C++에는 GC가 없으므로 exception safety guarantee를 준수하지않으면 리소스 leak까지 일어날 수 있다.
- Basic Exception Safety
이는 exception이 던져졌을때 resource leak은 없지만, 상태변화가 있을 수 있다는 것이다.
#include <exception>
#include <iostream>
int g = 0;
int divide(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("divide by 0");
}
return a / b;
}
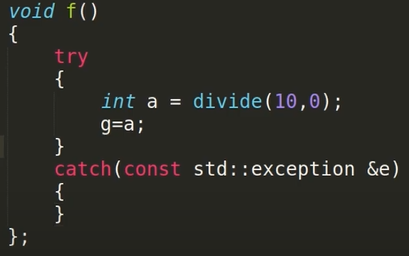
void f()
{
g = 1;
std::cout << divide(10, 0) << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "g : " << g << std::endl;
try
{
f();
}
catch (const std::exception &e)
{
std::cout << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}위와 같이 글로벌 변수를 선언하고
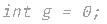
exception이 일어날 함수에서 변수가 바뀌는 경우 상태변화가 있다고 본다.

-
Strong Exception Safety
exception이 던져졌을때 resource leak, 상태변화가 모두 없는 경우이다.
이는 위의 코드에서 상태변화가 일어날 수 있는 코드를 exception이 던져질 수 있는 함수보다 나중에 넣으면 된다.

이러면 exception이 일어나면 g = 1;은 실행되지않고 stack unwinding이 일어나므로 exception시 상태변화가 일어나지않는다. -
no throw guarantee
exception이 던져지지않는 함수를 말한다.앞선 코드들에서는 f() 함수에 try catch문이 없어 main()함수에게 발생한 exception을 넘겼는데,
위와 같이 try catch문이 있다면 더 이상 propagation이 일어나지않으므로 no throw guarantee를 준수한다.
default constructor, destructor, move, swap은 exception을 던지게되면
c++ exception handling이 꼬이게되므로 exception을 던져서는 안된다.