The Internet: a "nuts and bolts" view
인터넷의 구성 요소를 알아보자.
- 수많은 connected
computing devices존재:- hosts = end systems**
- running network apps at Internet's "edge"
Packet switches: host가 보내고자 하는 데이터를 packet(chunk of data)단위로 쪼개서 포워딩하는 역할- routers, switches
Communication links- fiber, copper, radio, satellite 등 전송선이 다양하다.
- transmission rate: bandwidth
Networks- device, router, link들의 collection을 말함.
- Internet을 네트워크들의 네트워크라고 함 (interconnected ISPs)
protocols은 메시지를 보내고 받는 것을 제어함
- HTTP, streaming video, TCP, IP, WiFi, Ethernet
The Internet: a "service" view
- application에 서비스를 제공해주는 Infrastructure
- 분산 application에 프로그래밍 인터페이스를 제공
What's a Protocol?
컴퓨터(device)들의통신 규약이다.
프로토콜은 네트워크 entity끼리 메시지를 전송하거나 수신할 때 어떤 action을 취할지에 대한 형식, 순서를 정의한다.
Network Edge
network edge
- network edge에는 각종 hosts와 data centers가 존재
access networks, physical media
- hosts(end system)이 인터넷에 접속하기 위해 가장 먼저 만나는 네트워크를 말함.
- network edge에 존재
network core
- 오로지
중개만을 위함 - 오직
라우터들로만구성되어 있음
Access Network and physical media
Q. How to conect end systems to edge router?
- residential access nets
- institutional access networks (school, company)
- mobile access networks (WiFi, 4G/5G)
What to look for
- access network의 전송 속도
- 공유해서 사용하는 네트워크인가, 혼자만 사용하는 네트워크인가
- 24-52 Mbps dedicated downstream transmission rate
- 3.5~16 Mbps dedicated upstream transmiission rate
upstream은 클라이언트나 로컬 기기에서 서버로 보내지는 데이터 또는 보내는 것이며, downstream은 반대 과정을 말함
Wireless local area networks(WLANs)
- typically within or around building(~100ft)
속도, 무료
Wide-area celluar access networks
- provided by mobile, celluar network operator(10's km)
이동성, 유료
Hosts: sends packet of data
hosts sending functions:
- 어플리케이션 계층에서 message를 받음
- message를 L bits 길이의 chunk(known as packets) 단위로 쪼갬
- 전송 속도 R로 access network에 packet을 전송
- 링크 전송 속도 = link capacity = bandwidth
packet transmission rate
= time needed to transmit L-bit packet into link
= L(bits) / R(bits/sec) =패킷 크기/전송속도
- 링크 전송 속도 = link capacity = bandwidth
Links: physical media
link: transmitter와 receiver 사이에 이들을 연결하는 존재
- guided media:
- 유선
- 반드시는 아니지만 대부분 point-to-point
- copper, fiber, coax
- unguided media:
- 무선
- 주변 모든 host에게
- e.g. radio
- Wireless radio
- 무선
- broadcast and "half-duplex"
- broadcast: 한 사람이 주변 모든 사람에게 (point-to-point와 반대 개념)
- half-duplex: link로 연결된 두 주체(A, B)에게 보낼 수 있지만, A가 B에게 보내는 동시에 B가 A에게 보낼 수 없는 구조
- 유선에 비해 상대적으로 속도 느림
- 반사, 물체에 의한 방해, 간섭 등 환경의 영향을 받음
Network core
The network core
- 오직 라우터로만 이루어짐
- packet-switching
- 하나의 라우터에서 또 다른 라우터로 포워딩
- 각 패킷은 최대 link capacity로 전송
Packet switching: store-and-forward
→ 라우터는 먼저 패킷을 완전히 수신한 다음, 다음 link로 송신한다.
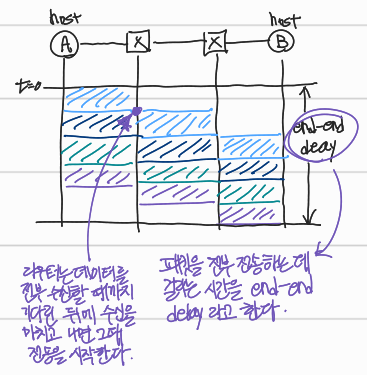
- transmission delay: L-bit packet을 R bps로 송신할 때 걸리는 transmission delay는 L/R seconds이다
- store-and-forward: 패킷을 완전히 수신한 다음, 다음 link로 송신한다
- end-end delay: propagation delay를 고려하지 않으면, 위 그림에서의 end-end delay는 2L/R이다
Packet-switching: queuing delay, loss
Packet queuing and loss: output link가 보낼 수 있는 packet의 크기(bandwidth)보다 큰 크기의 input이 들어오면 queuing delay가 발생한다.
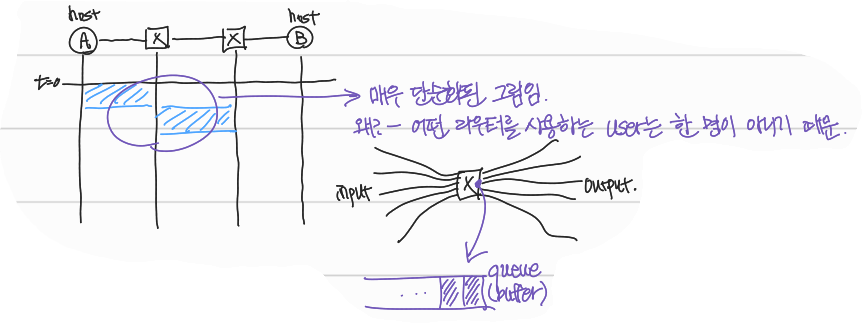
위 그림처럼, 라우터는 하나의 host만을 위해 존재하지 않는다. 여러 end-systems이 하나의 router를 공유한다.
router는 input이 들어와 이 input의 목적지에 따라 어떤 output link로 보낼지 결정한다.
위 그림의 라우터로 들어오는 input이 output link의 capacity를 초과하면 queue(buffer)에 대기하게 된다. 이 때, queue(buffer)도 정해진 용량이 존재하며, 들어오는 packet이 극단적으로 많아지면, queue에도 packet이 들어오지 못해 packet drop되며, packet loss가 발생한다.
Two key network-core functions
Forwarding
- local action: 각각의 router 관점에서, packet을 적절한 output link로 전달하는 것을 말함.
Routing
- global action: packet의 네트워크 전체의 관점에서 출발지에서 목적지까지 전송하는 기능을 말함.
Alternative to packet switching: circuit-switching
end-end resources allocated to reserved for "call" between source and destination
→ source와 destination 사이에 circuit(또는 channel)을 "예약"함
- dedicated resources:
no sharing→ 독점적으로 사용- 전송 속도 보장. 하지만 circuit의 개수가 한정되어있기 때문에 사용량이 많으면 callback될 수 있음
- circuit segment idle if not used by call(no sharing)
→ circuit switching을 사용하는 PSTN을 예시로 들어보면, 통화중 목소리를 보내지 않아도(circuit에 아무런 신호가 전송되지 않아 낭비되어도) 해당 circuit을 공유하지 않음
→ 즉, circuit-switching은 packet-switching보다는 네트워크 사용 효율이 떨어짐
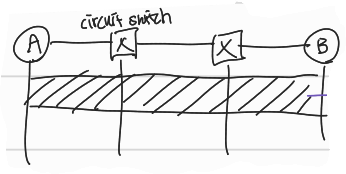
→ 데이터를 packet 단위로 쪼개지 않고 전용 channel을 예약했으므로 해당 channel(circuit)으로 데이터를 전부 전송한다.
Circuit Switching: FDM and TDM
packet switching과 circuit switching은 저속의 다수의 data stream이 모여 하나의 고속의 data stream이 되는 것은 동일하다. 그러나 packet switching은 하나의 circuit을 랜덤하게(on-demand) 사용하므로 statistical multiplexing이라고 한다.
-
Frequency Division Multiplexing(FDM)
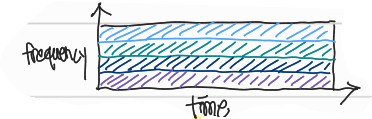
→ circuit을 frequency 기준 4개의 circuit으로 쪼개서 사용자 한 명 당 all time 1/4의 대역폭을 사용 -
Time Division Multiplexing(TDM)
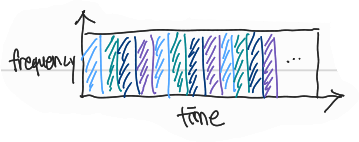
→ circuit을 time 기준 4x4 circuit으로 쪼개서 사용자 한 명 당 1/4 시간을 나눠 사용
- multiplexing: packet-switching/circuit-switching이 사용하는 방법. 저속의 여러 data stream이 모여 하나의 고속의 data stream이 되는 것
- de-multiplexing: 고속의 data stream이 여러 개의 저속의 data stream으로 나뉨
packet switching versus circuit switching
- packet switching allows more users to use netowrk!
- Example
- 1Gb/s link
- each user:
- 100Mb/s when "active"
- active 10% of time
- → circuit-switching: 10 users
- → packet-swtiching: with 35 users, 35명의 user를 받아들였을 때, 특정 시간에 10명 초과의 user가 active 상태일 화귤ㄹ이 0.0004
- Is Packet Switching a "Slam Dunk Winner"?
- packet-switching은 "bursty" 데이터일 경우 장점이 더욱 부각
- packet-switching은 네트워크 혼잡이 발생할 수 있음(queuing delay packet loss, buffer overflow)
- circuit switching은 전송 속도를 보장
Internet structure: a "network of networks"
- 모든 access network가 연결된 Mesh 구조 → O(N^2)
- access network를 연결하는 global ISP → O(N)
- ISP A, ISP B, ISP C ...
- ISP끼리 연결하는 IXP(Internet Exchange Provider)
- peering link: ISP끼리 직접 연결하기도 함
- access network끼리 지역적으로 연결되는 regional ISP
- 기존에 있는 network를 사용하지 않고, 자신만의 network를 형성해 end user에게 본인이 제공하는 서비스를 빠르게 전달하는 content provider network