Generative Modeling by Estimating Gradients of the Data Distribution[NeurIPS-2019]
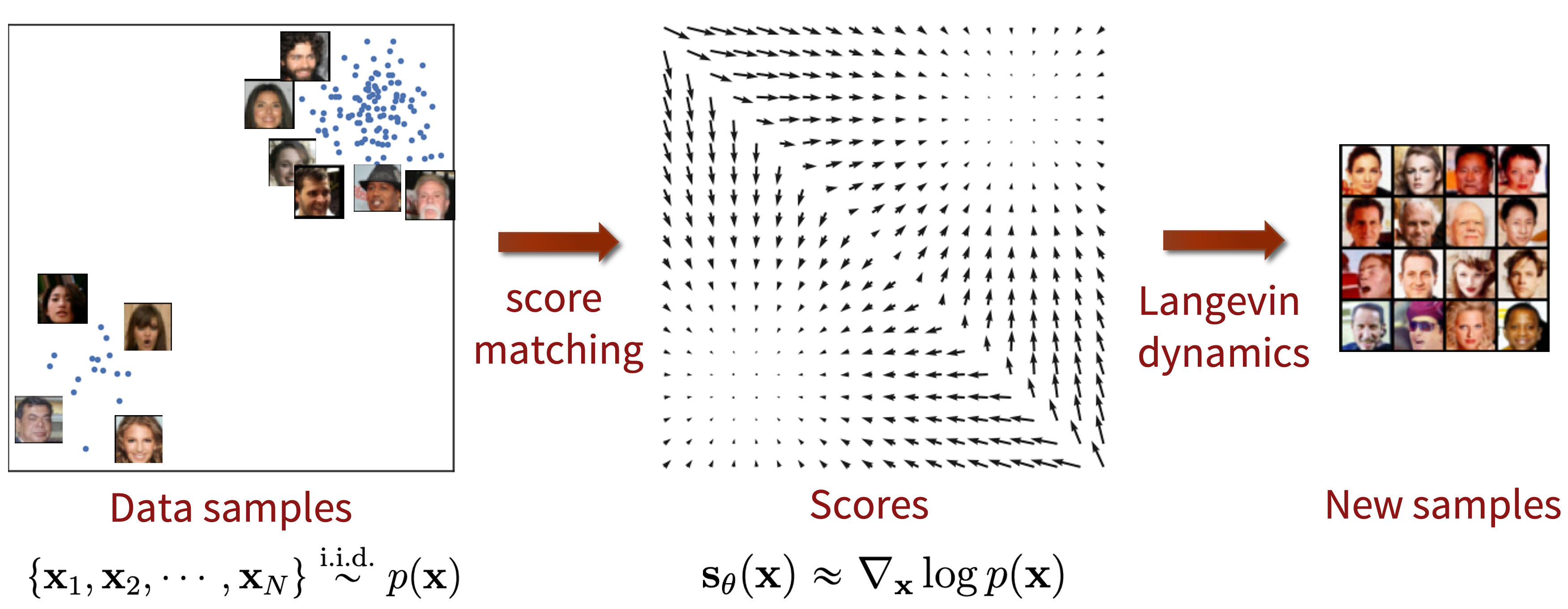
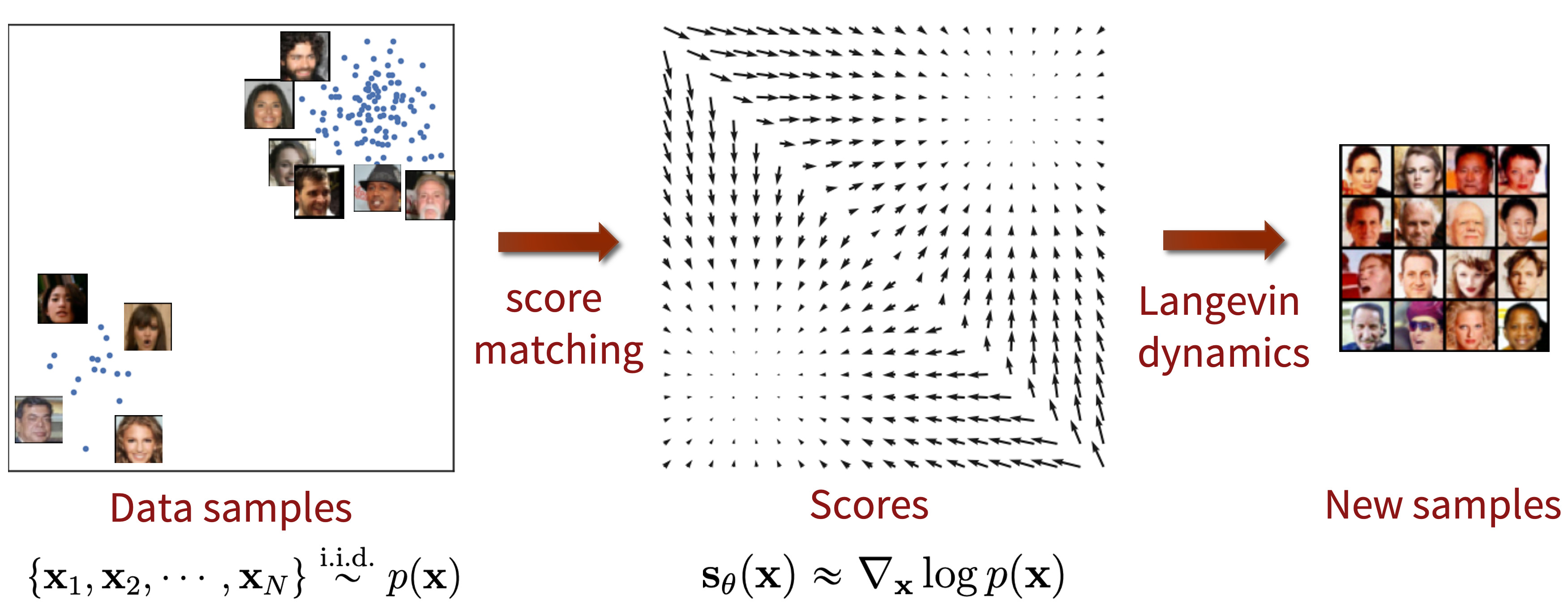
1. score-based generative model
-로그함수밀도의 gradient인 score를 추정하여 sampling 이때, score는 로그 데이터 밀도가 가장 많이 증가하는 방향을 가리키며 score matching method로 훈련된 neural network를 통해 data의 vector feild를 학습
-이후 Langevin dynamics를 통해 random initial sample를 high density regions으로 점진적으로 이동시켜 samples를 생성
2. denoising score-matching
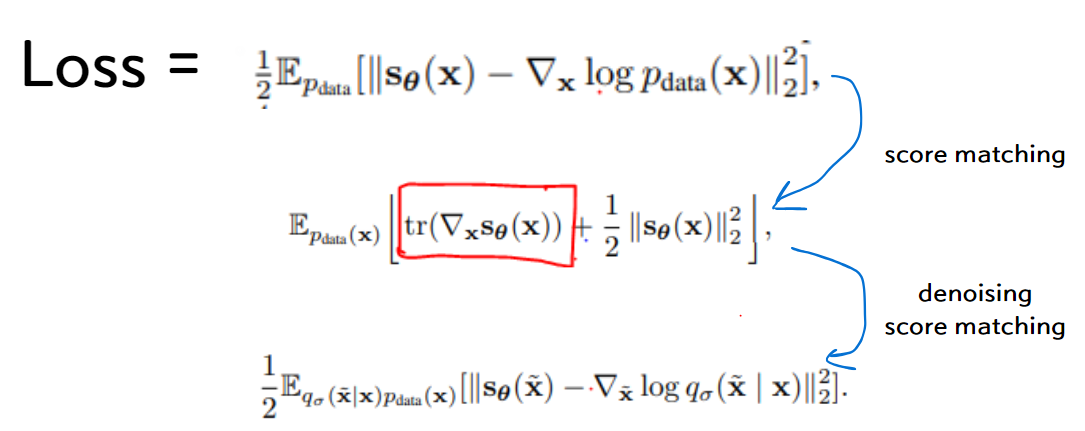
: original data X가 주어졌을때 가우시안 noise를 추가한 X'의 score
- 이때, 가우시안 noise가 충분히 작다면 original data X의 score로 근사 가능
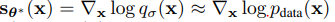
[Vincent, Pascal. "A connection between score matching and denoising autoencoders." Neural computation 23.7 (2011): 1661-1674.]
3. score network
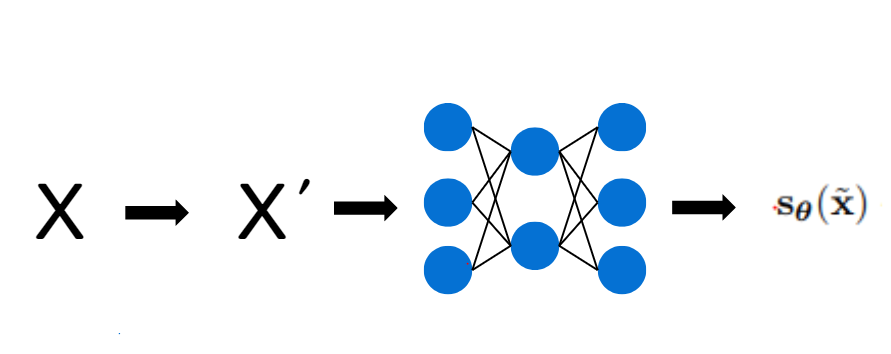
- denosiong score matching을 통해 학습
- 논문에서의 score network는 U-net을 사용
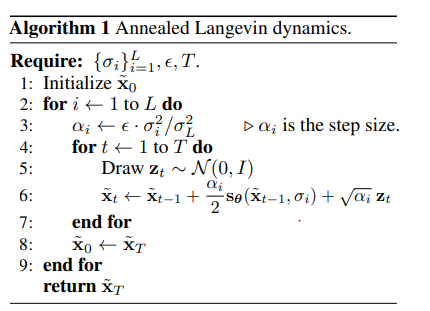
4. Langeivin dynamics
-
score network가 잘 학습이 되었다면 모든 데이터 공간상에서 score를 추정할 수 있음
-
random noise로 시작하여 현재 시점에서의 추정된 score를 기반하여 update
-
score를 통해 high density regions에 도달하면 original data와 유사한 data 생성 가능
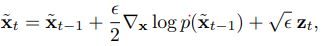
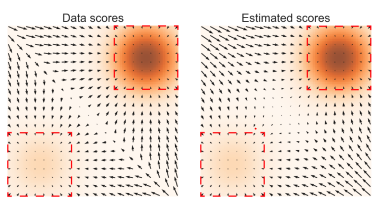
5. problem in low density regions
- data distribution의 low density regions에서는 data samples의 부족으로 score 추정이 부정확하며 langeving dynamics sampling에 악영향을 끼침
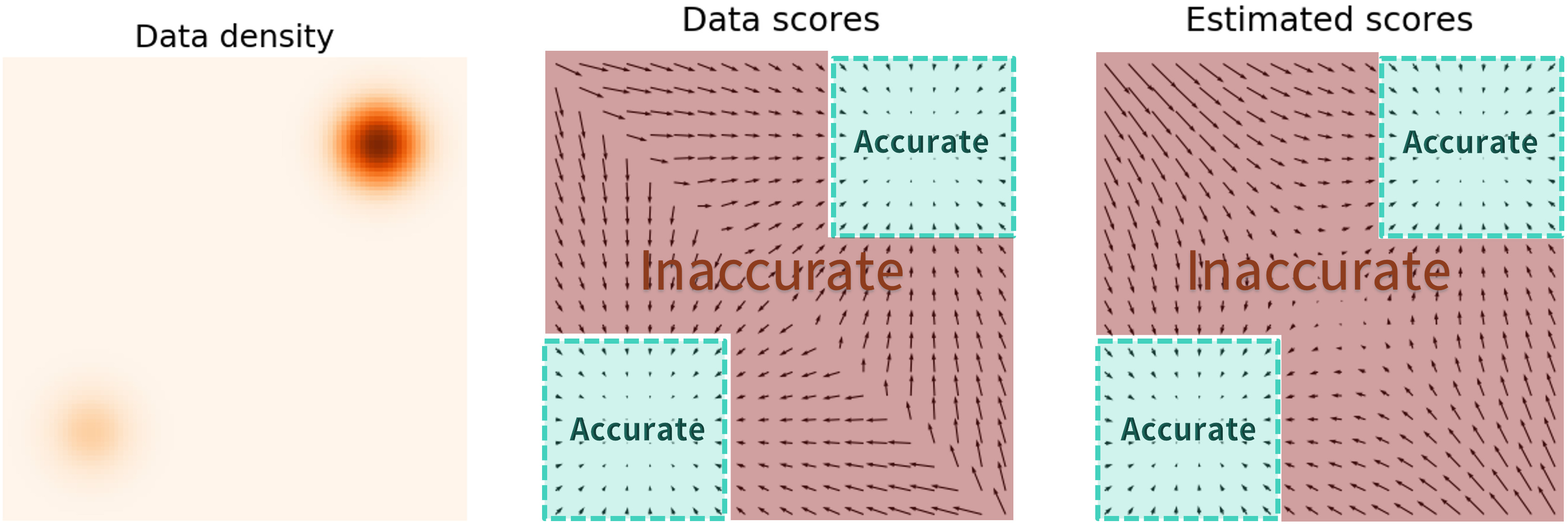
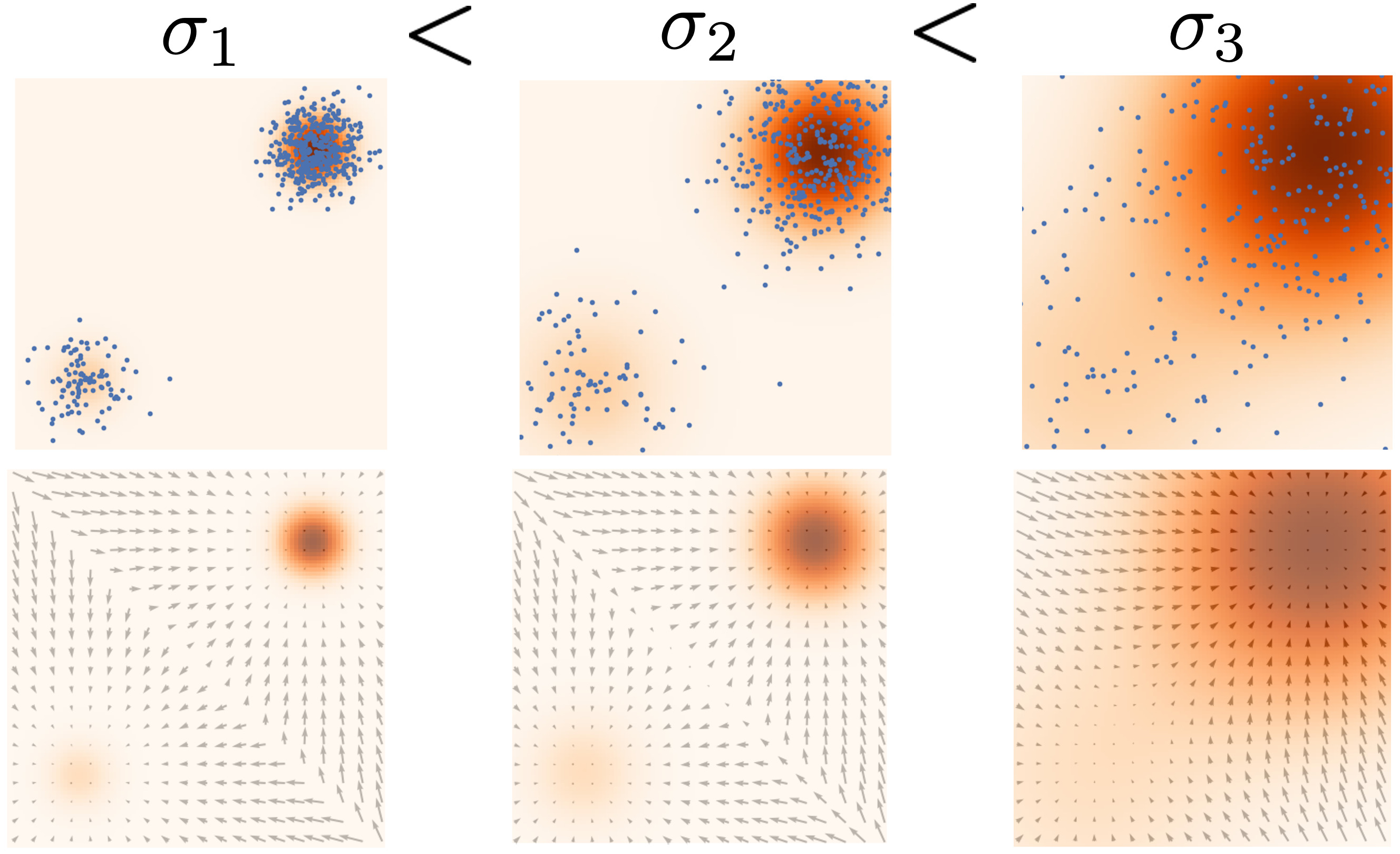
6. Noise Conditional Score network(NCSN)

-
큰 noise는 데이터 포인터를 원래 위치에서 많이 벗어나게 하여 저밀도 지역까지 데이터가 확산
-
하지만 너무 큰 noise는 데이터의 특성을 왜곡시켜 실제 분포를 잘못 학습할 수 있음
-
작은 noise는 데이터의 특성을 잘 보존하지만 low density regions에 대해 score 추정이 부정확
multiple scale of noise
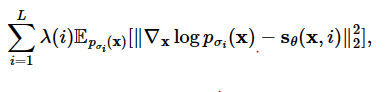
7.Annealed Langevin dynamics.