Creating a network app
write programs that:
- end-system(host)에서 작동하도록 만들어야 함.
- network 통신이 가능하도록
network core를 위한 application을 만들 필요는 없음. - network core는 3계층 장비인 router로만 구성되기 때문
서비스 형태에 따라 2가지로 나뉨
1) client-server paradigm 2) peer-to-peer architecture
client-server paradigm
server
- client로부터 서비스를 요청받아 해당 서비스를 응답
- IP address 항상 동일
clients - IP address를 동적으로 할당받음
- client끼리는 직접 communication하지 않음
peer-to-peer architecture
- 서버라는 존재가 없음
- end system끼리 직접 communication
- end-system이 host와 server의 역할을 모두 함 (
self-scalability)
→ end-system이 또다른 end-system에 어떤 서비스를 요청할 수도 있고, 또 다른 end-system에서 요청한 서비스에 응답하여 서비스를 제공할 수도 있음
Processes Communicating
process: 호스트 상에서 돌아가는 프로그램을 "프로세스"라고 함.
- 동일한 하나의 호스트 내에서 돌아가는 프로세스는 inter-process communication을 함(OS)
- 서로 다른 호스트 상에 존재하는 프로세스는 message를 교환하여 communication함
client process: communication을 시작하는 프로세스를 말함
server process: 컨택되길 기다리는 프로세스를 말함
Socket
- 네트워크 통신을 제공하는 인프라와 어플리케이션을 연결하는 네트워크 주체를 socket이라고 한다
- 프로세스끼리 통신하기 위해 거치는 일종의 네트워크 interface이다

Addressing Processes
- 메시지를 받고 처리할 식별자가 있어야 함
- 식별자는 IP address와 Port Number를 모두 포함함
- IP address: host 주소 체계
- Port Number: Process 주소 체계
network layer는 host-to-host 통신을 제어하고 transport layer에서는 process-to-process 통신을 제어함
What transport service does an app need?
- data integrity
- 데이터 손실이 절대 일어나면 안되는 통신/오디오같은 경우 손실이 조금은 괜찮음
- timing
- 실시간성, delay 고려
- throughput
- 데이터 전송 속도가 빨라야 하는 경우
- security
Internet transport protocols sevices
TCP service
- reliable transport
- flow control
- congestion control
- does not provide: timing, minimum throughput guarantee, security
- connection-oriented
UDP service
- unreliable transport
- does not provide: reliability, flow control, congestion control, timing, minimum throughput guarantee, security or connection-setup
Web and HTTP
HTTP: Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
- 클라이언트와 server는 HTTP라고 하는 프로토콜에 의해 통신함
HTTP usesTCP - 클라이언트는 통신하기 위해 Port번호 80으로 서버에게 TCP connection을 시작한다
HTTP is"stateless"
HTTP connections: two types
Non-persistent HTTP
1) TCP connection opened
2) TCP connection을 통해 최대 1개의 object 전송
3) TCP connection closed
Persistent HTTP
1) TCP connection opened
2) multiple objects가 client와 server 사이에 전송될 수 있음
3) TCP connection closed
Non-persistent HTTP: Example
1a) HTTP client가 server에 TCP connection 시도
1b) HTTP server accepts connection
2) HTTP client가 message를 요청
3) HTTP server는 message에 응답
4) TCP server closed TCP connection
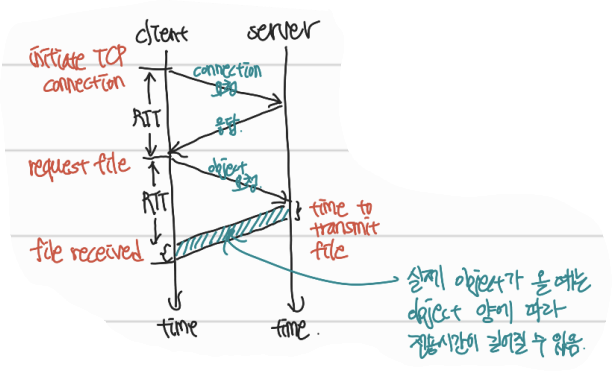
- RTT(Round Trip Time): 왕복 시간
Non-persistent HTTP response time: 2RTT + file transmission time
Maintaining user/server state: cookies
HTTP의 GET/Response interaction은 stateless하다
- 따라서 web sites와 client browser는 transaction 사이의 state를 저장하기 위해 cookies를 남김
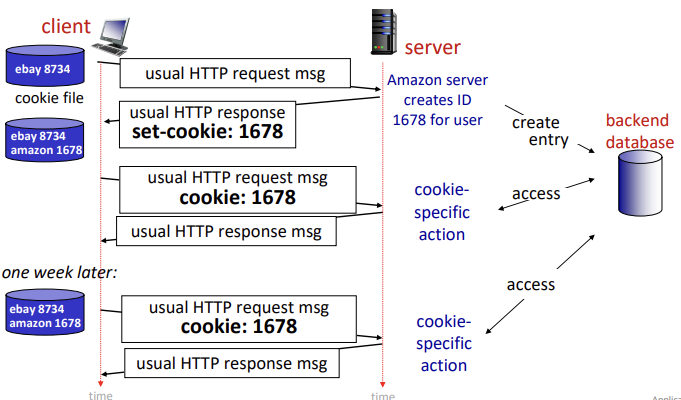
- client가 server에 처음 HTTP 요청을 보내면 server는 해당 client 고유의 식별자(= 쿠키)를 생성해 응답한다.
- 이 때부터 client는 요청할 때마다 쿠키를 함께 server에 보내게 되고, server에 저장되어 있는 식별자를 통해 specific action을 취할 수 있다.
What cookies can be used for:
- 인증절차 없이도 user 확인 가능
- 추천
...
Web Cache(proxy server)
Goal: origin server에 접근하지 않고도 client의 request에 response하자
→ 이를 위해 web cache 사용

→ client가 요청한 object가 proxy server에 존재한다면 즉시 응답하고, 없다면 origin server에 접근
- proxy server는 client와 server의 역할을 겸함 (
self-scalability) - Why web caching?
- 응답 시간을 빠르게 access하기 위해 (cache는 origin server보다 client에 더 가까이 있기 때문)
- 조직의 access link에 traffic을 줄일 수 있음
Three Major components:
- user agents
→ 이메일 프로그램을 말함 - mail servers
- simple mail transfer protocol

User Agent
- a.k.a. mail-reader
Email: mail server - mailbox: user에게 수신되는(incoming) messages
- message queue: user가 송신하는(outgoing) messages
- SMTP protocol:
- client: 메시지를 보내는 mail server
- server: 메시지를 수신하는 mail server
- E-mail은 port 25번을 통해 TCP를 사용해서 email message를 보냄
- 전송 3단계 과정
- handshaking
- transfer of messages
- closure
Scenario: Email Transfer
1) email message를 compose
2) mail server의 outgoing queue에 적재
3) SMTP는 수신자의 mail server에 TCP connection
4) TCP connection을 통해 메시지를 보냄
5) 수신자의 mail server의 mailbox에 적재
6) 메시지 read
Mail access protocol
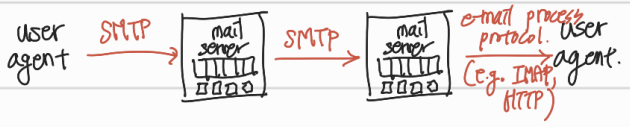
- SMTP: server와 server 사이의 통신, 또한 발송하는 user agent가 mail server의 message queue로 message를 전송할 때에도 SMTP가 사용됨
- IMAP, HTTP: 수신자의 mail server에서 수신자로 전송할 때에는 SMTP 프로토콜 사용X
DNS(Domain Name System)
- 수많은 서버의 Domain Name과 IP주소가 매핑되어 있는 분산 데이터 저장소
→ domain name을 실제 네트워크가 통신하는 기반인 IP주소로 변환해 돌려줌
DNS: services, structure
DNS services
- hostname to IP address translation
- host aliasing
- load distribution
Q. Why not centralize DNS? - single point of failure
- traffic volume
- distant centralized database
- maintenance
A. dosen't scale! - centralized하면 scalable하지 않음!
- 분산형이기 때문에 쉽게 확장 가능함
Local DNS name servers
원래 DNS service는 root, top-level 순서로 domain name을 탐색하는데, web cache처럼 local로 가지고 있는 cache memory가 존재함
Domain name resolution: iterated query

Iterated query
: 계층적으로 따라가며 query가 흐름
Domain name resolution: recursive query
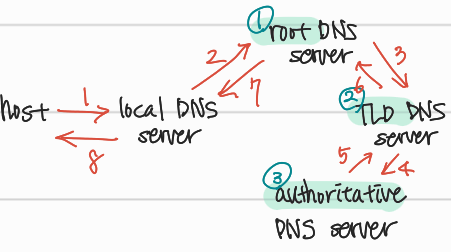
→ 이 방식도 가능은 하나, 현실적으로 Iterated query를 사용한다. 왜냐하면 recursive 방식은 root에 부하가 몰리고, iterative 방식은 local에 부하가 몰리기 때문이다.
- iterative 방식이 분산형의 장점을 잘 살린 구조이다