
custom-shopping Project
-
기존 팀 프로젝트인 shopping을 리팩토링한 쇼핑몰 프로젝트
-
실제 쇼핑몰 서비스 환경을 생각하여 테스트 시도
-
실제로 동시에 같은 상품을 여러명이 주문을 하거나 취소했을 때 상황을 가정
-
통합 테스트를 통해 전체 흐름을 파악하도록 함
-
동시성 테스트
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount); CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount); CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(threadCount); // 성공 횟수 , 실패횟수, 총 시도 횟수 AtomicInteger successCount = new AtomicInteger(0); AtomicInteger failCount = new AtomicInteger(0); AtomicInteger totalAttemptCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
-
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_COUNT);-
고정된 개수의 스레드 풀을 생성
-
THREAD_COUNT만큼 스레드를 미리 만들어두고 작업을 넣으면 스레드가 재사용 되면서 병렬 실행됨
-
-
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_COUNT);-
스레들이 모두 작업을 마칠 때까지 기다리기 위한 장치
-
스레드 수만큼 카운트를 설정해놓고 각 스레드가 작업 끝낼 때마다
latch.countDown()호출 → 1씩 감소. -
latch.await()하면 모든 스레드가 완료될 때까지 블로킹 됨
-
-
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(THREAD_COUNT);-
특정 지점에서 모든 스레드가 동시에 출발하도록 하는 장치
-
스레드 풀로 실행하면 스레들이 시작 타이밍이 조금 다르기 때문에 사용
-
barrier.await()→ 스레드 수가 모이면 동시에 실행 시작
-
테스트 코드
기본 설정
@SpringBootTest @ActiveProfiles("test") public class NoRockTest { @Autowired private OrderService orderService; @Autowired private TestDataFactory testDataFactory; @Autowired private ProductRepository productRepository; private Product product1; private Product product2; private Product product3; private List<Product> products; private int originalStock; private int threadCount = 10; private int orderQuantity = 20; private int maxRetry = 100; @BeforeEach void setup() { product1 = testDataFactory.createProduct("상품1", "상품1 설명", 1000, 200); product2 = testDataFactory.createProduct("상품2", "상품2 설명", 2000, 200); product3 = testDataFactory.createProduct("상품3", "상품3 설명", 500, 200); products = List.of(product1, product2, product3); originalStock = product1.getStock(); }
주문 생성
상황 : 10명에 사용자가 동시에 같은 상품을 주문하였을 때 재고 변동 상황을 파악하기 위한 테스트
총 재고 200개 상품을 1명 당 20개씩 주문하여 주문 후 총 재고는 0으로 예상하고 테스트 시도
결과 : 데드락 발생
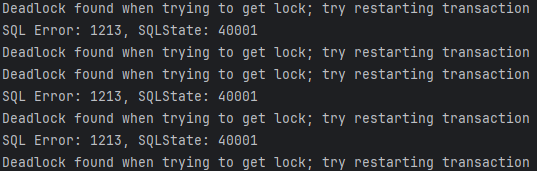
-
주문 생성 시 → 배타 락(X-LOCK)으로 데드락 발생
-
배타 락 (X-LOCK) : 한 트랜잭션이 특정 데이터(행, 테이블 등)를 수정할 때 다른 트랜잭션이 동시에 접근하지 못하도록 걸리는 락
-
쓰기 쿼리(UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT)는 대부분 DB에서 기본적으로 배타락 발생
-
데드락 발생 이유
10개 스레드가 같은 상품들 주문(product1, product2, product3) → 스레드 마다(product1, product2, product3)을 다른 순서로 업데이트 1. 스레드 1 - 락 A 획득 ✅ - 락 B 시도 → B는 스레드 2가 이미 획득 → 대기 2. 스레드 2 - 락 B 획득 ✅
주문 생성 (락이 없는 경우)
@Test void 락이_없는_주문_생성() throws InterruptedException { List<User> users = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { User user = testDataFactory.createUser( "test" + i + "@example.com", "password" + i, "user" + i, "address" + i ); users.add(user); } // 스레드 풀, 동기화 도구 , 스레드 수 = 주문자 수 ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount); CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount); CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(threadCount); // 성공/실패, 총시도횟수 AtomicInteger successCount = new AtomicInteger(0); AtomicInteger failCount = new AtomicInteger(0); AtomicInteger totalAttemptCount = new AtomicInteger(0); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 스레드 풀에 주문 요청 보냄 (for문을 통해 보내기만 함) for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { final int index = i; // 요청 받은 걸 병렬적(동시에)으로 실행 executor.submit(() -> { // 장바구니 목록 List<CartItem> cartItems = testDataFactory .cartItems(users.get(index), products, orderQuantity); int attemptCount = 0; boolean success = false; while (!success && attemptCount < maxRetry) { attemptCount++; try { // 동시 시작 barrier.await(); // 락이 없는 주문 생성 orderService.saveOrder(users.get(index), cartItems); success = true; successCount.incrementAndGet(); totalAttemptCount.addAndGet(attemptCount); } catch (Exception e) { if (attemptCount == maxRetry) { failCount.incrementAndGet(); totalAttemptCount.addAndGet(attemptCount); System.err.println("주문 실패 : " + e.getMessage()); } } } latch.countDown(); }); } // 메인 스레드 대기 latch.await(); // 상품 1로 확인 Product productAfterTest = productRepository.findById(product1.getId()) .orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException(ErrorCode.PRODUCT_NOT_FOUND)); int retryCount = totalAttemptCount.get() - successCount.get(); int finalStock = productAfterTest.getStock(); int expectStock = originalStock - (successCount.get() * orderQuantity); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("=== 락 없이 주문 생성 테스트 결과 ==="); System.out.println("한 스레드당 실행 횟수 : " + maxRetry + "번 실행"); System.out.println("총 소요 시간(ms) : " + (endTime - startTime)); System.out.println("성공 수 : " + successCount.get()); System.out.println("실패 수 : " + failCount.get()); System.out.println("총 시도 횟수(재시도 포함) : " + totalAttemptCount.get()); System.out.println("재시도 횟수 : " + retryCount); System.out.println("기존 재고량 : " + originalStock); System.out.println("주문 수량 합계 (성공 스레드 x 주문 수량) : " + (successCount.get() * orderQuantity)); System.out.println("예상 재고량 : " + expectStock); System.out.println("실제 재고량 : " + finalStock); if (finalStock != expectStock) { System.out.println("동시성 문제 발생 → 재고 수량 불일치"); } else if (retryCount > 0) { System.out.println("동시성 문제 발생 → 재시도가 있었음"); } else { System.out.println("재시도 없음, 재고 수량 정상"); } // 스레드 풀 종료 executor.shutdown(); }
주문 취소(락이 없는 경우)
상황 : 10명에 사용자가 같은 상품 주문 후 동시에 같은 상품을 취소하였을 때 재고 변동 상황을 파악하기 위한 테스트
총 재고 200개 상품을 1명 당 20개씩 주문 후 재고량 0에서 주문을 취소하여 재고량 200개로 예상하고 테스트 시도
데드락 방지
단 product1 만 주문 취소하도록 하여 데드락 상황을 피하도록 유도 → 한 상품에 대해서 배타락이 걸려 데드락이 발생하지 않음
결과 : Lost Update 발생
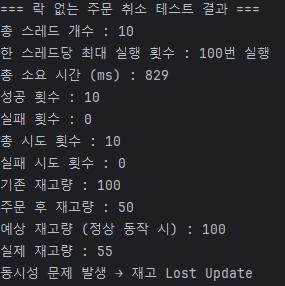
-
주문 취소 시 → Lost Update 발생하여 재고량이 일치하지 않은 문제 발생
- Lost Update : 동시에 데이터가 수정될 때 나중에 온 요청이 이전 결과를 덮어써 앞서 반영된 변경이 사라지는 문제
주문 취소
@Test void 락이_없는_주문_취소() throws InterruptedException { List<User> users = new ArrayList<>(); List<Long> orderIds = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { User user = testDataFactory.createUser( "test1" + i + "@example.com", "pass" + i + "word", "testUser" + i, "test" + i + "Address"); users.add(user); List<CartItem> cartItems = testDataFactory.cartItems(user, products, orderQuantity); Long orderId = orderService.saveOrder(user, cartItems).getOrderId(); orderIds.add(orderId); } Product productAfterOrder = productRepository.findById(product1.getId()) .orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException(ErrorCode.PRODUCT_NOT_FOUND)); // 주문 후 재고량 int orderAfterStock = productAfterOrder.getStock(); ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount); CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount); CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(threadCount); AtomicInteger successCount = new AtomicInteger(0); AtomicInteger failCount = new AtomicInteger(0); AtomicInteger totalAttemptCount = new AtomicInteger(0); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { final int index = i; executor.submit(() -> { int attemptCount = 0; boolean success = false; while (!success && attemptCount < maxRetry) { attemptCount++; try { barrier.await(); orderService.cancelOrder(users.get(index), orderIds.get(index)); success = true; successCount.incrementAndGet(); totalAttemptCount.addAndGet(attemptCount); } catch (Exception e) { if (attemptCount == maxRetry) { failCount.incrementAndGet(); totalAttemptCount.addAndGet(attemptCount); System.out.println("주문 취소 실패 : " + e.getMessage()); } } } latch.countDown(); }); } latch.await(); Product productAfterCancel = productRepository.findById(product1.getId()) .orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException(ErrorCode.PRODUCT_NOT_FOUND)); int expectStock = originalStock; int actualStock = productAfterCancel.getStock(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("=== 락 없는 주문 취소 테스트 결과 ==="); System.out.println("총 스레드 개수 : " + threadCount); System.out.println("한 스레드당 최대 실행 횟수 : " + maxRetry + "번 실행"); System.out.println("총 소요 시간 (ms) : " + (endTime - startTime)); System.out.println("성공 횟수 : " + successCount.get()); System.out.println("실패 횟수 : " + failCount.get()); System.out.println("총 시도 횟수 : " + totalAttemptCount.get()); System.out.println("실패 시도 횟수 : " + (totalAttemptCount.get() - successCount.get())); System.out.println("기존 재고량 : " + originalStock); System.out.println("주문 후 재고량 : " + orderAfterStock); System.out.println("예상 재고량 (정상 동작 시) : " + expectStock); System.out.println("실제 재고량 : " + actualStock); if (actualStock != expectStock) { System.out.println("동시성 문제 발생 → 재고 Lost Update"); } else { System.out.println("정상적으로 처리"); } executor.shutdown(); }
락의 필요성과 선택 기준
- 주문 생성, 주문 취소 시 데이터 정합성을 위해 락이 필요하다는 사실을 테스트를 통해 확인
낙관락
-
충돌이 거의 발생하지 않을 때 사용하는 락
-
데이터를 읽고, 갱신 시점에 충돌 여부 검사
-
락을 사용하지 않아 성능이 좋음, 데드락 가능성 낮음
-
충돌 시 반드시 재시도가 필요함
-
-
ex) 읽기 위주 기능, 쓰기 경쟁이 적은 데이터에서 사용
비관락
-
충돌이 잦은 경우에 사용하는 락
- 락을 먼저 걸고 데이터에 접근
-
장점
-
DB row 단위에 락을 걸기 때문에 데이터 정합성 측면에서 안전함
-
동시성 문제 해결이 확실함, 높은 격리 수준 보장
-
-
단점
-
락으로 인해 성능 저하, 데드락 발생 가능성
-
서버 확장성의 제한
-
분산락
-
Redisson을 이용한 분산락
-
장점
-
분산 서버 환경 지원 → 여러 서버에서 동시 접근 가능
-
DB row 락보다 인 메모리 기반의 Redis 사용으로 성능 우수
-
데이터 정합성 확보 , 데드락 위험 감소(TTL 설정으로 자동 만료)
-
-
단점
-
Redis 장애 시 락 안전성 문제 발생
-
구현 난이도가 높음 (락 범위 설정, 트랜잭션 범위 설정 등)
-
최종 선택
-
Redisson 분산락 사용
- 쇼핑몰 프로젝트에서 주문/재고와 같이 여러 서버에서 동시에 접근할 수 있는 자원에 대해 안전하게 락을 보장해야한다고 생각하여 선택
