Before DRF
- 사용자가 API URL 호출
- 웹 서버가 요청을 수신하여 Django Application Server에 전달
- Request 전달
- 요청을 미들웨어에 전달
- URLConf에서 적합한 뷰 탐색
적합한 뷰가 없다면 404 에러 전달 - 뷰의
dispatch메서드 호출(Request 객체 전달)
🧐 클래스가 어떻게 View로 전환될까?
as_view함수 때문이다.
DRF Flow
dispatch 호출
DRF의 dispatch 함수의 주석을 보면 다음과 같이 나와 있다.
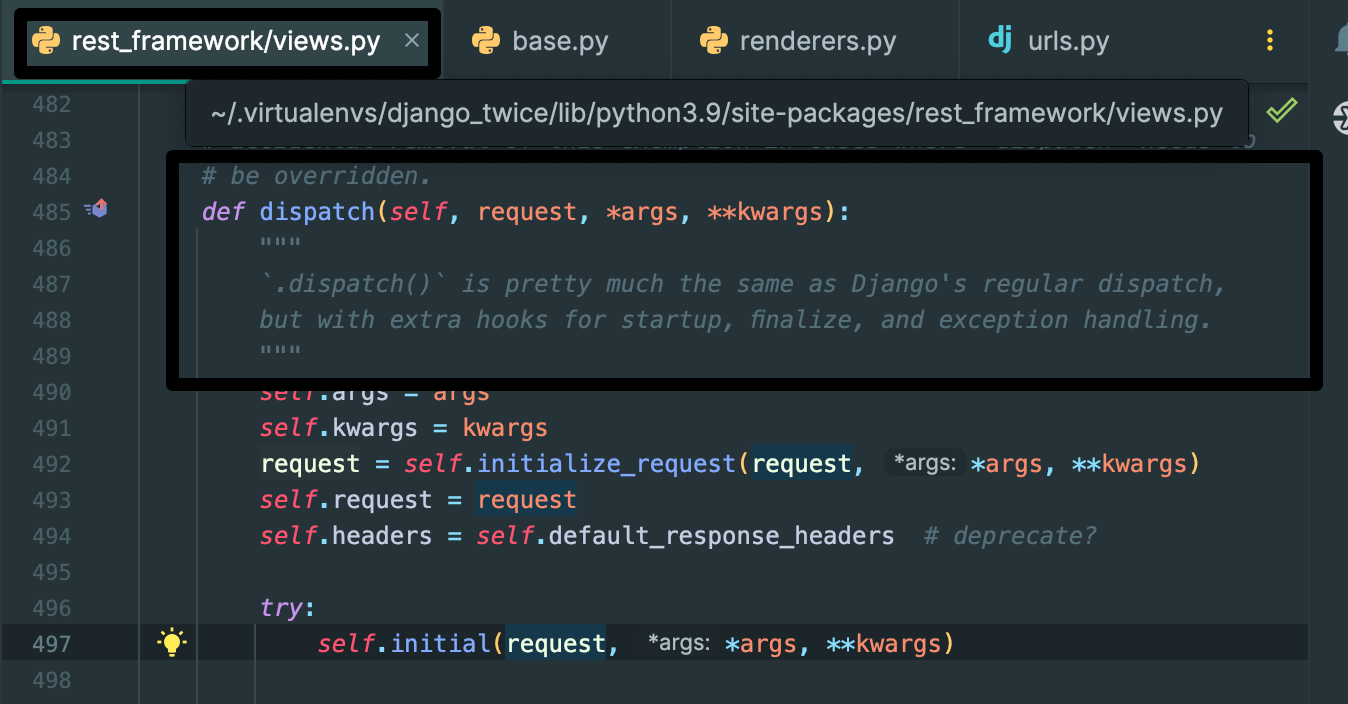
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
// django 일반 디스패치와 거의 동일하며, 시작, 최종화 및 예외 처리를 위한 추가 훅이 존재합니다.
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""dispatch()은 request와 response의 중개자 역할을 한다.
HTTP 메서드의 Request를 해석하는 일을 담당한다.(Ex, Get Or Psot...)
클라이언트가 URL을 입력하면 URLConf를 통해 View에 요청정보가 전달되는 데 Class형 View는 as_view()를 통해 전달 받고 이 때 dispatch 메서드가 자동으로 호출된다.
유저 인증, 권한 확인
dispath 함수를 보면 self.initial을 호출하는 것을 볼 수 있다.(매개변수로 request를 넘긴다.)
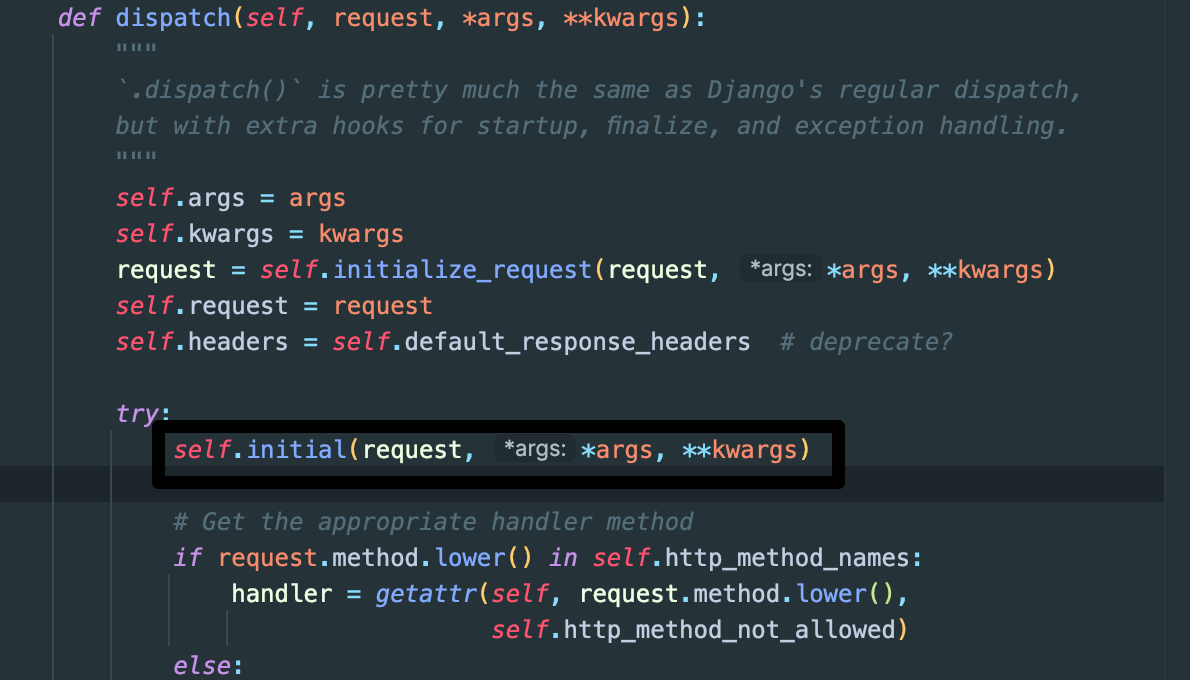
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
매서드 핸들러 전에 발생하는 일 처리
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs)
# Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
# 컨탠츠?
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg
# Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
# 버전관리 핸들링
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme
# Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
# 요청 확인(인증, 권한)
self.perform_authentication(request)
self.check_permissions(request)
self.check_throttles(request)핸들러 선택
dispatch() 메서드는 요청 메서드에 적합한 핸들러를 검색합니다.
적합한 핸들러가 없다면 MethodNotAllowed(405) 에러를 발생합니다.
try:
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
# Get the appropriate handler method
# method_name 배열은 아래에 있습니다 :)
# 소문자로 변경한 요청 메서드가 http_method_names에 있다면
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
# 현재 class에 메서드를 찾아 있으면 해당 handler반환 없으면 에러 발생
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
# 없으면 에러 발생
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc)# method_name 배열
http_method_names = [
"get",
"post",
"put",
"patch",
"delete",
"head",
"options",
"trace",
]
# 없을 시 호출하는 메서드
def http_method_not_allowed(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
request.method가 handler method와 일치하지 않으면 에러를 발생합니다.
If `request.method` does not correspond to a handler method,
determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
raise exceptions.MethodNotAllowed(request.method)
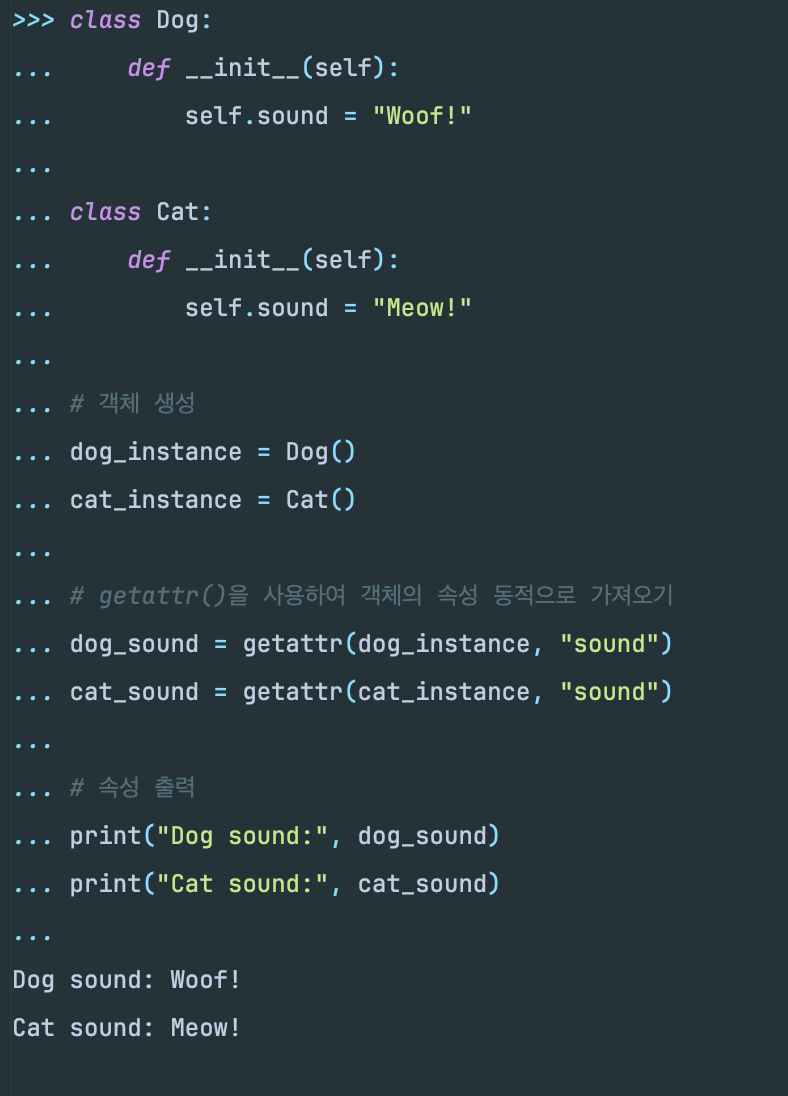
# object에 name이 있으면 반환, 없다면 3번째 인자 실행하는 built.py 함수
def getattr(object, name, default=None): # known special case of getattr
"""
getattr(object, name[, default]) -> value
Get a named attribute from an object; getattr(x, 'y') is equivalent to x.y.
When a default argument is given, it is returned when the attribute doesn't exist; without it, an exception is raised in that case.
"""
pass