Stack : a file of stacks
Last-In First-Out(LIFO)
the most recent data comes first
Abstract Data Type(ADT) of Stack
1. Object : a linear list of n elements
2. Operation
- create() ::= Create a Stack
- is_empty(s) ::= Checks if the stack 's' is empty
- is_full(s) ::= Checks if the stack is full
- push(s, e) ::= Add element 'e' to the top of the stack
- pop(s) ::= Return element at the top of the stack and then delets it
- peek(s) ::= Retruns the element at the top of the stack without deleting it
1. push() : add data to the stack
2. pop() : delete data from the stack
Stack application
Return output in reverse order to an input
Ex) undo function in editor, remember return address from function call
int main(){
int i = 3;
sub1(i); //↓
...
}
int sub1(int a){
int j = 5;
sub2(j); //↓ //↑
...
}
void sub2(int b){ //↑
...
}Stack Implementation using Arrays
Pros
- The implementaion is simple
- Insertion or deletion operations are fast
List using array와 달리 overhead가 일어나지 않는다!
(list array의 단점이 stack에서는 적용X)
Cons
- the stack size is limited
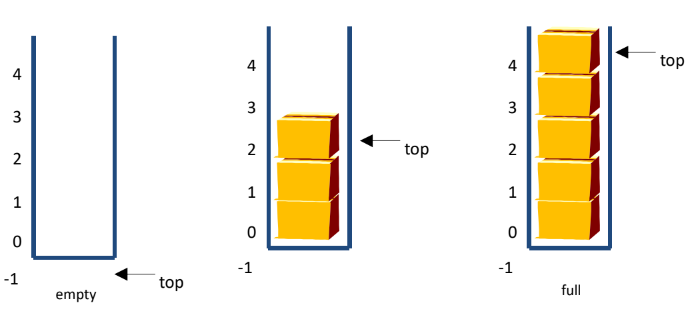
1D array stack[]
- 'top' : points to the most recently typed data in the stack
- 'stack[0]' : the first element
- 'stack[top]' : the last element
- If the stack is empty, top = -1
Operation Pseudo Code
- 'is_empty(s)'
is_empty(S)
if top = -1
then return TRUE
else return FALSE- 'is_full(s)'
is_full(S)
if top = (MAX_SIZE-1)
then return TRUE
else return FALSE- 'push(s, e)'
push(S, x)
if is_full(S)
then error"overflow"
else
top ← top+1
stack[top] ← x- 'pop(s)'
pop(S)
if is_empty(S)
then error"underflow"
else
e ← stack[top]
top ← top-1
return eC Code
typedef int element;
typedef struct{
element stack[MAX_STACK_SIZE];
int top;
}StackType;
//Stack initialization
void init(StackType *s){
s->top = -1;
}
int is_empty(StackType *s){
return (s->top == -1);
}
int is_full(StackType *s){
return (s->top == (MAX_STACK_SIZE - 1));
}
void push(StackType *s, element item){
if (is_full(s)){
fprintf(stderr, "Stack is full");
return;
}
else s->stack[++(s->top)] = item;
}
else pop(StackType *s){
if (is_empty(s)){
fprintf(stderr, "Stack is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
else return s->stack[(s->top)--];
}
element peek(StackType *s){
if(is_empty(s)){
fprintf(stderr, "Stack is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
else return s->stack[s->top];
}Linked Stack
implemented using a linked list
Pros
- The stack size is not limited
Cons
- The implementation is complex
- takes a long time to insert or delete
(compare to stack using array)
Code
1. 구조체 정의
typedef int element;
typedef struct StackNode{
element item;
struct StackNode *link;
}StackNode;
typedef struct{
StackNode *top; //address of the last node
}LinkedStackTypel;2. push
void push(LinkedStackType *s, element item){
StackNode *temp = (StackNode *)malloc(sizeof(StackNode));
if(temp == NULL){
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation error\n");
exit(1);
}
else {
temp->item = item;
temp->link = s->top;
s->top = temp;
}
}3. pop
void pop(LinkedStackType *s){
if(is_empty(s)){
fprintf(stderr, "Stack is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
else {
StackNode *temp = s->top;
int item = temp->item;
s->top = s->top->link;
free(temp);
return item;
}
}Stack Application
1. Parenthesis Check
바로 이전의 값(괄호)과 비교해야 하므로 LIFO property
- Type of parentheses
- brackets: '[', ']'
- braces: '{', '}'
- parentheses: '(', ')'
- Condition
1.1 The number of left parentheses and right parentheses must be the same
1.2 The left parenthesis must precede the right parenthesis
1.3 The left and right parentheses of different types should not cross each other
Example
- { A[(i+1)] = 0; } → No error
- if(( i==0 ) && ( j==0 ) → Condition 1.1 violation
- A[ (i+1] ) = 0; → Condition 1.3 violation
ppt 사진첨부
Algorithm overview
-
if we encounter the left parenthesis, inserts it into the stack
-
if we encounter the right parenthesis, check if the stack is empty.
if the stack is empty, it violates 'Condition 1.1' or 'Condition 1.2'.
otherwise, we remove the top parenthesis from the stack and check to see if it matches the right parenthesis.
if the parentheses are mismatched, it violates 'Condition 1.3' -
if the parentheses remain on the stack after checking the last parentheses, it returns 0 (false) because it violates condition 1, otherwise it returns 1 (true)
Pseudo code
check_matching(expr)
while (if not end of input expr)
ch ← The next character in expr
switch (ch)
case '(' : case '[' : case'{'
insert ch into the stack
break
case ')' : case ']' : case '}':
if (the stack is empty)
then error
else take out open_ch from the stack
if (ch and open_ch are not the same pair)
then error
break
if (stack is not empty)
then errorC code
int check_matching(char *in){
StackType s;
char ch, open_ch;
int i, n = strlen(in);
init(&s);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
ch = in[i];
switch (ch){
case '(' : case '[' : case'{'
push(&s, ch);
break
case ')' : case ']' : case '}':
if (is_emptu(&s)) return FALSE;
else {
open_ch = pop(&s);
if((open_ch == '(' && ch != ')') ||
(open_ch == '[' && ch != ']') ||
(open_ch == '{' && ch != '}')){
return FALSE;
}
break;
}
}
}
if (!is_empty(&s)) return FALSE;
return TRUE;
}main함수에서 사용
int main(){
if(check_matching("{A[(i+1)] == 0;}") == TRUE)
printf("Success\n");
else
printf("Fail\n");
}2. Calculation of Formulas
Formula expression
- Infix : 우리가 알고있는 형태의 식 표현법
- Prefix : operater operand operand 형태
ex) +2*34 → +2 12 → 14 - Postfix : operand operand operator 형태
ex) 234*+ → 2 12+ → 14
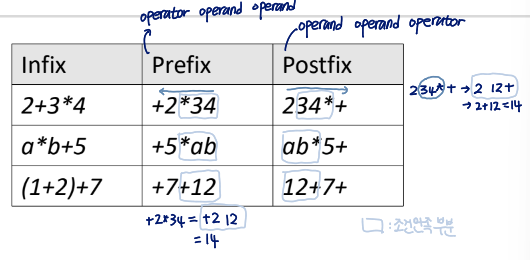
Calculation of formula on a computer
Infix expression -> Postfix expression -> Calculation
ex) 2+3*4 → 234*+ → 14
1. Calculation of postfix notation
- Scan formulas from left to right
- If it is an operand, store it in the stack
- If it is an operator, fetch the required number of operands from the stack
- Stores the operation result back into the stack
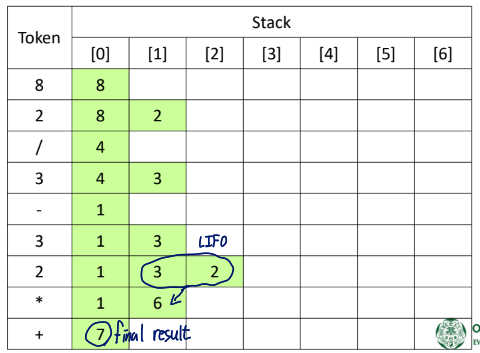
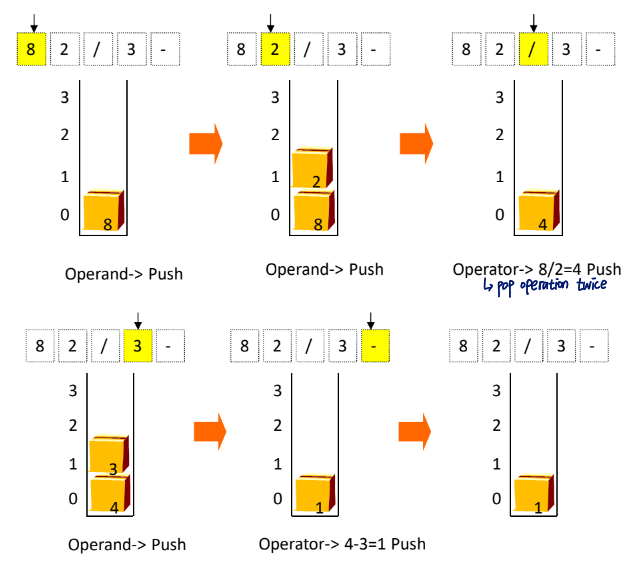
Algorithm overview
pseudo code
Create and initialize stack s.
for entry in postfix expression
if (the item is an operand)
push (s, item)
if (the item is operator op)
then second ← pop(s)
first ← pop(s)
result ← first op second //op : + - *
push(s, result)
final_result ← pop(s);Code
int eval(char exp[]){
int op1, op2, value, i = 0;
int len = strlen(exp);
char ch;
StackType s;
init(&s);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++){
ch = exp[i];
if (ch != '+' && ch != '-' && ch != '*' && ch != '/'){
value = ch - '0'; //아스키코드 사용하여 알맞은 정수값으로 변환
push (&s, value);
}
else {
op2 = pop(&s);
op1 = pop(&s);
switch (ch) {
case '+': push(&s, op1 + op2); break;
case '-': push(&s, op1 - op2); break;
case '*': push(&s, op1 * op2); break;
case '/': push(&s, op1 / op2); break;
}
}
}
return pop(&s);
}main함수에서의 사용
void main(){
int result;
printf("Postfix expression: 8 2 / 3 - 3 2 * +\n");
result = eval("82/3-32*+");
printf("Result: %d\n", result);
}2. Infix to Postfix expression
- the order of the operands is the same
- the order of operators is different (priority order)
→ Operators can be stored on the stack and output them
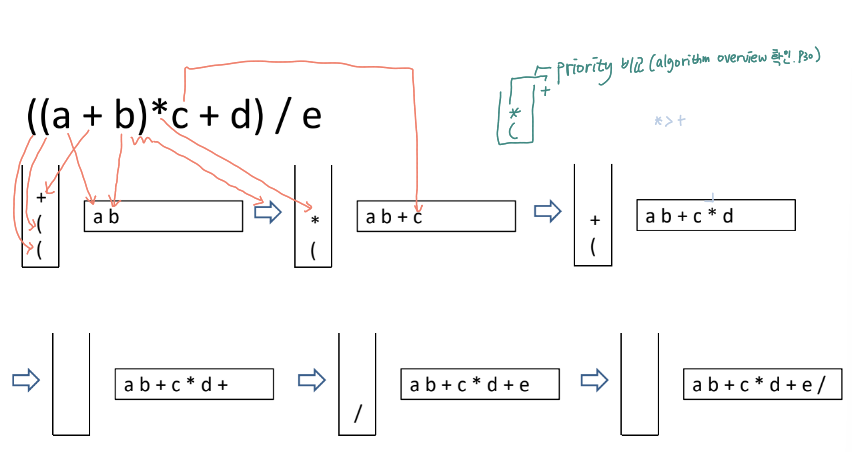
Algorithem overview
- Output when the operand is encountered
- When the operator is encountered, it is stored on the stack
- Operator's priority
3.1 if operator in the stack has higher priority than or equal to current operator, output operators on the stack - Parenthesis
4.1 the left parenthesis is treated as the operator with the lowest priority
4.2 if the right parenthesis appears, output all the operators stacked on the left parenthesis
Pseudo Code
infix_to_postfix(exp)
Create and initialize stack s
while(exp has character to process)
ch ← Character to be processed next
switch (ch)
case operator:
while (peek(s) priority >= ch priority)
e ← pop(s)
Output e
push(s, ch);
break;
case Left parenthesis:
push(s, ch);
break;
case Right parenthesis:
e ← pop(s);
wile(e != left parenthesis)
output e
e ← pop(s)
break;
case operand:
Output ch
break;
while (not is_empty(s))
do e ← pop(s)
Output eC code
- operator 우선순위 반환함수
int prec(char op){
switch(op){
case'(': case ')': return 0;
case'+': case '-': return 1;
case'*': case '/': return 2;
}
}- 'infix_to_porstfix' 정의
void infix_to_postfix(char exp[]){
int i = 0;
char ch, top_op;
int len = strlen(exp);
STackType s;
init(&s); //stack initialization
for(i = 0; i<len; i++){
ch = exp[i];
switch(ch){
case '+': case '-': case '*': case '/': //operator인 경우
//operator의 우선순위가 스택의 top보다 낮거나 같은 경우
while(!is_empty(&s) && (prec(ch) <= prec(peek(&s)))
printf("%c", pop(&s)); //stack의 operator 출력
push(&s, ch);
break;
case '(': //left parenthesis
push(&s, ch);
break;
case ')': //right parenthesis
top_op = pop(&s);
//left parenthesis가 나올 때까지 stack의 operators 출력
while(top_op != '(');{
printf("%c", top_op);
top_op = pop(&s);
}
break;
default: //operand인 경우
printf("%c", ch); //바로 출력
break;
}
}
while(!is_empty(&s)) //stack에 남아있는 operator들 모두 출력
printf("%c", pop(&s));
}- main함수에서의 사용
void main(){
infix_to_postfix("(2+3)*4+9");
}3. Maze Search Problem
이동 가능한 곳을 current position on the stack에 저장 후, 이동 불가능한 곳(dead end)에 도달한 경우 저장한 값을 뽑아서 그곳으로 이동
Algorithm
Pseudo code
Initialize stack s, exit position x, and mouse position
while (if the current position is not an exit)
do mark your current location as visited
if(the top, bottom, left, and right positions of
the current location have not yet been visited
and can be visited)
then push the positions onto the stack
if(is_empty(s)) then failure
else
take one position out of the stack and set
as the current loaction
success;Code
element here = {1,0}, entry = {1,0};
char maze[MAX_SIZE][MAZ_SIZE] = {maze 모양 그려넣은 것,,}
void push_loc(StackType *s, int r, int c){
if (r < 0 || c < 0) return;
if(maze[r][c] != '1' && maze[r][c] != '.'){
element tmp;
tmp.r = r;
tmp.c = c;
push(s, tmp)
}
}
void main(){
int r, c;
StackType s;
init(&s);
here = entry;
while(maze[here.r][here.c] != 'x'){
r = here.r;
c = here.c;
maze[r][c] = '.'; //visited
push_loc(&s, r-1, c); //top
push_loc(&s, r+1, c); //bottom
push_loc(&s, r, c-1); //left
push_loc(&s, r, c+1); //right
if (is_empty(&s)){
//while 도중에 stack이 비면 더이상 갈 곳이 없다는 것 → Fail
printf("Fail\n");
return;
}
else here = pop(&s);
}
printf("Success\n");
}