반복적으로 융합
각각의 해상도가 갖는 정보를 다른 해성도 stream에 전달하여 정보를 융합
고해상도: 공간상의 높은 위치 정보 민감도를 가짐
저해상도: 넓은 receptive field로 인해 상대적으로 풍부한 의미 정보(sementic information)를 가짐
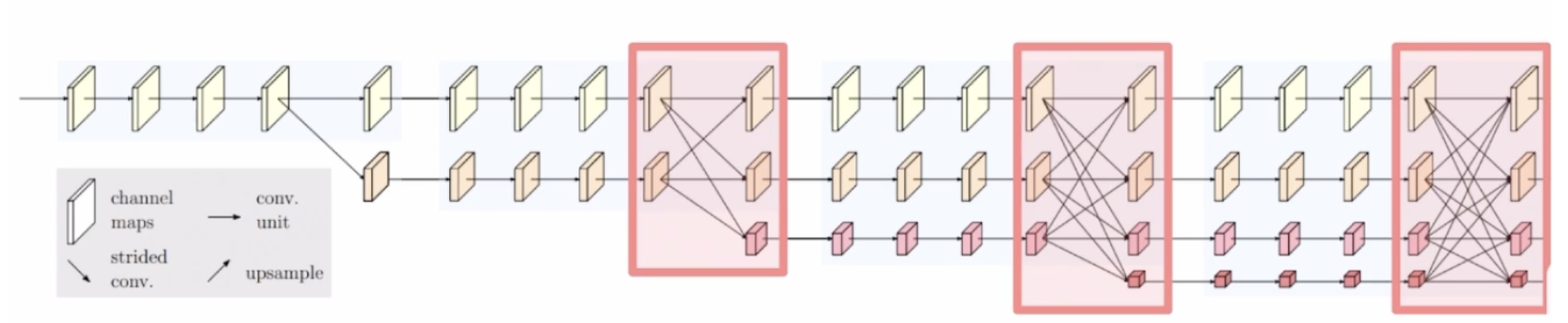
2.2 다중 해상도 정보 생성 및 병렬 처리
- 고해상도 conv stream을 시작으로 점차 해상도를 줄여 저해상도 stream을 새롭게 생성
- 새로운 stream이 생성될 때 해상도는 이전단계의1/2로 감소
해상도를 줄여 넓은 receptive field를 갖는 특징을 고해상도 특징과 함께 학습함.
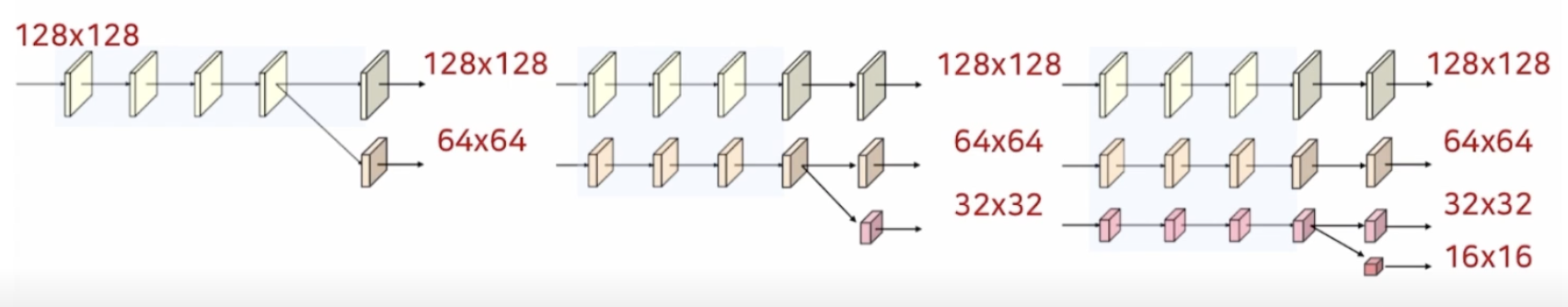
Repeated Multi-Resolution Fusions
- 저해상도 정보를 고해상도 stream에 전달: Bilinear upsampling(사이즈)연산, 1x1 conv연산(채널)
- 고해상도 정보를 저해상도 stream에 전달: Stride Convolution(정보 손실을 최소화하기 위해 pooling대신 사용)
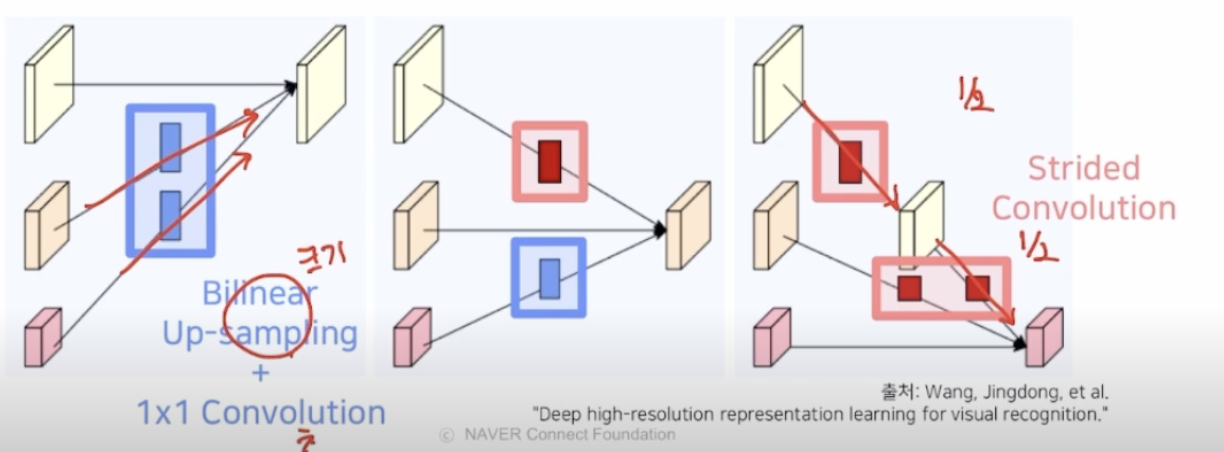
2.3 정리
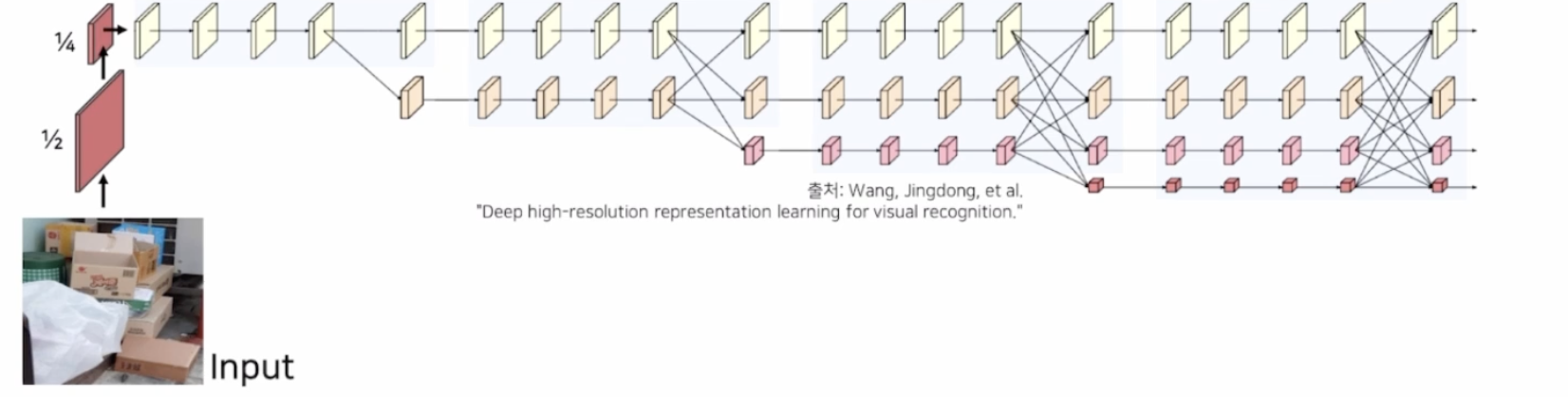
- 입력 이미지의 해상도를 1/4로 축소
- 1/4 해상도는 그대로 유지하면서 새로운 저해상도 stream을 생성하여 서로의 정보들을 융합
- 모든 해상도 정보를 합한 후 원래 이미지 크기로 bilinear upsampling하여 최종 결과 출력
3. HRNet의 세부 구조 및 구현
HRNet도 resnet과 같이 residual block이 존재한다.
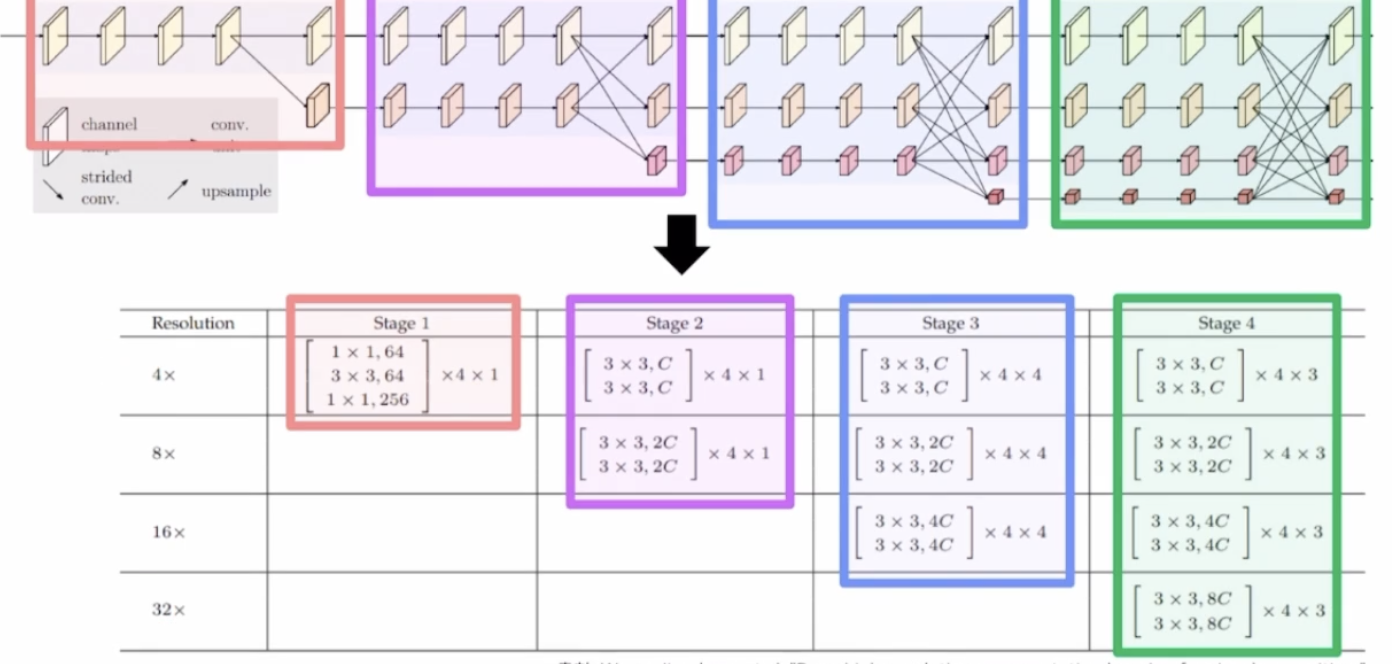
stage2,3,4를 보면 C라는 변수가 존재하는데 이는 HRNet뒤에 붙는 숫자를 의미한다.
eg) HRNet-48
3.1 코드
- 입력이미지 1/4로 축소
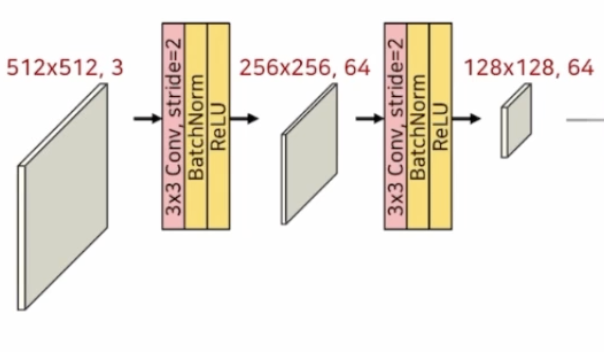
class StemBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.block = nn.Sequential(#stride=2를 적용하여 1/2로 축소
nn.Conv2d(3,64,kernel_size=3,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64,64,kernel_size=3,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, inputs):
return self.block(inputs)
2. stage 1
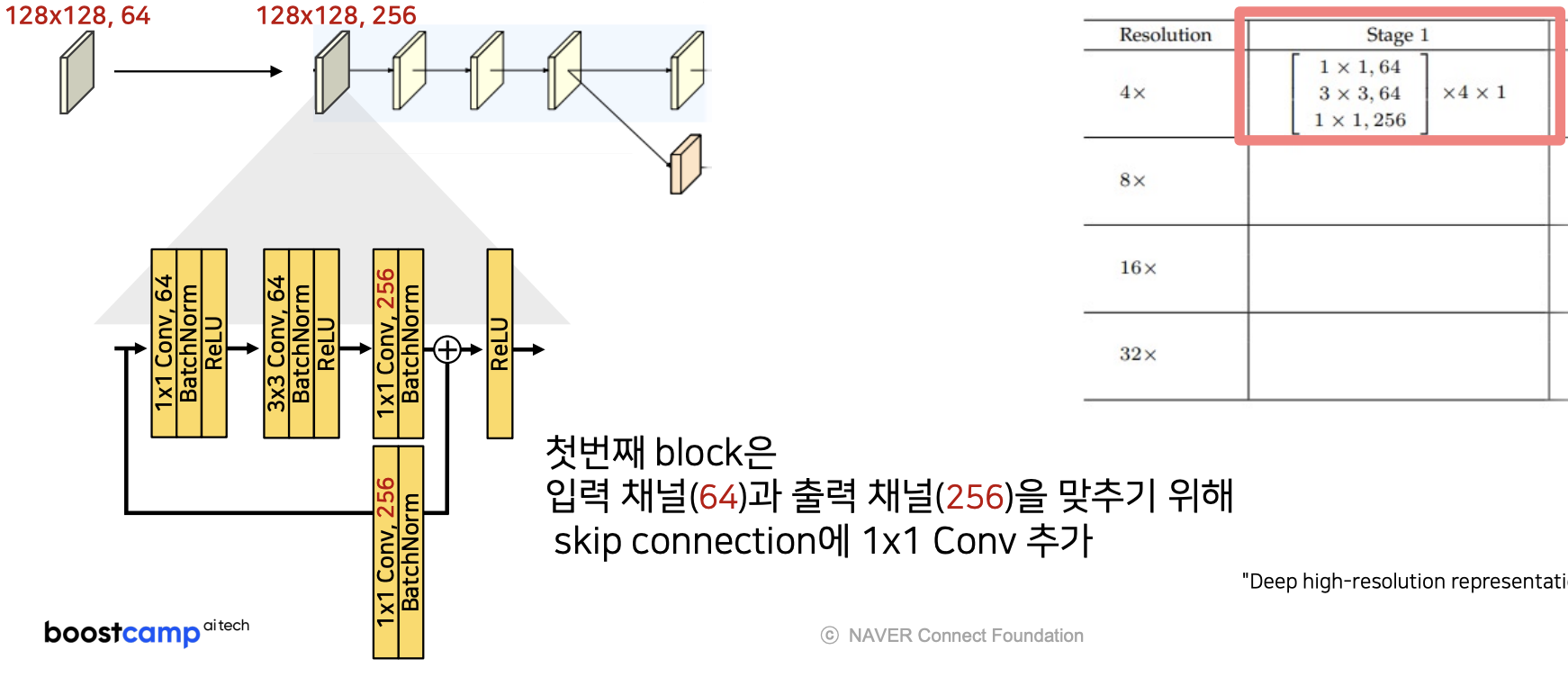
class Stage01Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channel):
super().__init__()
self.block = nn.Sequential(#stride=2를 적용하여 1/2로 축소
nn.Conv2d(in_channel,64,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64,64,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64,256,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU()
)
if in_channel == 64:
self.identity_block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel,256,kernel_size=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.in_channels = in_channel
def forward(self, inputs):
identity = inputs
out = self.block(inputs)
#첫번째 block에서 입출력 채널이 다르기 때문에 identity block을 사용하여 채널을 맞춰준다
if self.in_channels == 64:
identity = self.identity_block(identity)
out += identity
return self.block(inputs)3. stage1에서 하위 stream 생성
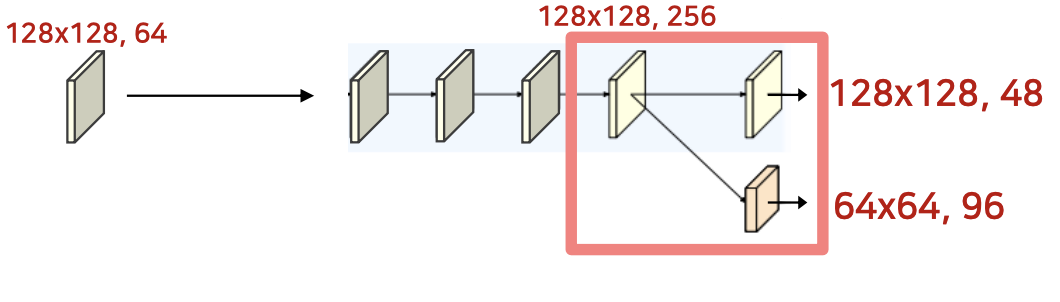
- strided Conv로 새로운 하위 stream 생성
- 이 단계부터 가장 높은 해상도의 stream의 채널 수를 48로 설정
- 새로운 stream의 해상도는 이전 단계 해상도의 1/2로 감소 및 채널 수는 2배 증가
class Stage01StreamGenerateBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
#채널을 48로 설정
self.high_res_block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256,48,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(48),
nn.ReLU())
#이미지의 사이즈를 1/2로 감소, 채널을 2배 증가 48 -> 96
self.medium_res_block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256,96,kernel_size=3,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(96),
nn.ReLU())
def forward(self, inputs):
out_high = self.high_res_block(inputs)
out_medium = self.medium_res_block(inputs)
return out_high ,out_medium
4. StageBlock
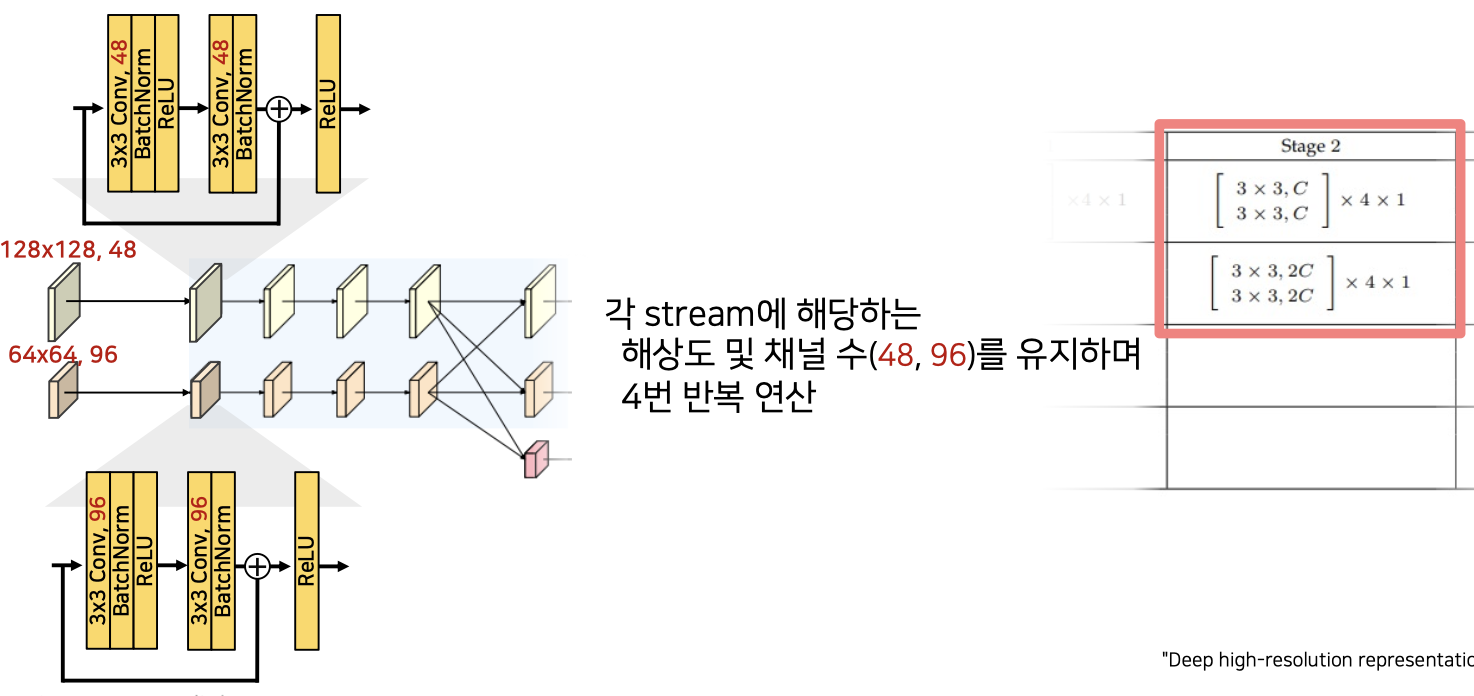
class StageBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels): #inchannel = 48 or 98
super().__init__()
self.block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,in_channels,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,in_channels,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self,inputs):
identity = inputs
out = self.block(inputs)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out- stage02
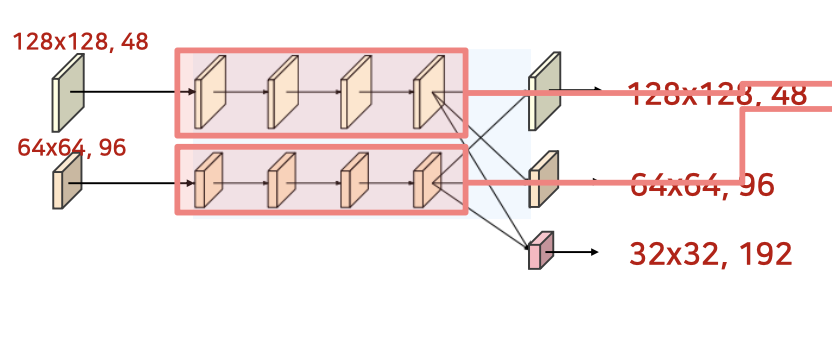
stage_block을 4개 반복하는 stage02부분 구현
class Stage02(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
high_res_block = [StageBlock(48) for _ in range(4)]
medium_res_block = [StageBlock(96) for _ in range(4)]
def forward(self,inputs):
out_high = high_res_block(inputs)
out_medium = medium_res_block(inputs)
return out_high, out_medium
Stage02Fuse
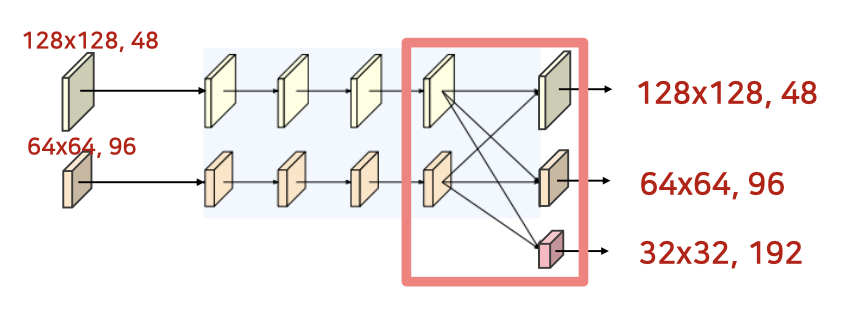
- strided convolution으로 하위 stream 생성
- Bilinear upsampling 및 1x1 conv으로 상위 stream생성
- 새로운 stream의 해상도는 이전 단계의 헤상도의 1/2로 감소 및 채널 수는 두배 증가
class Stage02Fuse(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super.__int__()
self.high_to_medium = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(48,96,kernel_size=3,stride=2,padding=1, bias = False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(96)
)
self.medium_to_high = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(96,48,kernel_size=1,padding=0, bias = False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(48)
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self,inputs_high,inputs_medium):
high_size = (input_high.size(-1), input_high.size(-2))
#1. medium input을 high input size로 upsampling
med2high = F.interpolate(inputs_medium, high_size, mode = 'bilinear', align_corners = True)
#2. 1에서 늘려준 이미지를 med channel에 맞게 1x1 conv 96 -> 48
med2high = self.medium_to_high(med2high)
#3. stride conv를 이용해 사이즈를 1/2로 축소하고 channel을 2배로 늘림
high2med = self.high_to_medium(inputs_high)
out_high = inputs_high + med2_high
out_medium = inputs_medium + high2med
out_high = self.relu(out_high)
out_medium = self.relu(out_medium)
return out_high, out_medium
