.png)
BFS의 개념
BFS는 최대한 적은 개수의 점을 들리는 방법을 탐색하게 된다.
최소 간선 or 최소 노드를 구할때 자주 사용된다.
Data를 뒤에서 추가하고 앞에서 꺼낼것이기 때문에 Queue Lib를 사용할 것이다.
DFS와의 차이
DFS는 깊이 우선 탐색으로 모든 node를 들러서 탐색하며, 모든 경로를 찾게 될 때 유용하다.
DFS 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int arr[100][100];
int used[100];
int main()
{
// Node 개수 & 간선 개수
int nodeCnt, edgeCnt;
cin >> nodeCnt >> edgeCnt;
for (int i = 0; i < edgeCnt; i++) {
int from, to;
cin >> from >> to;
// 인접 리스트 방식
arr[from][to] = 1;
}
queue<int> q;
// Root를 1로 설정
q.push(1);
// queue.empty(): queue가 비워졌는지 확인
while (!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front();
cout << now << " ";
q.pop();
for (int to = 1; to <= nodeCnt; to++) {
if (arr[now][to] == 0) continue;
// 이미 지난긴 길 무시
if (used[to] != 0) continue;
used[to] = 1;
q.push(to);
}
}
return 0;
}| 입력 | 그래프 | 출력 |
|---|---|---|
 |  | 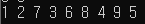 |
해당 Node에 도착하기 위한 간선 수
위 코드에서 변경되는 while 부분만 표기
while (!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int to = 1; to <= nodeCnt; to++) {
if (arr[now][to] == 0) continue;
// 이미 지난긴 길 무시
if (used[to] != 0) continue;
// to node까지의 간선 수
used[to] = used[now] + 1;
q.push(to);
}
}
// 4 node까지의 간선 수 구하기
cout << used[4]; // 결과 : 3마지막 꺼내지는 Node의 간선 수
위 코드에서 변경되는 while 부분만 표기
int cnt = 0;
// queue.empty(): queue가 비워졌는지 확인
while (!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front();
q.pop();
// 마지막으로 node가 pop되면 cnt는 고정
cnt = used[now];
for (int to = 1; to <= nodeCnt; to++) {
if (arr[now][to] == 0) continue;
// 이미 지난긴 길 무시
if (used[to] != 0) continue;
// to node까지의 간선 수
used[to] = used[now] + 1;
q.push(to);
}
}
cout << cnt; // 결과 : 4
```