출력될 형식
- JSON 형식
- 객체이름은 복합명사일경우 소문자+대문자+대문자
- 검출 확률은 내림차순으로
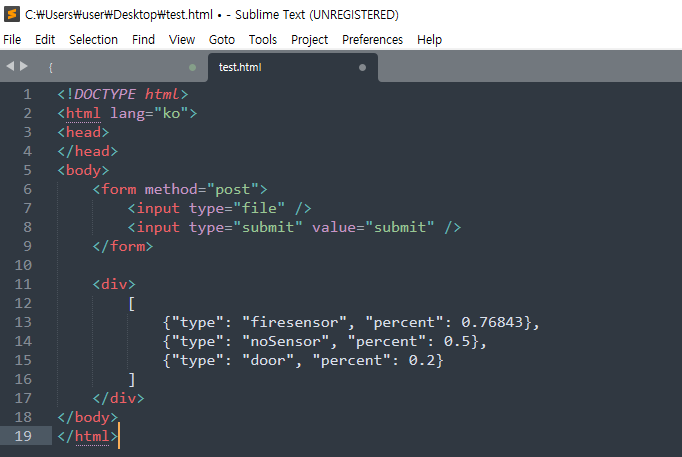
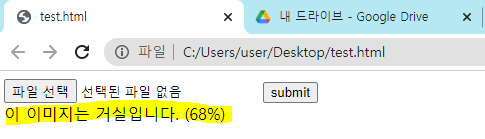
클래스 No. 대신 클래스명으로 출력 => detect.py 파일 수정
detect.py 파일에서 코드 부분을 아래와 같이 수정해야함
if save_txt: # Write to file
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywh
label = classes[int(cls)] if classes else cls
line = (label, *xywh, conf) if save_conf else (label, *xywh) # label format
with open(f'{txt_path}.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')


파이토치 모델 저장하기&불러오기
state_dict 란?
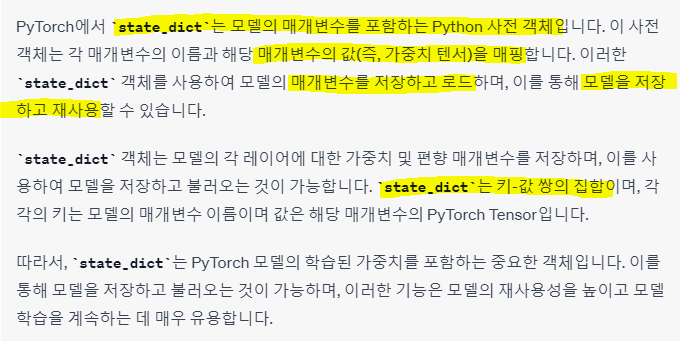
저장&불러오기 정의
model.save & model.load
모델 학습의 결과를 저장하기 위한 함수
모델 형태(architecture)와 parameter를 동시에 저장
-
직렬화(Serialize)와 역직렬화(Deserialize)를 통해 객체를 저장하고 불러옴
-
모델(Model)을 저장하는 방법은 Python의 피클(Pickle)을 활용하여 파이썬 객체 구조를 바이너리 프로토콜(Binary Protocols)로 직렬화
모델에 사용된 텐서(Tensor)나 매개 변수(Dictionary)를 저장합니다. -
모델(Model)을 불러오는 방법은 저장된 객체 파일을 역직렬화 하여 현재 프로세스의 메모리에 업로드
-
모델을 저장하는 경우에는 모델 학습이 모두 완료된 이후에 작성하거나, 특정 에폭이 끝날 때마다 저장 (모델 파일 확장자는 주로 .pt나 .pth)
모델 저장 (보통 state_dict 방식 사용)
1. 모델의 형태를 포함하여 저장하는 방법
torch.save(model, 'model.pth')
torch.load('model.pth')2. 학습된 모델의 매개변수(state_dict)만 저장하는 방법
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.pth')
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pth'))state_dict 방식은 pickle 형태로 저장, 이는 클래스를 포함하는 파일에 대한 경로를 저장.
이 경로는 로드 시점에 사용되며, 이로 인해 이 모델을 다른 프로젝트에서 사용하게 될 경우 정상적으로 모델이 로드가 안될 수도 있음. serialization (직렬화) 안될수도 있음
모델 불러오기
import torch
from torch import nn
class CustomModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CustomModel, self).__init__()
self.layer = nn.Linear(2, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer(x)
return x
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model = torch.load("model.pt", map_location=device)
print(model)
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
inputs = torch.FloatTensor([[1 ** 2, 1], [5 **2, 5], [11**2, 11]]).to(device)
outputs = model(inputs)
print(outputs)
구글 내드라이브 접근
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')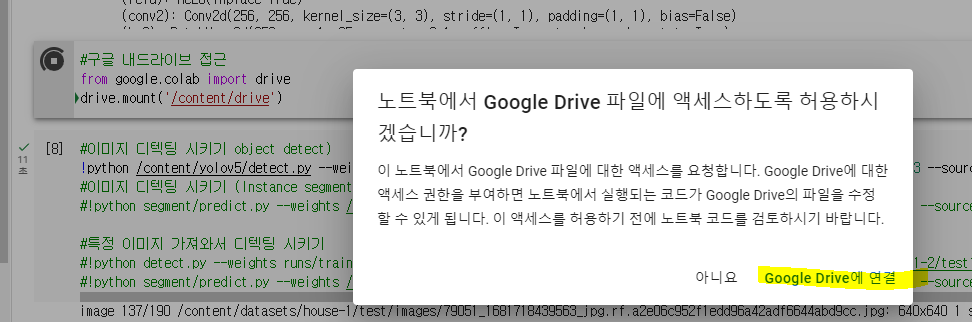
라벨링 된 정보 바꾸기