이번 글에서는 캐릭터를 원하는 방향으로 이동시키는 방법에 더해서 장애물을 추가하고 장애물이 있을 때는 그 방향으로 움직이지 못하게 하는 방법을 알아보겠습니다.
1. SpriteAnimator 컴포넌트 수정
- src/components/SpriteAnimator.vue 파일을 수정합니다.
<template>
<div :style="spriteStyle" class="sprite"></div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
frameWidth: {
type: Number,
required: true
},
frameHeight: {
type: Number,
required: true
},
animationSpeed: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
spriteSheet: {
type: String,
required: true
},
scale: {
type: Number,
default: 1
},
obstacles: { // 장애물 정보 리스트
type: Array,
default: () => []
}
},
data() {
return {
currentFrame: 0,
direction: 2,
isMoving: false,
x: 0,
y: 0,
moveSpeed: 2,
frames: {
idle: [
[12, 13, 14, 15],
[8, 9, 10, 11],
[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7]
],
move: [
[34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21],
[22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27]
],
die: [40, 41, 42, 43]
},
pressedKeys: new Set()
}
},
computed: {
spriteStyle() {
return {
width: `${this.frameWidth}px`,
height: `${this.frameHeight}px`,
backgroundImage: `url(${this.spriteSheet})`,
backgroundPosition: `-${this.getCurrentAnimationFrame() * this.frameWidth}px -0px`,
backgroundRepeat: 'no-repeat',
transform: `scale(${this.scale})`,
transformOrigin: 'top left',
position: 'absolute',
left: `${this.x}px`,
top: `${this.y}px`
}
}
},
mounted() {
this.startAnimation()
window.addEventListener('keydown', this.handleKeydown)
window.addEventListener('keyup', this.handleKeyup)
this.updateMovement()
},
beforeUnmount() {
this.stopAnimation()
window.removeEventListener('keydown', this.handleKeydown)
window.removeEventListener('keyup', this.handleKeyup)
},
methods: {
startAnimation() {
this.animationInterval = setInterval(() => {
if (this.isMoving) {
this.currentFrame = (this.currentFrame + 1) % this.frames.move[this.direction].length
} else {
this.currentFrame = (this.currentFrame + 1) % this.frames.idle[this.direction].length
}
}, this.animationSpeed)
},
stopAnimation() {
clearInterval(this.animationInterval)
},
getCurrentAnimationFrame() {
if (this.isMoving) {
return this.frames.move[this.direction][this.currentFrame]
} else {
return this.frames.idle[this.direction][this.currentFrame]
}
},
handleKeydown(event) {
this.pressedKeys.add(event.key)
this.updateDirectionAndMovement()
},
handleKeyup(event) {
this.pressedKeys.delete(event.key)
this.updateDirectionAndMovement()
},
updateDirectionAndMovement() {
if (this.pressedKeys.size === 0) {
this.isMoving = false
return
}
this.isMoving = true
if (this.pressedKeys.has('ArrowUp')) {
this.direction = 0 // Up
}
if (this.pressedKeys.has('ArrowRight')) {
this.direction = 1 // Right
}
if (this.pressedKeys.has('ArrowDown')) {
this.direction = 2 // Down
}
if (this.pressedKeys.has('ArrowLeft')) {
this.direction = 3 // Left
}
},
moveCharacter() {
let newX = this.x
let newY = this.y
if (this.pressedKeys.has('ArrowUp')) {
newY -= this.moveSpeed
}
if (this.pressedKeys.has('ArrowRight')) {
newX += this.moveSpeed
}
if (this.pressedKeys.has('ArrowDown')) {
newY += this.moveSpeed
}
if (this.pressedKeys.has('ArrowLeft')) {
newX -= this.moveSpeed
}
if (!this.isCollision(newX, newY)) { // 장애물 충돌 시에는 이동하지 못함
this.x = newX
this.y = newY
}
},
// 충돌 여부를 확인하는 메서드
isCollision(newX, newY) {
for (let obstacle of this.obstacles) {
if (
newX < obstacle.x + obstacle.width &&
newX + this.frameWidth * this.scale > obstacle.x && // x 충돌 확인
newY < obstacle.y + obstacle.height &&
newY + this.frameHeight * this.scale > obstacle.y // y 충돌 확인
) {
return true // 충돌 발생 시 true 반환
}
}
return false // 충돌 없을 시 false 반환
},
updateMovement() {
this.moveCharacter()
requestAnimationFrame(this.updateMovement)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.sprite {
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
1.1. SpriteAnimator.vue 코드 상세 설명
1.1.1. props
- obstacles는 장애물의 위치를 표시합니다.
1.1.2. Methods
- isCollision
- 캐릭터의 새로운 위치와 모든 장애물의 위치를 비교해 충돌 여부를 판단합니다.
- moveCharacter
- 방향에 따라 캐릭터의 위치를 업데이트하되, 장애물 충돌 시에는 이동하지 못합니다.
2. 컴포넌트 사용
- 이제 App.vue 파일에 장애물을 추가합니다.
<template>
<div id="app">
<SpriteAnimator
:frameWidth="24"
:frameHeight="24"
:animationSpeed="100"
:spriteSheet="spriteSheetPath"
:scale="2"
:obstacles="obstacles"
/>
<!-- 장애물을 렌더링 -->
<div
v-for="(obstacle, index) in obstacles"
:key="index"
:style="getObstacleStyle(obstacle)"
class="obstacle"
></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import SpriteAnimator from '@/components/SpriteAnimator.vue'
import spriteSheetPath from '@/assets/Girl-Sheet.png'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
SpriteAnimator
},
data() {
return {
spriteSheetPath,
obstacles: [ // 장애물 정보 등록
{ x: 100, y: 100, width: 50, height: 50 },
{ x: 200, y: 150, width: 50, height: 50 },
{ x: 150, y: 300, width: 50, height: 50 }
// 원하는 만큼 장애물을 추가할 수 있습니다.
]
}
},
methods: {
// 장애물의 스타일을 동적으로 생성하는 메서드
getObstacleStyle(obstacle) {
return {
position: 'absolute', // 장애물의 위치를 고정합니다.
left: `${obstacle.x}px`, // 장애물의 x 좌표
top: `${obstacle.y}px`, // 장애물의 y 좌표
width: `${obstacle.width}px`, // 장애물의 너비
height: `${obstacle.height}px`, // 장애물의 높이
backgroundColor: 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.5)' // 장애물의 색상 (반투명 빨간색)
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
position: relative;
width: 100%;
}
.obstacle {
position: absolute;
background-color: rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.5); /* 장애물의 색상 */
}
</style>2.1. App.vue 코드 상세 설명
2.1.1. Data
- obstacles는 배열은 장애물의 위치와 크기 정보를 담고 있으며, 이를 바탕으로 장애물을 화면에 표시합니다
2.1.2. Methods
- getObstacleStyle 메서드는 각 장애물의 위치와 크기를 반영하여 스타일을 반환합니다.
2.1.3. Style
- obstacle 클래스는 장애물의 배경색을 지정합니다.
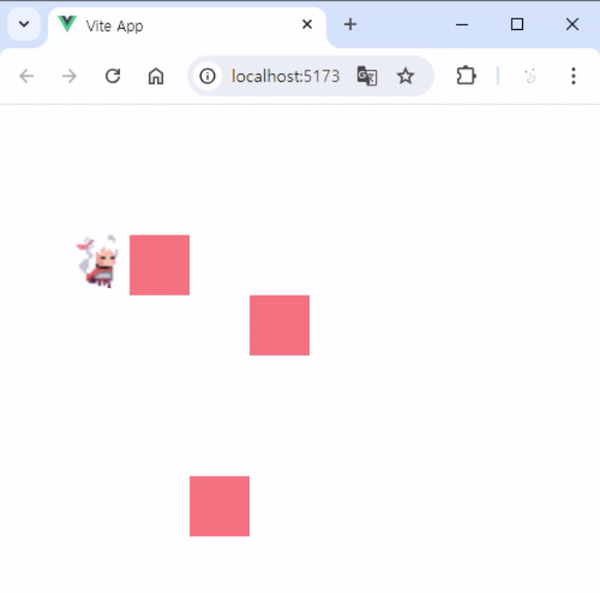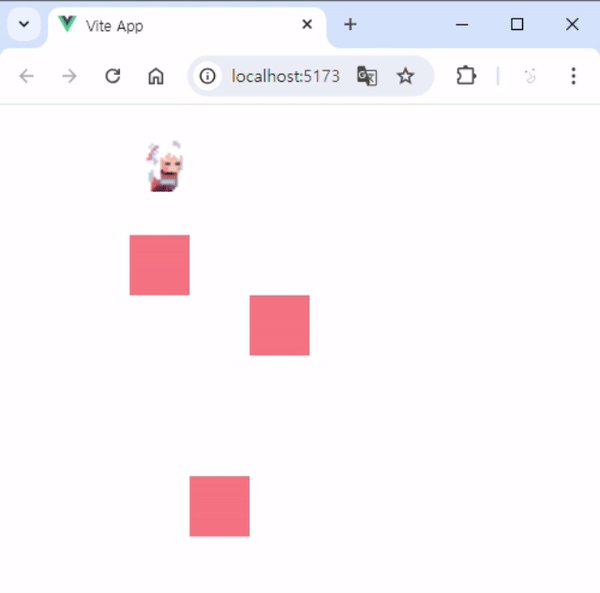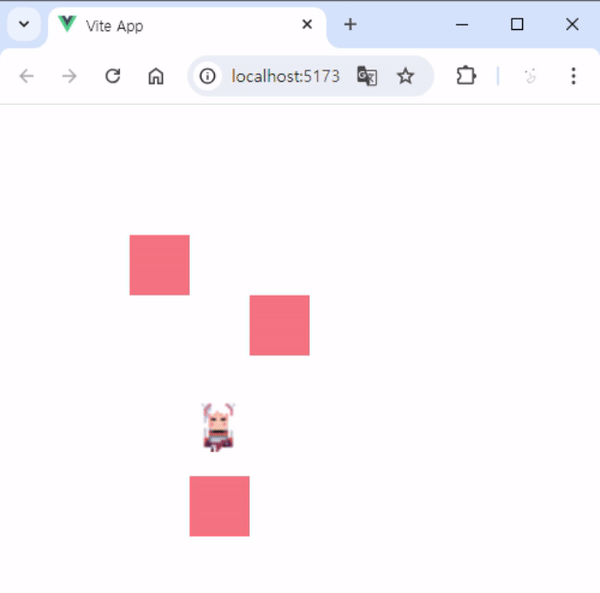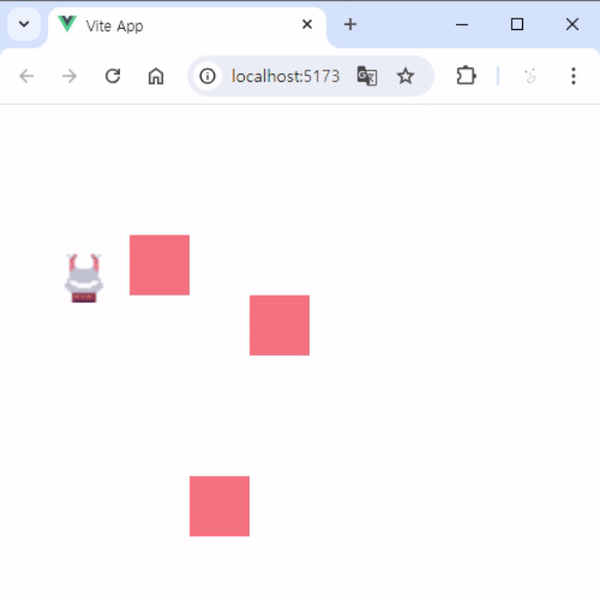
3. 실행 결과
- 실행하면 아래 사진과 같이 동작을 볼 수 있습니다.
- 장애물이 있을 때는 그 방향으로 움직일 수 없습니다.