Summary
- Goal: GPT 안에서 factual association의 evidence를 찾아라!
- Approach :
- Where : 어디에서 중요한 역할을 하는지 찾기 위해 CAUSAL EFFECT ANalysis 적용
- How : 어떻게 fact를 Storage 하는지 찾기위해 개발한 ROME (Rank-One Model Editing) 이용해서 feed-forward의 weights 조정해서 특정 factual association들을 update 해봄.
- Findings
- middle-layer feed-forward modules step에서 factual prediction을 위한 mediation 역할을 하고 있단 것을 발견
- computational mechanism을 바로 manipulation하는 것이 실현 가능하다는 것 입증
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.05262
github: https://rome.baulab.info/
youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_NMQyOu2HTo&t=6s
Introduction
# Background
https://chloamme.github.io/2021/12/08/illustrated-gpt2-korean.html
- 대규모 모델들은 factual statement를 예측할 수 있음.
- ex. (Q)_"The Space Needle is located in the city of," (A)_"Seattle"
- 그렇다면 이 모델들은 knowledge를 어떻게 store하고 있을까?
- BERT 같은 양방향 + masked 모델에 관한 연구들은 있어왔는데, GPT 같은 단방향 + autoregressive 모델에 대한 연구는 아직까진 X.
# Research Question
- Where does a large language model GPT store its facts?
# Hypothesis
- GPT에서 factual association에 관한 증거는 localized computation과 관련이 있다!
- 얼마든지 directly하게 evidence는 수정될 수 있다.
# Approach
- (1) fact에 대해 recall하는 걸 관장하는 특정 모듈을 찾기 위해서 causal mediation analysis 방식을 적용하여 GPT 내 hidden state activations의 causal effect를 쫓아보자.
- (2) (1)의 결과 middle layer의 feedforward MLP가 subject name의 마지막 토큰을 처리할 때 decisive 하더라. 이를 입증하기 위해서 ROME (Rank-One Model Editing) method를 개발하여 feedforward layer의 작동을 결정하는 파라미터들을 조정해본다.
# Result
- ROME은 방법이 간단한데 비해 standard zero-shot relation extraction benchmark 실험에서 다른 editing model들과 비슷한 효과를 내었음
- counterfactual assertion 데이터셋 공개함. 이 데이터셋으로 ROME이 어려운 테스크도 잘 한다는 것을 보여주기 위해 사용되었는데, 이 전에는 이 방식으로 pretraining 한 적 없음.
- 기존의 meta-learning, interpretability-based, fine-tuning 방식들은 generalization과 specificity 중 한 가지에서만 좋은 성능을 보였는데, ROME은 두 가지 모두 좋은 성능을 보였다.
Interventions on Activations for Tracing Information Flow
# Goal
Autoregressive transformer 모델의 파라미터 안에 facts가 어디에 위치해 있는지 찾기 위해서 causal effect를 보이는 specific hidden states 분석 및 탐지
- Method
(s,r)의 natural language prompt p가 있을 때 GPT가 o를 예측하기 task를 수행하면서 fact 찾아볼 것임! - Notation
- knowledge tuples t = (s, r, o)
- s, o : subject
- r : s와 o의 relation
- 각각의 variable들의 representation은 knowledge Graph에서 찾을 수 있음.
Example
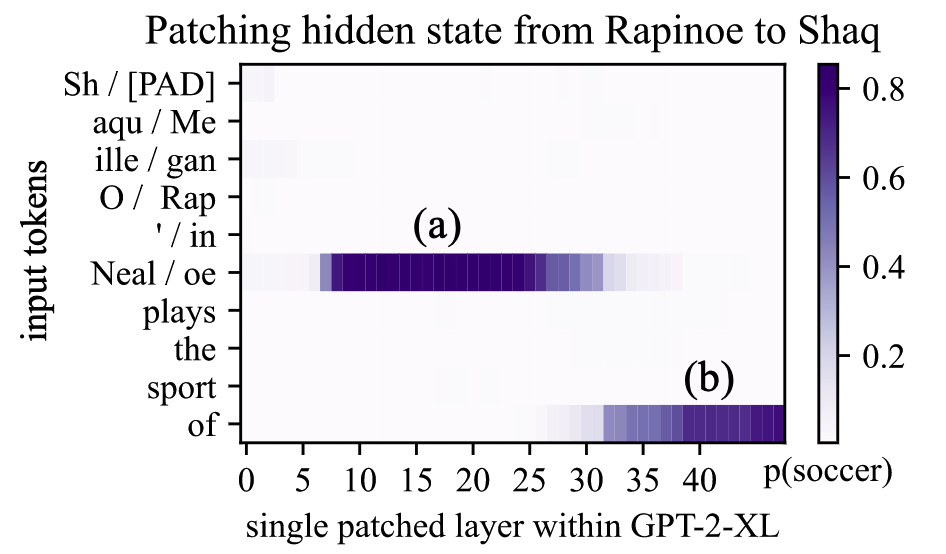
- s = Megan Rapinoe, r = plays sport professionally, o = soccer
 https://www.npr.org/2020/11/09/933018609/soccer-star-megan-rapinoe-on-equal-pay-and-what-the-u-s-flag-means-to-her
https://www.npr.org/2020/11/09/933018609/soccer-star-megan-rapinoe-on-equal-pay-and-what-the-u-s-flag-means-to-her
- s = Megan Rapinoe, r = plays sport professionally, o = soccer
- knowledge tuples t = (s, r, o)
- Background
Autoregressive transformer language model의 Hidden state들이 update되는 형식

- Notation
- Autoregressive transformer language model
- token
- probability distribution predicts next-token continuations of (last hidden state를 이용해서 final output 계산)
- 수식
- 초기값부터 시작해서 각각 layer는 전 단계의 output을 가지고 global attention (네모)과 local MLP (세모) 를 거쳐서 h update 함.
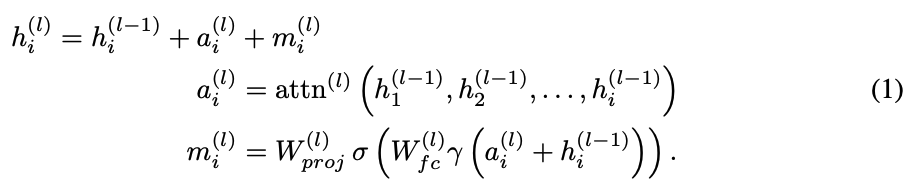
- 초기값부터 시작해서 각각 layer는 전 단계의 output을 가지고 global attention (네모)과 local MLP (세모) 를 거쳐서 h update 함.
- Notation
# Casual Tracing of Factual Assocations
-
[Fig1]의 (a),(b)
- inputs -> output (next word prediction)까지 많은 path가 존재함.
- fact를 recall하는 데 다른 것보다 더 중요한 hidden state variables가 있을까?

-
Causal mediation analysis (Vig et al., 2020b)
- Goal : quantifies the contribution of intermediate variables in causal graphs (Pearl, 2001)
- Method: 3가지 작동 방식을 수행하면서 model의 internal activation을 관찰하여 정답 예측을 하는 데 각 state의 contribution을 계산함.
- 1) Clean run (fig1.a) :
- predicts the fact
- x를 모델 G에 넣고, 모든 hidden activations 를 수집한다.
- ex) x : "The Space Needle is in downtown ___" => o = "Seattle"
- 2) Corrupted run (fig1.b):
- where the prediction is damaged
- network run 하기 전에 모델 입장에선 아직 자기가 뭘해야하는 지 모르는 상황이다. 그래서 초반에 추출된 hidden state들은 subject entity를 나타내는 데 불충분 (obfuscated) 하다. 그래서 모델은 subject에 대한 information을 lose해서 incorrect한 answer을 return하기 된다.
- 이 때를 논문에서는 모델 G가 corrupted activations 를 도출했다고 표현 함.
- 3) Corrupted-with-restoration run (fig1.c):
- tests the ability of a single state to restore the prediction
- If, "Corrupted run" 상황에서 모델이 다 정답 틀렸는데, 딱! 한 번! layer 에서 토큰 에 대해서는 정답을 맞췄다고 해보자.
- 그럼 이때 모델은 clean state 를 출력하게되고, 이후에는 further intervention 없이 잘 computation을 할 것이다.
- 이때, 우리는 다른 애들은 다 corrupted 되어있을지라도(obfuscated), 요런 몇몇의 clean state들이 정확한 fact를 recover하는데 도움이 된다면, 아~ 얘들의 causal importance를 가 상당하구나! (=fact 뽑는데 요부분이 evidence가 되는 거구나~) 라는 걸 알게 된다.
=> 그러니까 feature selection 할 때처럼 비교를 해보면서 얼마나 중요한지 볼 수 있단 거겠지?
- 1) Clean run (fig1.a) :
- Notation:
- : clean, corrupted, corrupted-with-restoration runs 상황에서 각각 를 도출할 확률 :
- Total effect (TE) =
- Indirect effect (IE) =
# Casual Tracing Results
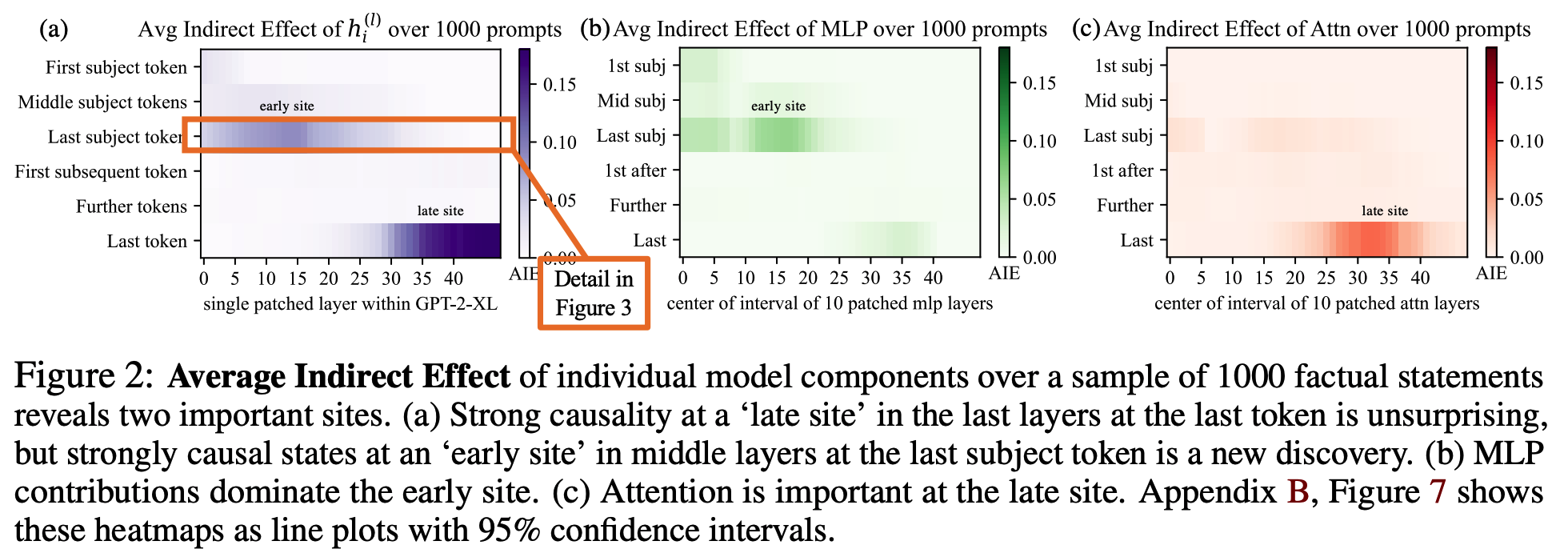
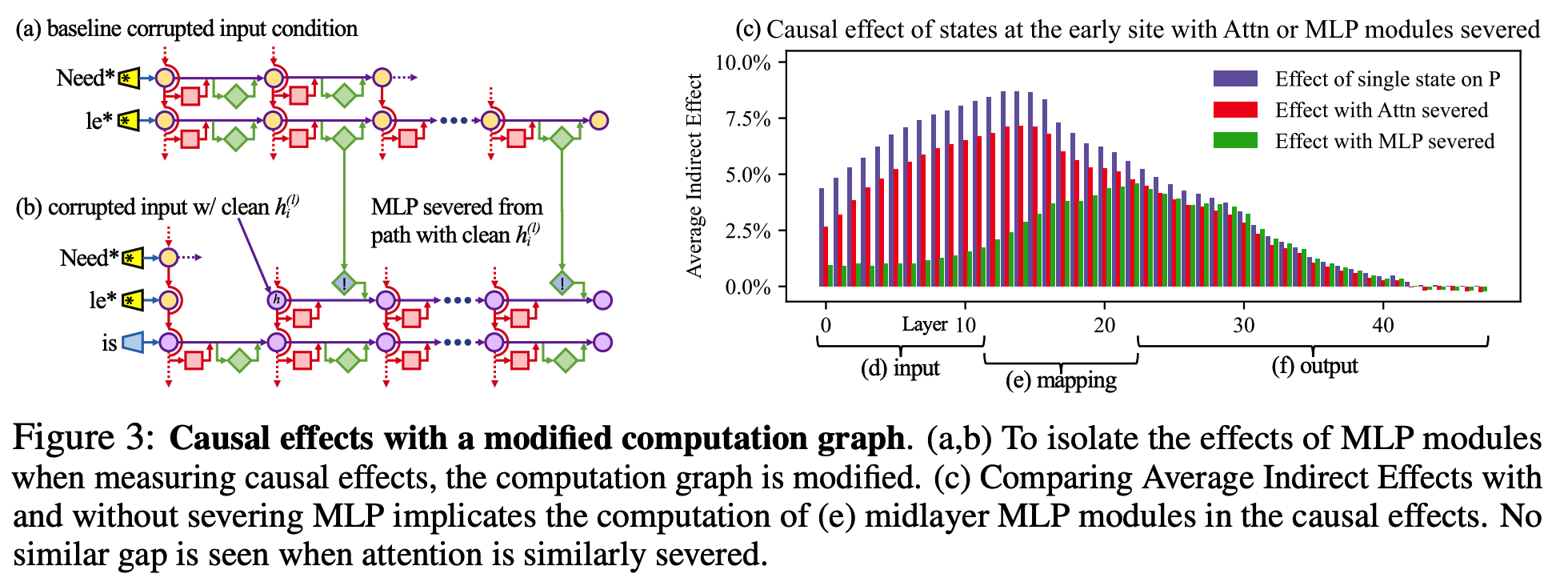
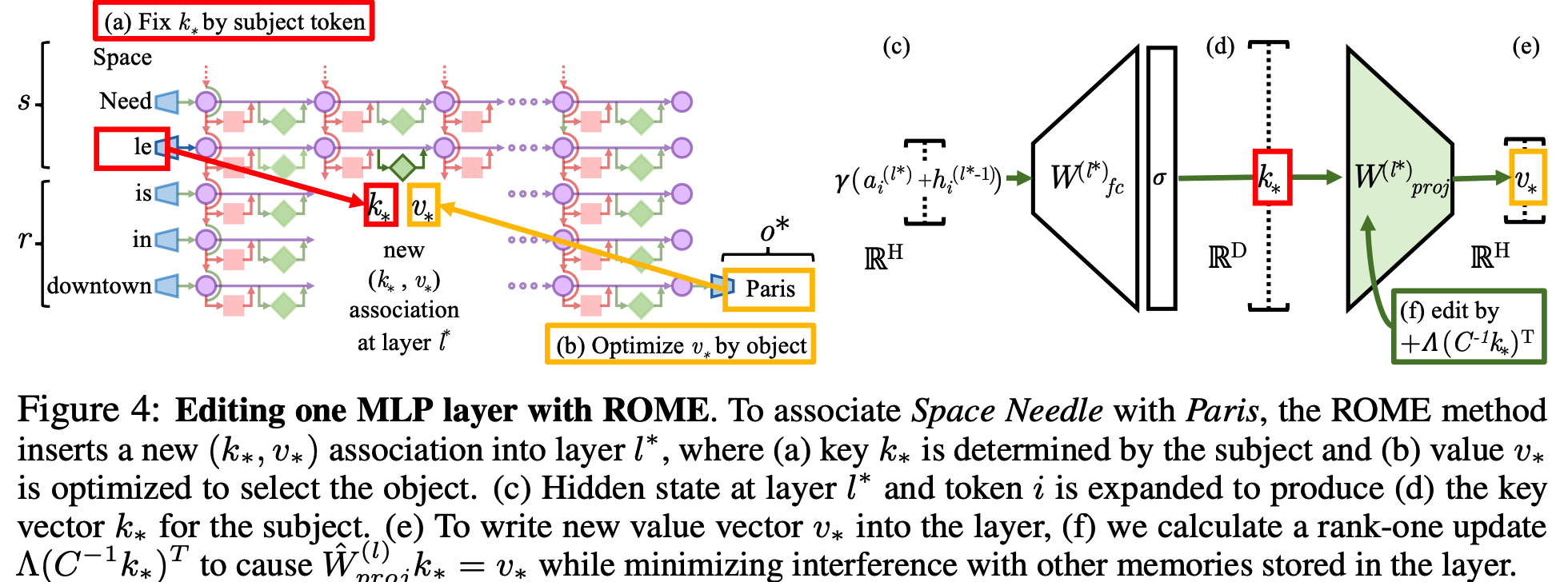
# The Localized Factual Association Hypothesis
Interventions on Weights for Understanding Factual Association Storage