coroutine : 유니티에서 코루틴을 사용하면 작업을 다수의 프레임에 분산할 수 있다.
특징
- 코루틴은 유니티 프레임워크에서 업데이트 이후에 실행된다.
- 코루틴 실행 중 yield를 만나면 값을 enmerator.Current를 통해 값을 return하고 enmerator.MoveNext를 통해 다음 yield가 없다면 코루틴이 종료되고 있다면 다음 yield retrun문으로 넘어간다.
C# 실습
다음 코드의 동작 순서를 확인한다.
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
IEnumerator<int> Test(bool cancel)
{
yield return 100;
yield return 50;
if (cancel)
{
yield break;
}
yield return 10;
}
IEnumerator<int> enmerator = Test(false);
while(enmerator.MoveNext() )
{
Console.WriteLine(enmerator.Current);
}
}
}인터페이스 IEnumerator을 확인하면
namespace System.Collections.Generic
{
//
// 요약:
// Supports a simple iteration over a generic collection.
//
// 형식 매개 변수:
// T:
// The type of objects to enumerate.
public interface IEnumerator<out T> : IEnumerator, IDisposable
{
//
// 요약:
// Gets the element in the collection at the current position of the enumerator.
//
// 반환 값:
// The element in the collection at the current position of the enumerator.
T Current { get; }
}namespace System.Collections
{
//
// 요약:
// Supports a simple iteration over a non-generic collection.
public interface IEnumerator
{
//
// 요약:
// Gets the element in the collection at the current position of the enumerator.
//
// 반환 값:
// The element in the collection at the current position of the enumerator.
object Current { get; }
//
// 요약:
// Advances the enumerator to the next element of the collection.
//
// 반환 값:
// true if the enumerator was successfully advanced to the next element; false if
// the enumerator has passed the end of the collection.
//
// 예외:
// T:System.InvalidOperationException:
// The collection was modified after the enumerator was created.
bool MoveNext();
//
// 요약:
// Sets the enumerator to its initial position, which is before the first element
// in the collection.
//
// 예외:
// T:System.InvalidOperationException:
// The collection was modified after the enumerator was created.
void Reset();
}
}다음과 같은 코드가 있다.
즉 IEnumerator는
current 반환값이 있고 bool변수를 반환하는 MoveNext를 통해 작동한다.
이를 바탕으로 예제동작을 확인하면
-
IEnumerator<int> enmerator = Test(false);초기화가 먼저 진행된다. -
while(enmerator.MoveNext())반복문 시작
IEnumerator<int> Test(bool cancel)
{
yield return 100;
yield return 50;
if (cancel)
{
yield break;
}
yield return 10;
}이후 MovneNext메서드에서 코루틴이 실행 가능한지 확인하는데 반환값이 총 3개 있는데 아직 한번도 반환값을 넘긴적이 없으므로 MonveNext는 true를 반환한다. MoveNext에서 true가 retrun된다.Current값에는 현재 반환값이 100이므로 100이 들어가게 된다. 즉 enmerator.MoveNext =true, enmerator.Current = 100이다.
4. while(enmerator.MoveNext() ) { Console.WriteLine(enmerator.Current); }
MoveNext가 true이고 current값이 100이므로 100이 출력된다.
- 이후 같은 과정을 통해 50, 10이 출력되고 10이 출려된 이후 MoveNext값에 현재 반환한 값들이 코루틴이 반환할 수 있는 return 갯수를 넘었기 때문에 false가 출력되어 while반복문이 중단된다. 파라미터가 true라면 중간에 코루틴을 중단하므로 MoveNext값이 되어 while문을 이탈하게 되기때문에 100, 50만 출력된다.
유니티 실습
예제
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.F10))
{
Debug.Log("코루틴 시작");
StartCoroutine(EscapeSceneCoroutine());
}
}
IEnumerator EscapeSceneCoroutine()
{
float ingtime = 0f;
while (ingtime <= 3f)
{
Debug.Log("코루틴 실행 중");
ingtime += Time.deltaTime;
yield return null;
}
} F10버튼을 눌럿을때 3초동안 코르틴이 동작하는 예제이다.
위의 C# 에제를 통해 코루틴의 동작순서를 예측하면
1. F10버튼을 눌럿을때 코루틴이 초기화되며 시작한다.
- 첫번째 주기에서 코루틴에서 반환이 한번 일어나야하지만 한번도 일어나지 않았으므로 MoveNext값이 true기 때문에 코루틴이 동작하면서 current 값에 null을 return 한다.
- 코루틴이 이미 한번 값을 반환했으므로 MoveNext가 false를 retrun 한다. -> 코루틴 함수는 더이상 동작하지 않는다.
- while(ingtime<=3f) 즉 F10버튼을 누르고 3초동안 while문은 true이므로 3초 동안 Debug.Log("코루틴 실행 중"); 를 출력한다.
실행 결과
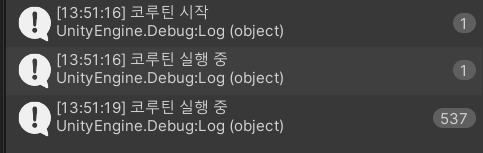
F10 버튼을 한번눌럿을때
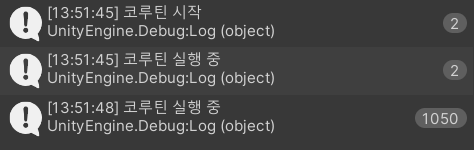
F10 버튼을 한번누르고 3초 후 다시한번 눌럿을때
