
1. 정의
배열 안에 또 다른 배열이 포함되어 있는 것을 2차원 배열이라고 한다.
ex.
const array = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]];array 라는 배열 안에 3개의 배열이 각각 0, 1, 2번째 위치에 포함되어 있는 구조이다.
2. 2차원 배열 만들기 예제
ex1.
const array = [];
const number1 = [1, 2, 3];
const number2 = [4, 5, 6];
const number3 = [7, 8, 9];
array.push(number1, number2, number3);
console.log(array); // [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]배열 메서드 push를 사용하여 2차원 배열을 만들 수 있다.
ex2.
다음은 JavaScript에서 table을 작성하여 HTML에 적용시키는 예제이다. 다음 HTML 코드를 JavaScript에서 2차원 배열로 적용시켜 구현해보려고 한다.
- HTML
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>- JavaScript
const table = document.createElement('table');
const trs = [];
const tds = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
let tr = document.createElement('tr');
trs.push(tr);
tds.push([]);
for (let j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
let td = document.createElement('td');
tds[i].push(td);
tr.appendChild(td);
}
table.appendChild(tr);
}
body.appendChild(table);
console.log(trs, tds);console 창에서 결과를 확인해보면 다음과 같다.
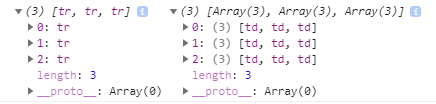
처음에 여기서 헷갈렸던 부분이 이중 반복문의 작동방식이었다. 생각해본 결과,
i = 0 일 때, j = 0, 1, 2
i = 1 일 때, j = 0, 1, 2
i = 2 일 때, j = 0, 1, 2
순으로 작동하는 것이라고 이해했다.
반복문의 특성은 어떤 특정한 조건이 거짓으로 판별될 때까지 반복하는 것이다.
따라서, 첫 반복문에서 i = 0으로 시작하고, 두 번째 반복문에서 j = 0으로 실행된다.
여기서 반복문의 특성을 다시 생각해보면, 아직 두 번째 반복문의 조건이 거짓이 아니므로, j = 1로 다시 실행된다.
j = 2까지 실행되고, j = 3이 되었을 때, j < 3 의 조건과 부합하지 않으므로 두 번째 반복문이 종료된다.
다시 첫 번째 반복문으로 돌아가서 i = 1로 실행되고 앞의 과정을 반복, i = 2, j= 2까지 실행한 후 반복문이 모두 종료된다.
Ref.
inflearn_웹 게임을 만들며 배우는 자바스크립트
https://medium.com/javascript-in-plain-english/javascript-multi-dimensional-arrays-7186e8edd03
https://www.javascripttutorial.net/javascript-multidimensional-array/
https://gent.tistory.com/296
https://smilerici.tistory.com/71
https://improver.tistory.com/42