안드로이드 디벨로퍼: https://developer.android.com/kotlin/coroutines?hl=ko
코루틴 Cancellation URL
- 코루틴 소개
기능
안드로이드 비동기 프로그래밍에 권장되는 솔루션입니다.
- 경량:
- 메모리 누수 감소
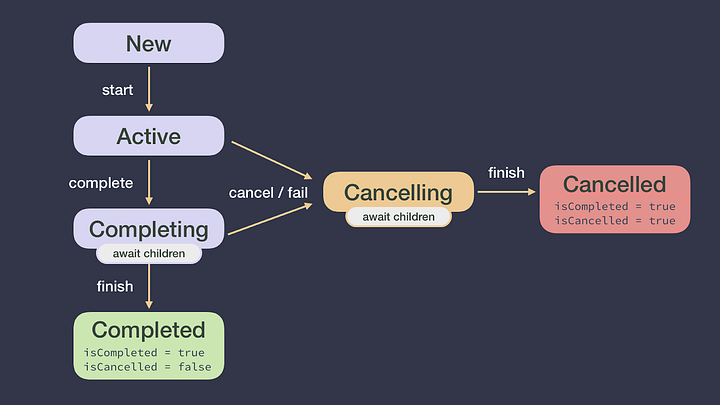
- 기본으로 제공되는 취소 지원
- Jetpack 통합
예시 개요
LoginRepository 에서는 Coroutine I/O 쓰레드를 사용한다.
LoginViewModel 에서는 Coroutine Default 쓰레드를 사용한다.
class LoginRepository(...) {
...
suspend fun makeLoginRequest(
jsonBody: String
): Result<LoginResponse> {
// Move the execution of the coroutine to the I/O dispatcher
return withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
// Blocking network request code
}
}
}class LoginViewModel(
private val loginRepository: LoginRepository
): ViewModel() {
fun makeLoginRequest(username: String, token: String) {
viewModelScope.launch {
val jsonBody = "{ username: \"$username\", token: \"$token\"}"
val result = try {
loginRepository.makeLoginRequest(jsonBody)
} catch(e: Exception) {
Result.Error(Exception("Network request failed"))
}
when (result) {
is Result.Success<LoginResponse> -> // Happy path
else -> // Show error in UI
}
}
}
}고급 코루틴 개념
장기 실행작업 관리
invoke call suspend resume
- suspend 는 현재 코루틴 실행을 일시중지하고 모든 로컬 변수를 저장합니다.
- resume은 저장된 위치로부터 정지된 코루틴을 계속 실행합니다.
suspend fun fetchDocs() { // Dispatchers.Main
val result = get("https://developer.android.com") // Dispatchers.IO for `get`
show(result) // Dispatchers.Main
}
suspend fun get(url: String) = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) { /* ... */ }기본 안전을 위해 코루틴 사용
- Dispatchers.Main
- Dispatchers.IO
- Dispatchers.Default
withContext 는 정지함수이므로 위의 get함수도 정지함수가 된다.
withContext()의 성능
네트워크 호출을 10번 호출하는 경우 withContext를 한번만 사용하면 콜백 구현 필요없이 스레드를 한번만 전환 하도록 Kotlin 에 지시할 수있습니다.
withContext를 여러번 호출해도 동일한 디스페처에 유지되고 스레드가 전환되지 않습니다. Default, IO 간의 전환을 최적화 합니다.
코루틴 시작
- launch: 결과를 반환하지 않습니다.
- async: 새 코루틴을 시작하고 await라는 정지 함수로 결과를 반환합니다.
async 정지 함수 이므로 정지 함수 또는 코루틴 내부에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
병렬분해
다른 코루틴 스코프를 정의했을 때 awiat()를 호출하여 두 async 작업이 모두 완료되도록 보장 합니다.
suspend fun fetchTwoDocs() =
coroutineScope {
val deferredOne = async { fetchDoc(1) }
val deferredTwo = async { fetchDoc(2) }
deferredOne.await()
deferredTwo.await()
val deferreds = listOf( // fetch two docs at the same time
async { fetchDoc(1) }, // async returns a result for the first doc
async { fetchDoc(2) } // async returns a result for the second doc
)
deferreds.awaitAll() // use awaitAll to wait for both network requests
}코루틴 개념
CoroutineScope
CoroutineScope 는 launch 또는 async를 사용하여 만든 코루틴을 추적합니다.
scope.cancel()을 호출하여 취소할 수 있습니다.
ViewModel 에는 ViewModelScope가 있고 Lifecycle에는 LifecycleScope가 있습니다.
그러나 CoroutineScope를 만들어 앱의 특정 레이어에서 코루틴 수명 주기를 제어해야하면 아래와같이 만들면 됩니다.
class ExampleClass {
// Job and Dispatcher are combined into a CoroutineContext which
// will be discussed shortly
val scope = CoroutineScope(Job() + Dispatchers.Main)
fun exampleMethod() {
// Starts a new coroutine within the scope
scope.launch {
// New coroutine that can call suspend functions
fetchDocs()
}
}
fun cleanUp() {
// Cancel the scope to cancel ongoing coroutines work
scope.cancel()
}
}작업
Job은 코루틴의 핸들입니다.
launch 또는 async로 만드는 각 코루틴은 코루틴을 고유하게 식별하고 수명 주기를 관리하는 Job 인스턴스를 반환합니다. Job을 CoroutineScope에 전달하여 코루틴의 수명주기를 추가로 관리할 수 있습니다.
class ExampleClass {
...
fun exampleMethod() {
// Handle to the coroutine, you can control its lifecycle
val job = scope.launch {
// New coroutine
}
if (...) {
// Cancel the coroutine started above, this doesn't affect the scope
// this coroutine was launched in
job.cancel()
}
}
}CoroutineContext
- Job: 코루틴의 수명 주기를 제어합니다.
- CoroutineDispatcher: 적절한 스레드에 작업을 전달합니다.
- CoroutineName: 디버깅에 유용한 코루틴 이름입니다.
- CoroutineExceptionHandler: 포착되지 않은 예외를 처리합니다.
class ExampleClass {
val scope = CoroutineScope(Job() + Dispatchers.Main)
fun exampleMethod() {
// Starts a new coroutine on Dispatchers.Main as it's the scope's default
val job1 = scope.launch {
// New coroutine with CoroutineName = "coroutine" (default)
}
// Starts a new coroutine on Dispatchers.Default
val job2 = scope.launch(Dispatchers.Default + CoroutineName("BackgroundCoroutine")) {
// New coroutine with CoroutineName = "BackgroundCoroutine" (overridden)
}
}
}