Spring Boot Actuator는 Spring Boot의 하위 프로젝트입니다. 적은 노력으로 애플리케이션에 여러 프로덕션 등급(grade) 서비스를 추가합니다. 이 가이드에서는 애플리케이션을 구축한 다음 이러한 서비스를 추가하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
What You Will Build
이 가이드에서는 Spring Boot Actuator를 사용하여 "Hello, world" RESTful 웹 서비스를 생성하는 과정을 안내합니다. 다음 HTTP GET 요청을 수락하는 서비스를 구축합니다.
$ curl http://localhost:9000/hello-world이에 대해 다음과 같은 JSON 응답을 받습니다.
{"id":1,"content":"Hello, World!"}프로덕션(또는 기타) 환경에서 서비스를 관리하기 위해 애플리케이션에 많은 기능이 추가되었습니다. 구축하는 서비스의 비즈니스 기능은 RESTful 웹 서비스 구축과 동일합니다. 결과를 비교하는 것이 흥미로울 수 있지만 이 가이드를 활용하기 위해 해당 가이드를 사용할 필요는 없습니다.
Starting with Spring Initalizr
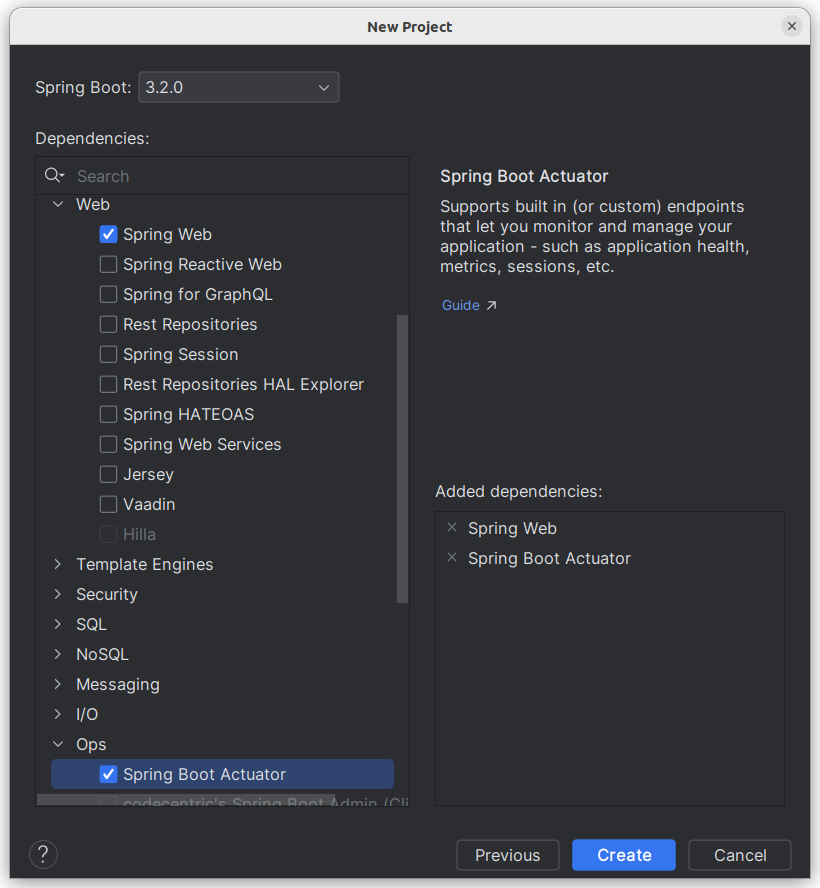
Run the Empty Service
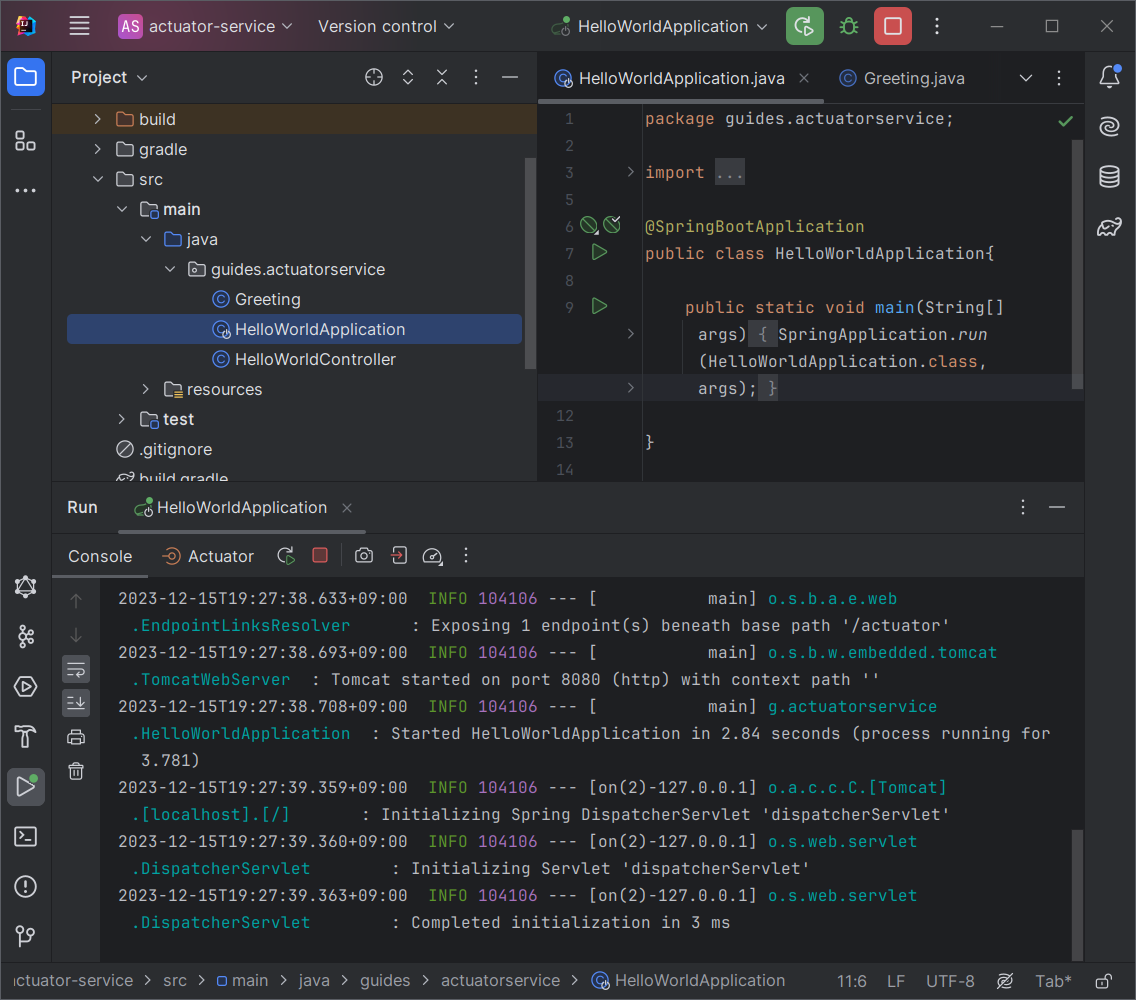
Spring initializr는 시작하는 데 사용할 수 있는 빈 애플리케이션을 생성합니다. 다음 예제(초기 디렉토리의 src/main/java/guides/actuatorservice/ActuatorServiceApplication)는 Spring Initializr에 의해 생성된 클래스를 보여줍니다.
@SpringBootApplication 주석은 classpath 및 기타 사항의 내용에 따라 (내장된 서블릿 컨테이너와 같은) 기본값 로드를 제공합니다. 또한 웹 엔드포인트를 활성화하는 Spring MVC의 @EnableWebMvc 주석을 활성화합니다.
이 애플리케이션에는 엔드포인트가 정의되어 있지 않지만, 무언가를 시작하고 Actuator의 일부 기능을 볼 수 있을 만큼 충분합니다. SpringApplication.run() 명령은 웹 애플리케이션을 시작하는 방법을 알고 있습니다. 다음 명령을 실행하기만 하면 됩니다.
$ ./gradlew clean build && java -jar build/libs/gs-actuator-service-0.1.0.jar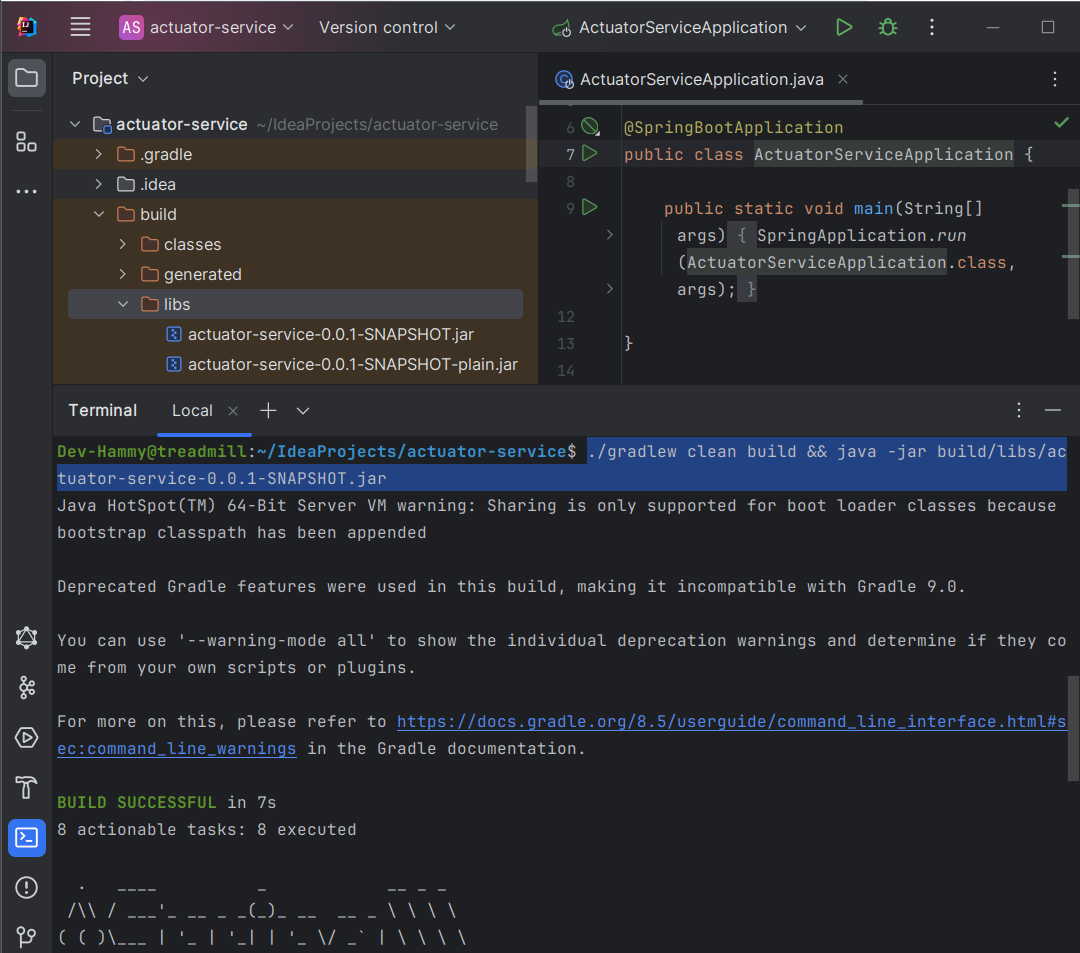
프로젝트 디렉터리의 build/libs 폴더를 열어보면 archive라고 하는 jar 파일들이 보입니다. 그 중 하나를 위 명령어 형식에 대입하여 실행하였습니다.
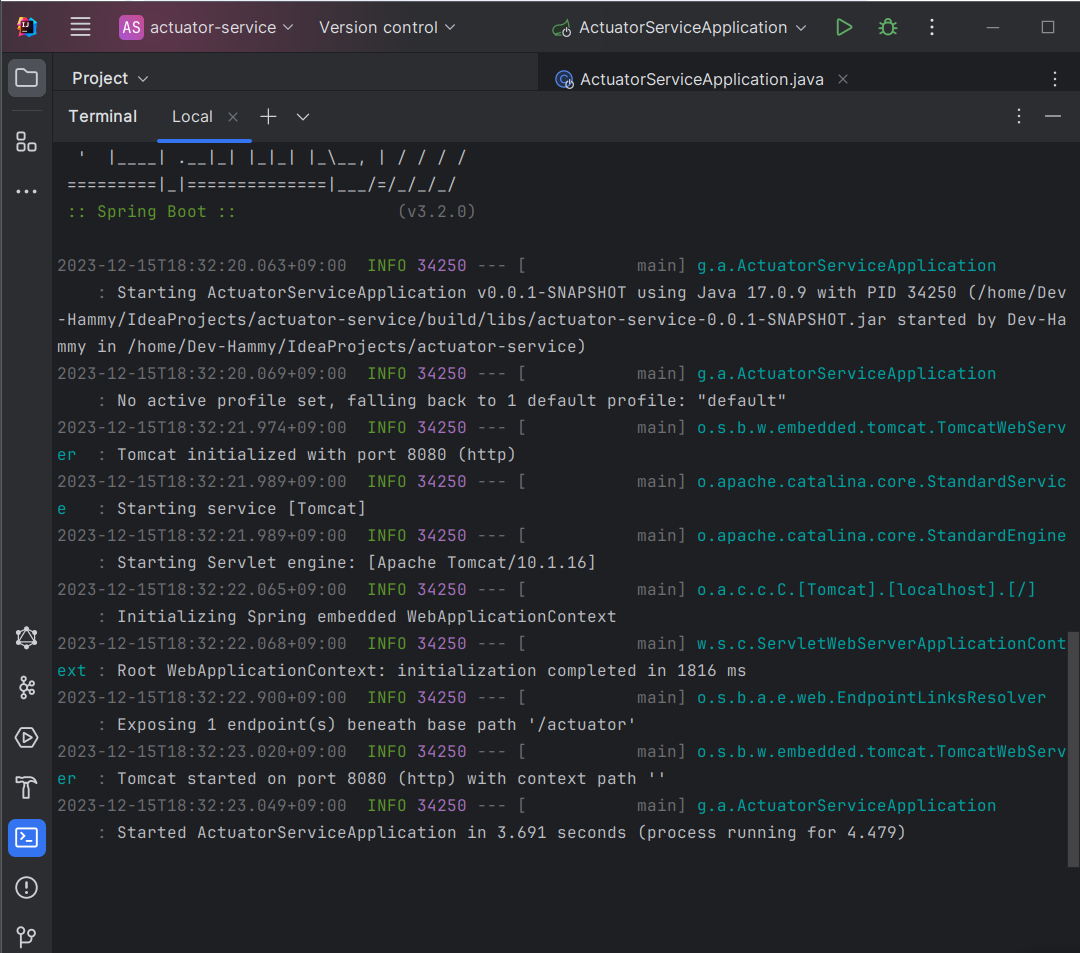
로그 내용은 아래와 같습니다.
-
애플리케이션 실행:
actuator-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar파일을 실행하여 Spring Boot 애플리케이션이 시작되었습니다. 이 애플리케이션은 Java 17.0.9에서 실행 중이며, 기본적으로 "default" 프로파일을 사용합니다. -
웹 서버 초기화: 내장 톰캣 (Embedded Tomcat)이 8080 포트에서 초기화되었습니다. 이 애플리케이션은
/actuator경로 아래에 1개의 엔드포인트를 노출하고 있습니다./actuator엔드포인트를 통해 애플리케이션의 상태 및 정보를 확인할 수 있을 것입니다.
아직 코드를 작성하지 않았는데 무슨 일이 일어나고 있나요? 답변을 보려면 서버가 시작될 때까지 기다렸다가 다른 터미널을 열고 다음 명령을 실행해 보십시오(출력과 함께 표시됨).
$ curl localhost:8080
// 출력결과
{"timestamp":1384788106983,"error":"Not Found","status":404,"message":""}
인텔리제이에서 첫번째 터미널을 통해 서버를 열었으니 새 터미널을 열어서 위 명령어를 실행해보겠습니다.
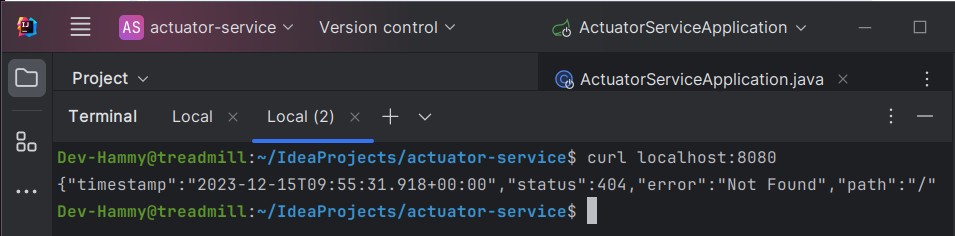
이전 명령의 출력은 서버가 실행 중이지만 아직 비즈니스 엔드포인트를 정의하지 않았음을 나타냅니다. 기본 컨테이너 생성 HTML 오류 응답 대신 Actuator /error 엔드포인트의 일반 JSON 응답이 표시됩니다. 서버 시작 시 콘솔 로그에서 기본적으로 제공되는 엔드포인트를 확인할 수 있습니다. /health 엔드포인트를 포함하여 이러한 엔드포인트 중 몇 가지를 시도해 볼 수 있습니다. 다음 예에서는 그 방법을 보여줍니다.
$ curl localhost:8080/actuator/health
{"status":"UP"}상태가 UP이므로 Actuator 서비스가 실행 중입니다.
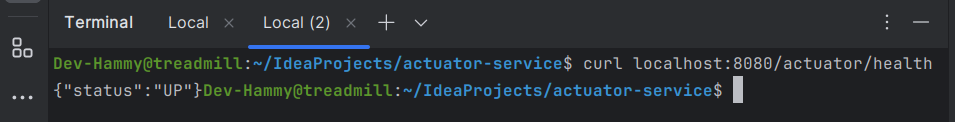
자세한 내용은 Spring Boot의 Actuator 프로젝트를 참조하세요.
Create a Representation Class
먼저, API가 어떤 모습일지 생각해 볼 필요가 있습니다.
선택적으로 이름 쿼리 매개변수를 사용하여 /hello-world에 대한 GET 요청을 처리하려고 합니다. 이러한 요청에 대한 응답으로 다음과 같은 인사말을 나타내는 JSON을 다시 보내려고 합니다.
{
"id": 1,
"content": "Hello, World!"
}id 필드는 인사말의 고유 식별자이며 content에는 인사말의 텍스트 표현이 포함됩니다.
인사말 표현을 모델링하려면 표현 클래스를 만듭니다. 다음 목록(src/main/java/guides/actuatorservice/Greeting.java)은 Greeting 클래스를 보여줍니다.
package guides.actuatorservice;
public class Greeting {
private final long id;
private final String content;
public Greeting(long id, String content) {
this.id = id;
this.content = content;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}이제 표현 클래스를 제공할 엔드포인트 컨트롤러를 생성해야 합니다.
Create a Resource Controller
Spring에서 REST 엔드포인트는 Spring MVC 컨트롤러입니다. 다음 Spring MVC 컨트롤러(src/main/java/guides/actuatorservice/HelloWorldController.java)는 /hello-world 엔드포인트에 대한 GET 요청을 처리하고 Greeting 리소스를 반환합니다.
package guides.actuatorservice;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
private static final String template = "Hello, %s!";
private final AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
@GetMapping("/hello-world")
@ResponseBody
public Greeting sayHello(@RequestParam(name = "name", required = false, defaultValue = "Stranger") String name) {
return new Greeting(counter.incrementAndGet(), String.format(template, name));
}
}인간 지향 컨트롤러와 REST 엔드포인트 컨트롤러의 주요 차이점은 응답이 생성되는 방식에 있습니다. 모델 데이터를 HTML로 렌더링하기 위해 뷰(예: JSP)에 의존하는 대신 엔드포인트 컨트롤러는 응답 본문에 직접 쓸 데이터를 반환합니다.
@ResponseBody 애너테이션은 Spring MVC에게 모델을 뷰로 렌더링하지 않고 반환된 객체를 응답 본문에 쓰도록 지시합니다. 이는 Spring의 메시지 변환기 중 하나를 사용하여 수행됩니다. Jackson 2가 classpath에 있기 때문에 요청의 Accept 헤더가 JSON을 반환해야 한다고 지정하는 경우 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter는 Greeting 개체를 JSON으로 변환하는 작업을 처리합니다.
Jackson 2가 classpath에 있는지 어떻게 알 수 있나요?
mvn dependency:tree또는./gradlew dependency를 실행하면 Jackson 2.x를 포함하는 자세한 종속성 트리를 얻을 수 있습니다. 또한spring-boot-starter-web에서 가져온/spring-boot-starter-json에서 가져온 것임을 확인할 수 있습니다.
애플리케이션 실행
사용자 정의 기본 클래스에서 또는 구성 클래스 중 하나에서 직접 애플리케이션을 실행할 수 있습니다. 이 간단한 예에서는 SpringApplication 도우미(helper) 클래스를 사용할 수 있습니다. 이것은 Spring Initializr가 당신을 위해 생성한 애플리케이션 클래스이며, 이 간단한 애플리케이션에서 작동하도록 수정할 필요조차 없습니다. 다음 목록(src/main/java/guides/actuatorservice/HelloWorldApplication.java)은 애플리케이션 클래스를 보여줍니다.
package guides.actuatorservice;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldApplication.class, args);
}
}일반적인 Spring MVC 애플리케이션에서는 @EnableWebMvc를 추가하여 DispatcherServlet 구성을 포함한 주요 동작을 활성화합니다. 그러나 Spring Boot는 classpath에서 spring-webmvc를 감지하면 자동으로 이 주석을 활성화합니다. 그러면 다음 단계에서 컨트롤러를 구축할 수 있도록 설정됩니다.
@SpringBootApplication 주석은 또한 @ComponentScan 주석을 가져오는데, 이는 Spring에게 해당 컨트롤러에 대한 guides.actuatorservice 패키지(다른 주석이 달린 구성 요소 클래스와 함께)를 검색하도록 지시합니다.
$ curl localhost:8080/hello-world
// 출력결과
{"id":1,"content":"Hello, Stranger!"}애플리케이션을 실행 시킨 상태에서 다른 터미널에 위 엔드포인트를 입력하고 아래와 같은 출력 결과를 확인할 수 있다.
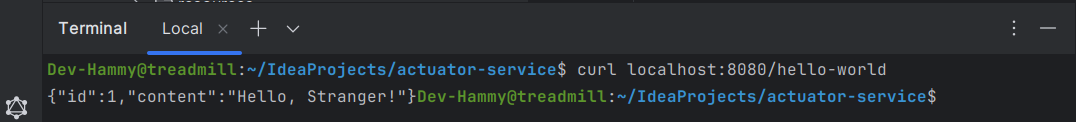
Switch to a Different Server Port
Spring Boot Actuator는 기본적으로 포트 8080에서 실행됩니다. application.properties 파일을 추가하면 해당 설정을 재정의할 수 있습니다. 다음 목록(src/main/resources/application.properties)은 필요한 변경 사항이 포함된 해당 파일을 보여줍니다.
server.port: 9000
management.server.port: 9001
management.server.address: 127.0.0.1일반적으로 management.server.port는 Actuator 엔드포인트에 대한 HTTP 요청을 처리하는 포트를 지정하며, management.server.address는 이러한 관리 기능을 사용할 수 있는 IP 주소를 나타냅니다. 예를 들어, 로컬에서만 Actuator 엔드포인트에 접근할 수 있도록 127.0.0.1 주소를 사용할 수 있습니다.
아무 구현 없이 actuator로 실행했던 그 명령어를 다시 실행해봅니다.
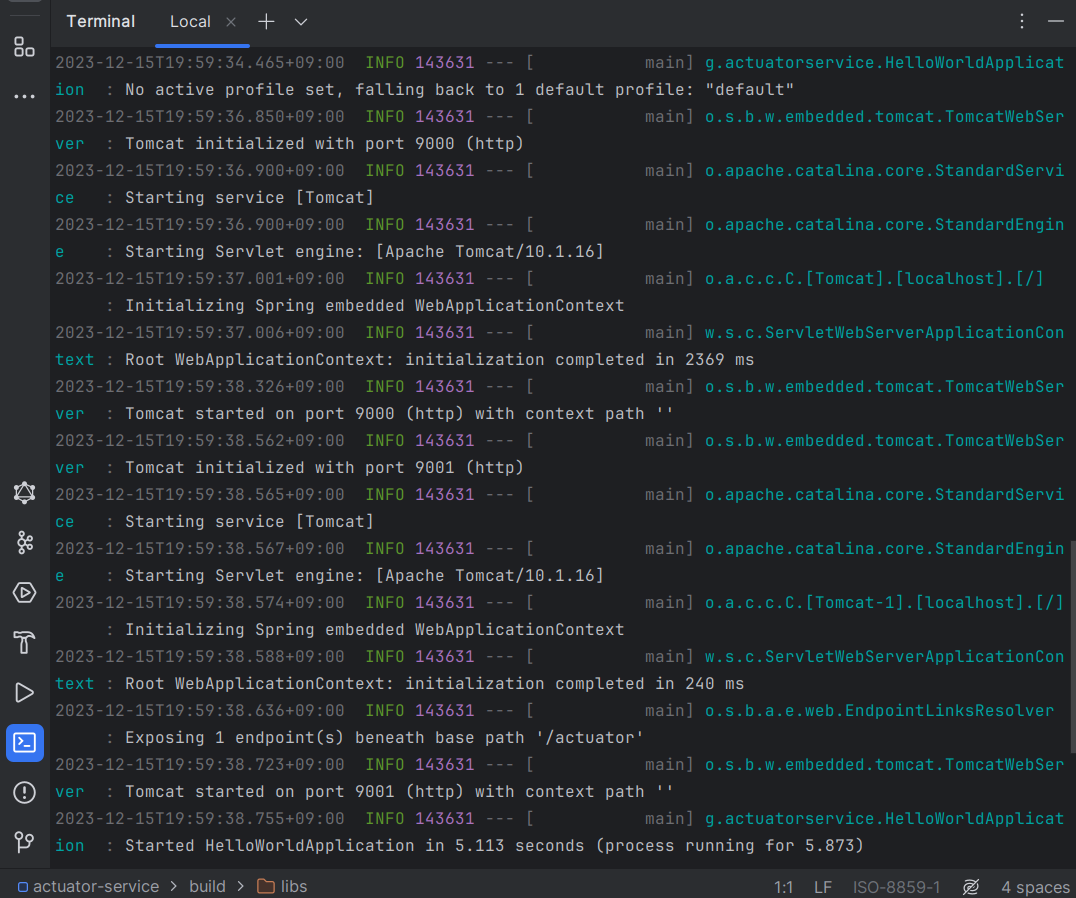
포트 9000에서 실행되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
아래 명령어를 다른 터미널에서 실행해서 포트가 각각 어떻게 실행 중인지 확인하는 방법도 있습니다.
$ curl localhost:8080/hello-world
// 출력 결과
curl: (52) Empty reply from server
$ curl localhost:9000/hello-world
// 출력 결과
{"id":1,"content":"Hello, Stranger!"}
$ curl localhost:9001/actuator/health
// 출력 결과
{"status":"UP"}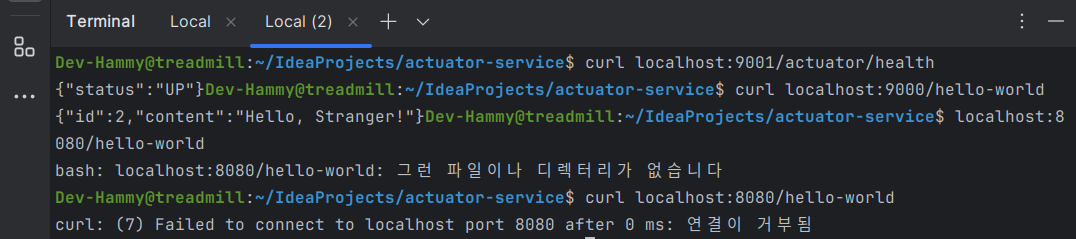
애플리케이션 테스트
애플리케이션이 작동하는지 확인하려면 애플리케이션에 대한 단위 및 통합 테스트를 작성해야 합니다. src/test/java/guides/actuatorservice/HelloWorldApplicationTests.java의 테스트 클래스는 다음을 보장합니다.
- 컨트롤러가 반응합니다.
- 관리 엔드포인트가 응답합니다.
테스트는 임의의 포트에서 애플리케이션을 시작합니다. 다음 목록은 테스트 클래스를 보여줍니다.
package guides.actuatorservice;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.server.LocalServerPort;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.assertj.core.api.BDDAssertions.then;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@TestPropertySource(properties = {"management.port=0"})
public class HelloWorldApplicationTests {
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Value("${local.management.port}")
private int mgt;
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate;
@Test
public void shouldReturn200WhenSendingRequestToController() throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
ResponseEntity<Map> entity = this.testRestTemplate.getForEntity(
"http://localhost:" + this.port + "/hello-world", Map.class);
then(entity.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
}
@Test
public void shouldReturn200WhenSendingRequestToManagementEndpoint() throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
ResponseEntity<Map> entity = this.testRestTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:" + this.mgt + "/actuator", Map.class);
then(entity.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
-
RANDOM_PORT를 사용하는 것은 애플리케이션을 테스트할 때 무작위 포트를 할당하여 테스트를 실행하는 것입니다. 이는 여러 테스트가 동시에 실행될 때 포트 충돌을 방지하고, 테스트 환경을 더 견고하게 만들어줍니다. 만약application.properties에서 포트를 지정하면, 특정한 포트 번호를 사용하게 됩니다. 그러나 대부분의 경우 테스트에 무작위 포트를 사용하는 것이 테스트를 더 견고하게 만들어주기 때문에RANDOM_PORT를 사용합니다. -
@ConfigurationProperties와@TestPropertySource는 모두 프로퍼티 값을 가져와 객체에 할당하거나 테스트에서 사용할 프로퍼티 소스를 지정하는 데 사용됩니다.
@ConfigurationProperties: 주로 애플리케이션의 설정을 관리하는데 사용되며, 외부 설정 파일(application.properties 또는 application.yml)에서 값을 가져와서 빈(bean)에게 주입합니다.@TestPropertySource: 단위 테스트에서만 사용되는 어노테이션으로, 특정한 프로퍼티 소스를 지정하여 테스트 시에 사용할 프로퍼티를 정의합니다.
-
@LocalServerPort는 내장 서버(예: 내장 톰캣)의 랜덤 포트를 가져오기 위해 사용됩니다.@Value어노테이션을 사용하여 외부 설정 파일에서 지정한 값을 가져올 수도 있습니다. -
@Value어노테이션은 스프링의Environment에서 프로퍼티 값을 주입받기 위해 사용됩니다. 외부 설정 파일(application.properties 등)에 있는 값을 가져와 필드에 주입할 때 사용됩니다. -
RestTemplate:
- RESTful 웹 서비스와 상호 작용하기 위한 Spring의 클라이언트 측 HTTP 통신을 담당하는 클래스입니다.
- RESTful 웹 서비스의 엔드포인트에 HTTP 요청을 보내고, 응답을 받아오는 등의 작업을 수행합니다.
- GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 등의 HTTP 메서드를 사용하여 원격 서버와 통신할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
- 응답을 받아오는 방법은
RestTemplate을 사용하여 직접 파싱하거나,ResponseEntity형태로 받을 수 있습니다.
-
ResponseEntity:
- HTTP 응답의 상태 코드, 헤더 및 바디 등을 담는 Spring의 클래스입니다.
ResponseEntity를 통해 받아온 HTTP 응답을 처리하고, 응답의 상태 코드나 헤더 등을 접근하거나 확인할 수 있습니다.- 보통
RestTemplate을 사용하여 원격 서버로부터 받은 응답을ResponseEntity형태로 받아와서 응답을 처리하거나 분석합니다.
-
간단히 말하면,
RestTemplate은 RESTful 웹 서비스와의 통신을 담당하고, 이를 통해 받은 HTTP 응답은ResponseEntity를 사용하여 처리하거나 분석합니다.RestTemplate을 통해 요청을 보내고 응답을 받은 후, 그 응답을ResponseEntity로 wrapping하여 상세한 처리를 할 수 있습니다. -
ResponseEntity는 HTTP 응답 전체를 나타내는 반면,@ResponseBody는 HTTP 응답의 바디(body) 부분만을 처리하는데 사용됩니다.ResponseEntity를 사용하면 응답의 상태 코드나 헤더 등을 보다 세밀하게 다룰 수 있습니다. -
SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")는 컴파일러에게 제네릭 타입 관련된 경고를 억제하는 것으로,ResponseEntity를 제네릭으로 사용할 때 타입 안정성에 관한 경고를 숨기는 역할을 합니다.
테스트 결과
> Task :compileJava UP-TO-DATE
> Task :processResources UP-TO-DATE
> Task :classes UP-TO-DATE
> Task :compileTestJava
> Task :processTestResources NO-SOURCE
> Task :testClasses
22:41:48.899 [Test worker] INFO org.springframework.test.context.support.AnnotationConfigContextLoaderUtils -- Could not detect default configuration classes for test class [guides.actuatorservice.HelloWorldApplicationTests]: HelloWorldApplicationTests does not declare any static, non-private, non-final, nested classes annotated with @Configuration.
22:41:49.066 [Test worker] INFO org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTestContextBootstrapper -- Found @SpringBootConfiguration guides.actuatorservice.HelloWorldApplication for test class guides.actuatorservice.HelloWorldApplicationTests
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v3.2.0)
2023-12-15T22:41:49.670+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] g.a.HelloWorldApplicationTests : Starting HelloWorldApplicationTests using Java 17.0.9 with PID 344181 (started by Dev-Hammy in /home/Dev-Hammy/IdeaProjects/actuator-service)
2023-12-15T22:41:49.674+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] g.a.HelloWorldApplicationTests : No active profile set, falling back to 1 default profile: "default"
2023-12-15T22:41:51.268+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port 0 (http)
2023-12-15T22:41:51.283+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2023-12-15T22:41:51.284+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/10.1.16]
2023-12-15T22:41:51.366+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2023-12-15T22:41:51.369+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] w.s.c.ServletWebServerApplicationContext : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 1665 ms
2023-12-15T22:41:52.157+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port 42087 (http) with context path ''
2023-12-15T22:41:52.278+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port 0 (http)
2023-12-15T22:41:52.281+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2023-12-15T22:41:52.282+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/10.1.16]
2023-12-15T22:41:52.300+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat-1].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2023-12-15T22:41:52.301+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] w.s.c.ServletWebServerApplicationContext : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 137 ms
2023-12-15T22:41:52.327+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.s.b.a.e.web.EndpointLinksResolver : Exposing 1 endpoint(s) beneath base path '/actuator'
2023-12-15T22:41:52.387+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port 36653 (http) with context path ''
2023-12-15T22:41:52.403+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [ Test worker] g.a.HelloWorldApplicationTests : Started HelloWorldApplicationTests in 3.127 seconds (process running for 4.853)
2023-12-15T22:41:53.593+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [1-auto-2-exec-1] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat-1].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServletRegistration'
2023-12-15T22:41:53.594+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [1-auto-2-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServletRegistration'
2023-12-15T22:41:53.595+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [1-auto-2-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 1 ms
2023-12-15T22:41:53.828+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [o-auto-1-exec-1] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2023-12-15T22:41:53.828+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [o-auto-1-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2023-12-15T22:41:53.830+09:00 INFO 344181 --- [o-auto-1-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 2 ms
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM warning: Sharing is only supported for boot loader classes because bootstrap classpath has been appended
> Task :test
Deprecated Gradle features were used in this build, making it incompatible with Gradle 9.0.
You can use '--warning-mode all' to show the individual deprecation warnings and determine if they come from your own scripts or plugins.
For more on this, please refer to https://docs.gradle.org/8.5/userguide/command_line_interface.html#sec:command_line_warnings in the Gradle documentation.
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 7s
4 actionable tasks: 2 executed, 2 up-to-date
오후 10:41:54: Execution finished ':test --tests "guides.actuatorservice.HelloWorldApplicationTests"'.