문제 인식
현재 서비스에서는 재고 수량을 관리하는 로직이 존재하며,
여러 요청이 동시에 들어올 경우 동시성 이슈가 발생하는 구조다.
이를 직접 눈으로 확인하고 싶어서,
재고 수량을 단순히 1 감소시키는 API를 작성하고 K6를 활용해 부하 테스트를 진행했다.

동시성 테스트 with K6
테스트 스크립트
- 아래 가상 유저 10명이 동시에 요청하는 스크립트
import http from 'k6/http';
import { sleep } from 'k6';
export const options = {
scenarios: {
simultaneous_requests: {
executor: 'per-vu-iterations', // 각 VU가 동시에 시작
vus: 10, // VU 수
iterations: 1, // 각 VU가 한 번만 실행
maxDuration: '1s', // 전체 시뮬레이션 시간
},
},
};
export default function() {
http.post('http://localhost:8080/inventories/test');
}k6 스크립트 실행
# k6 run script.js실행 결과
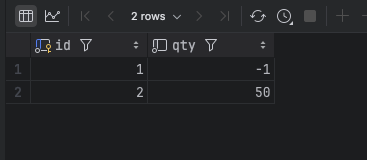
테스트 결과, 10명의 요청 중 1건만 반영
예상대로 Lost Update 현상 발생
→ 가장 마지막에 커밋된 요청만 반영되고, 나머지는 모두 무시됨
🤔 간단한 synchronized? → 실패
@Transactional 환경에서 단순 synchronized 블록을 사용해 보았지만,
스레드 락은 한 프로세스 내에서만 유효하기 때문에 멀티 프로세스/분산 환경에서는 무의미했다.
또한, 트랜잭션 내부에서 락을 걸더라도,
커밋 시점 이전에 다른 스레드가 과거 값을 읽는 문제가 생김 → 실패
synchronized는 JVM 레벨의 락
synchronized 키워드는 Java 객체 수준에서 락을 거는 메커니즘이며
이 락은 JVM 내부에서 관리되며, JVM 프로세스 안에 있는 여러 스레드 간의 동시 접근을 막는 용도로 동작
따라서 JVM 밖, 즉 다른 프로세스에서 실행되는 코드와는 락이 공유되지 않아 전혀 제어할 수 없음.
synchronized는 JVM 내부(= 단일 프로세스 내)에서만 유효한 락이다.
즉, 멀티 프로세스 환경이나 분산 시스템에서는 동시성 보장이 되지 않는다.
@Transactional
fun updateQty(id: Long) {
synchronized(lock) {
// synchronized 블록 안의 코드는 하나의 스레드만 접근 가능
...
}
}동시성 해결 방안 탐색
재고 수량 감소 로직에서 사용할 수 있는 대표적인 동시성 제어 방식은 다음과 같다
- Pessimistic Lock (비관적 락)
- Optimistic Lock (낙관적 락)
- Named Lock (DB 메타데이터 락)
- Redis 기반 분산 락 (Lettuce / Redisson)
1. Pessimistic Lock
- 실제로 DB 에 Lock 을 거는 방법
- 배타적 Lock, 즉 Lock 을 가져온 이후 다른 트랜잭션이 해당 Lock 이 해제되기까지 대기하게됨.
조회시 Lock 을 걸고 테스트.
@Repository
interface InventoryDetailRepository :
JpaRepository<InventoryDetail, Long>,
InventoryDetailRepositoryDSL {
@Lock(LockModeType.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE)
@Query("SELECT i FROM InventoryDetail i WHERE i.id = :id")
fun findByIdWithLock(id: Long): Optional<InventoryDetail>
}결과를 보면 잘 적용된 것 같다.
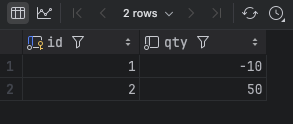
select
...
id1_0.updated_at
from
inventory_detail id1_0
where
(
id1_0.deleted_at IS NULL
)
and id1_0.id=? for update하지만 락을 획득할 때까지 트랜잭션이 대기하기 때문에,
성능상 병목이 발생할 가능성이 높고 일반적으로 추천되지는 않는다.
(충돌이 많이 발생하는 DB 테이블에 한해서는 권장한다고 한다)
2. Optimistic Lock
- Lock 을 사용하지 않고 버전을 따로 명시함으로써 데이터 정합성을 맞추는 방법
- 데이터를 읽은 후 update 할 때 현재 버전이 맞는지 확인 → 즉 재시도 로직이 필요함
@Version 추가
@Entity
@Table(
name = "inventory_detail",
)
class InventoryDetail : AutoIncrementIdEntity() {
...
@Version
var version: Long? = null
}
그리고 기존 DB 테이블의 버전을 0으로 초기값 세팅하고 한번 요청해보자.
확인해보니 충돌처리에 대한 부분을 따로 처리하지 않으면 ObjectOptimisticLockingFailureException 이 에러가 발생한다고 한다
2024-09-01T21:46:41.349+09:00 ERROR 50605 --- [nio-8080-exec-7] o.a.c.c.C.[.[.[/].[dispatcherServlet] : Servlet.service() for servlet [dispatcherServlet] in context with path [] threw exception [Request processing failed: org.springframework.orm.ObjectOptimisticLockingFailureException: Row was updated or deleted by another transaction (or unsaved-value mapping was incorrect) : [com.~~.InventoryDetail#1]] with root cause이후 좀 더 방안을 찾아보고 재시도 로직을 추가했다
@Lock(LockModeType.OPTIMISTIC)
@Query("SELECT i FROM InventoryDetail i WHERE i.id = :id")
fun findByIdWithLock(id: Long): Optional<InventoryDetail>
@Retryable(
value = [Exception::class],
maxAttempts = 50,
backoff = Backoff(delay = 1000),
)
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
fun updateQty(id: Long) {
try {
val inventoryDetail =
inventoryDetailRepository.findByIdWithLock(id).orElseThrow {
throw GeneralException.with(GeneralMsgType.NOT_FOUND_INVENTORY)
}
inventoryDetail.updateQty(inventoryDetail.getQty() - 1)
inventoryDetailRepository.saveAndFlush(inventoryDetail)
} catch (e: ObjectOptimisticLockingFailureException) {
log.error("Optimistic locking 충돌 발생 !! : ${e.message}")
throw e
} catch (e: PersistenceException) {
log.error("PersistenceException 발생: ${e.message}")
throw RuntimeException("PersistenceException 발생", e)
} catch (e: Exception) {
log.error("기타 예외 발생: ${e.message}", e)
throw e
}
}하지만 실제 테스트에서는 StaleObjectStateException 예외가 계속 발생했고,
예외가 트랜잭션 경계 밖에서 발생하는 경우가 많아 catch로 포착되지 않았다.
→ Spring Retry, 예외 핸들링 등을 복잡하게 구성했지만 결국 실패로 결론지었다.
(https://developer.jboss.org/thread/131217)
(https://stackoverflow.com/questions/30236145/not-able-to-catch-org-hibernate-staleobjectstateexception)
3. Named Lock
MySQL의 GET_LOCK, RELEASE_LOCK을 활용하여
이름 기반으로 락을 획득하고 해제하는 방식이다.
이름을 가진 Lock 을 획득한 후 해제할 때까지 다른 세션은 이 Lock 을 획득할 수 없음
- 주의. 트랜잭션이 종료될 때 Lock 이 자동으로 해제되지 않으며 별도의 명령어로 해제를 수행해주어야 함
Pessimistic Lock과 비슷하지만 Pessimistic Lock 은 테이블의 Row, Table 단위로 Lock 을 거는 것이며Named Lock은 metadata 에 Lock 을 거는 방법 즉, 공유자원 (Name) 에 대한 Lock 을 거는 것
이 방식은 데이터 소스를 서로 다른 것으로 사용하는게 좋다고 이야기한다
이유는 커넥션 풀이 부족해지는 이슈가 생긴다
구조 설계
- InventoryWithNamedLockService: 락 획득/해제 담당
- InventoryUpdater: 실제 재고 수량 감소 처리
두개의 서비스로 구현
(트랜잭션의 경계와 락의 생명주기를 명확히 관리하기 위함)
부모-자식 구조로 구현
- 부모 : 락을 획득 및 해제하는 책임을 가짐, 트랜잭션 경계를 넘어 락을 관리
- 자식 : 실제 트랜잭션의 비즈니스 로직 처리
interface InventoryDetailRepository :
JpaRepository<InventoryDetail, Long>,
InventoryDetailRepositoryDSL {
@Query(
value = "select get_lock(:key, 3000)",
nativeQuery = true,
)
fun getLock(key: String)
@Query(
value = "select release_lock(:key)",
nativeQuery = true,
)
fun releaseLock(key: String)
}
@Service
class InventoryWithNamedLockService(
private val inventoryDetailRepository: InventoryDetailRepository,
private val inventoryUpdater: InventoryUpdater,
) {
private val log = logger()
@Transactional
fun updateQty(id: Long) {
try {
inventoryDetailRepository.getLock(id.toString())
inventoryUpdater.updateQty(id)
} finally {
inventoryDetailRepository.releaseLock(id.toString())
}
}
}
@Service
class InventoryUpdater(
private val inventoryDetailRepository: InventoryDetailRepository,
) {
private val log = logger()
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
fun updateQty(id: Long) {
val inventoryDetail =
inventoryDetailRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow {
throw GeneralException.with(GeneralMsgType.NOT_FOUND_INVENTORY)
}
inventoryDetail.updateQty(
inventoryDetail.getQty() - 1,
)
log.info("qty : {}", inventoryDetail.getQty())
}
}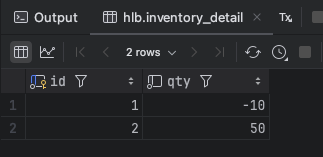
동시성 문제 해결. 안정적으로 동작.
그러나, 트랜잭션 종료 시 락이 자동 해제되지 않음 → 직접 해제 필요
4. Redis 분산 락
대표적으로 두 가지 방식이 있다고 한다
- Lettuce
- setnx 명령어로 분산락 구현,
spin lock 방식 (계속 lock을 확인) - 별도의 재시도 로직 필요
- setnx 명령어로 분산락 구현,
- Redisson
- pub-sub 기반으로 lock 구현
- 채널을 만들고 lock 을 획득하려는 스레드가 구독하여 lock 을 해제하려는 스레드 쪽에서 알려주면 안내를 받은 스레드가 lock 을 획득하는 방식
- 별도의 재시도 로직 필요하지 않음
4-1. Lettuce
이것도 Named Lock 과 비슷한 방식으로 구현된다 단지 Redis 를 활용할 뿐.
일단 Redis setnx 명령어를 통해 key 와 value 를 설정해주는 RedisRepository 를 구현하자
@Component
class RedisLockRepository(
private val redisTemplate: RedisTemplate<String, String>,
) {
fun lock(key: Long): Boolean? =
redisTemplate
.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(generateKey(key), "lock", Duration.ofMillis(3000))
fun unlock(key: Long): Boolean = redisTemplate.delete(generateKey(key))
fun generateKey(key: Long) = key.toString()
}이후 부모-자식 구조를 통해
부모 레이어는 Redis 의 key 에 대한 Lock 해제 및 획득을 구현 (spin lock)
자식 레이어는 기존 재고 수량 처리 로직
@Service
class InventoryLettuceLockService(
private val redisLockRepository: RedisLockRepository,
private val inventoryUpdater: InventoryUpdater,
) {
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
fun updateQty(id: Long) {
while (!redisLockRepository.lock(id)!!) {
Thread.sleep(100)
}
try {
inventoryUpdater.updateQty(id)
} finally {
redisLockRepository.unlock(id)
}
}
}이후 Redis io 관련 로그
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [nio-8080-exec-4] o.s.d.redis.core.RedisConnectionUtils : Fetching Redis Connection from RedisConnectionFactory
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [nio-8080-exec-4] io.lettuce.core.RedisChannelHandler : dispatching command AsyncCommand [type=DEL, output=IntegerOutput [output=null, error='null'], commandType=io.lettuce.core.protocol.Command]
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [nio-8080-exec-4] i.lettuce.core.protocol.DefaultEndpoint : [channel=0x26ca5e1a, /127.0.0.1:50710 -> localhost/127.0.0.1:6379, epid=0x1] write() writeAndFlush command AsyncCommand [type=DEL, output=IntegerOutput [output=null, error='null'], commandType=io.lettuce.core.protocol.Command]
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [nio-8080-exec-4] i.lettuce.core.protocol.DefaultEndpoint : [channel=0x26ca5e1a, /127.0.0.1:50710 -> localhost/127.0.0.1:6379, epid=0x1] write() done
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [ioEventLoop-4-1] i.lettuce.core.protocol.CommandHandler : [channel=0x26ca5e1a, /127.0.0.1:50710 -> localhost/127.0.0.1:6379, epid=0x1, chid=0x1] write(ctx, AsyncCommand [type=DEL, output=IntegerOutput [output=null, error='null'], commandType=io.lettuce.core.protocol.Command], promise)
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [ioEventLoop-4-1] i.lettuce.core.protocol.CommandEncoder : [channel=0x26ca5e1a, /127.0.0.1:50710 -> localhost/127.0.0.1:6379] writing command AsyncCommand [type=DEL, output=IntegerOutput [output=null, error='null'], commandType=io.lettuce.core.protocol.Command]
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [ioEventLoop-4-1] i.lettuce.core.protocol.CommandHandler : [channel=0x26ca5e1a, /127.0.0.1:50710 -> localhost/127.0.0.1:6379, epid=0x1, chid=0x1] Received: 4 bytes, 1 commands in the stack
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [ioEventLoop-4-1] i.lettuce.core.protocol.CommandHandler : [channel=0x26ca5e1a, /127.0.0.1:50710 -> localhost/127.0.0.1:6379, epid=0x1, chid=0x1] Stack contains: 1 commands
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [ioEventLoop-4-1] i.l.core.protocol.RedisStateMachine : Decode done, empty stack: true
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [ioEventLoop-4-1] i.lettuce.core.protocol.CommandHandler : [channel=0x26ca5e1a, /127.0.0.1:50710 -> localhost/127.0.0.1:6379, epid=0x1, chid=0x1] Completing command AsyncCommand [type=DEL, output=IntegerOutput [output=1, error='null'], commandType=io.lettuce.core.protocol.Command]
2024-09-02T00:15:25.310+09:00 DEBUG 55356 --- [nio-8080-exec-4] o.s.d.redis.core.RedisConnectionUtils : Closing Redis Connection그치만 해당 방식은 예상하듯 spin lock 방식이므로 redis 의 부하를 줄 수 있음
추천하지 않음.
4.2 Redisson
기존 Observer 패턴과 비슷하게 채널을 구독한 이후 다른 세션이 Lock 을 해제할 경우 관련 이벤트에 대한 알림을 주고,
구독한 다른 세션이 해당 이벤트를 받아서 Lock 을 획득하는 방식
Redis 명령어로 알아보자.
구독
127.0.0.1:6379> subscribe ch1
1) "subscribe"
2) "ch1"
3) (integer) 1
publish
127.0.0.1:6379> publish ch1 hello
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379>
구독
1) "message"
2) "ch1"
3) "hello"pub_sub 기반이므로 Lettuce 보다 Redis 부하가 줄어든다, Redisson 라이브러리에서 이미 Lock 획득 및 해제가 구현되어 있으므로 명령어를 사용하는 RedisRepository 는 필요 없다
@Service
class InventoryRedissonLockService(
private val redissonClient: RedissonClient,
private val inventoryUpdater: InventoryUpdater,
) {
private val log = logger()
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
fun updateQty(id: Long) {
val lock = redissonClient.getLock(id.toString())
try {
val enabled = lock.tryLock(10, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
if (!enabled) {
log.info("Redis Lock 획득 실패 Key : {}", id)
return
}
inventoryUpdater.updateQty(id)
} catch (e: InterruptedException) {
throw RuntimeException(e)
} finally {
lock.unlock()
}
}
}비교적 비즈니스 로직이나 관련된 에러 처리가 없어서 간단하다.
테스트 결과는 정상 작동하며 구현 또한 간단하다
그러나 락 해제 실패 문제, 락이 획득하지 못했을 경우 자동 해제 시간 설정 등 여러가지 요인들을 생각해야 한다 그리고 Redis 라는 외부 자원을 활용하는 만큼 예상하지 못하는 이슈들이 생겨날 수도 있다
이외에도 메시지 큐를 활용한 동시성 제어 등이 존재한다
추가로 K6 를 활용하면서 동시성 테스트를 진행했는데 좀 찾아보니 TPS (Transaction Per Seconds) 에 대한 테스트도 가능해 보인다
- 동시 요청에 대한 처리량 측정
간단히 여태까지의 동시성 테스트 스크립트를 돌려서 결과를 보면,
execution: local
script: script.js
output: -
scenarios: (100.00%) 1 scenario, 10 max VUs, 40s max duration (incl. graceful stop):
* simultaneous_requests: 1 iterations for each of 10 VUs (maxDuration: 10s, gracefulStop: 30s)
data_received..................: 1.6 kB 1.3 kB/s
data_sent......................: 1.2 kB 934 B/s
http_req_blocked...............: avg=1.87ms min=1.82ms med=1.85ms max=2.02ms p(90)=1.92ms p(95)=1.97ms
http_req_connecting............: avg=618.8µs min=553µs med=615.49µs max=704µs p(90)=675.2µs p(95)=689.6µs
http_req_duration..............: avg=766.22ms min=292.99ms med=761.23ms max=1.23s p(90)=1.14s p(95)=1.18s
{ expected_response:true }...: avg=766.22ms min=292.99ms med=761.23ms max=1.23s p(90)=1.14s p(95)=1.18s
http_req_failed................: 0.00% ✓ 0 ✗ 10
http_req_receiving.............: avg=77.89µs min=59µs med=68.5µs max=131µs p(90)=110.3µs p(95)=120.65µs
http_req_sending...............: avg=293.3µs min=177µs med=316µs max=366µs p(90)=346.19µs p(95)=356.1µs
http_req_tls_handshaking.......: avg=0s min=0s med=0s max=0s p(90)=0s p(95)=0s
http_req_waiting...............: avg=765.85ms min=292.64ms med=760.96ms max=1.23s p(90)=1.14s p(95)=1.18s
http_reqs......................: 10 8.050875/s
iteration_duration.............: avg=770.42ms min=297.84ms med=765.39ms max=1.24s p(90)=1.14s p(95)=1.19s
iterations.....................: 10 8.050875/s
vus............................: 3 min=3 max=3
vus_max........................: 10 min=10 max=10여기의 http_reqs 를 보면 10개의 요청이 들어갔고 1초에 8번의 요청을 처리할 수 있다고 볼 수 있다
회고 및 정리
- Pessimistic Lock : 구현은 간단하며 강력한 락을 통해 동시성 제어 그러나 성능 저하 및 병목현상 발생
- Optimistic Lock : 트랜잭션 병렬성 확보 및 충돌시 예외 처리가 복잡하다
- Named Lock : 간단한 DB 락을 통한 구현 락 수동해제 필요 및 커넥션을 점유함
- Redis Lettuce : 쉬운 분산 락 구현,
Redis 부하 및 SpinLock 구조 - Redis Redisson : 안정적인 분산 락 구현, 외부 의존성 과 설정이 필요
2025.10.05 회고 정리
- 잘못된 사실이 하나 있었다 바로
Redis Lettuce라이브러리가 SpinLock 구조로 구현되었다기 보다는 그렇게 개발자가 사용하는 것 이다 - 즉, 동작 방식은 개발자가 그렇게 사용한 것 라이브러리는 그런 동작방식의 강제성이 없었다
- 참고한 블로그