List : a set of ordered items
Example
- 요일 : 일요일, 월요일, 화요일, ...., 토요일
- a list of text messages in mobile phone
Operations in List
- add new items to the end, the beginning, and middle of the list
- delete an existing item from an arbitrary position in the list
- delete all items
- replace existing items
- check whether the list has a specific item
- return the item at a specific position in the list
- count the number of items in the list
- displays all items in the list
표 넣기
List Implementation
1. Arrays
- pros
- simple to implement
- cons
- overhead when inserting or deleting
- the number of items is limited
2. Linked list
- pros
- insertion and deletion are efficient
- size is not limited
- cons
- complex implementation
확실히 array보다 코드 작성할 때 어렵다..
- complex implementation
List using Array
1. Store items in 1D array in order
L = (a,b,c,d,e)
2. Insertion operation
the items after insertion, position should be moved
Ex) 1에서의 array L의 2번 인덱스에 item을 삽입하면 d,e는 각각 position을 바꿔야 함 →overhead
3. Delete operation
the items after delete, position should be moved
insertion operation과 같은 느낌
Code
1. 구조체를 통한 정의
typedef int element;
typedef struct {
int list[MAX_LIST_SIZE]; //define array
int length; //the number of items
}ArrayListType;- the type of items in list is defined as element
- 'list' : save the items in 1D array(list)
- 'length' : the number of items
2. 초기화
//list initialization
void init(ArrayListType* L){
L->length = 0;
}3. 'is_empty' and 'is_full'
int is_empty(ArrayListType *L){
return L->length == 0;
}
int is_full(ArrayListType *L){
return L->length == MAX_LIST_SIZE;
}4. Add
//position : location to be inserted
// item : element to be inserted
void add(ArrayListType *L, int position, element item){
is (!is_full(L) && (position >= 0) && (position <= L-> length)) {
int i;
for(i = (L->length-1); i>= position; i--)
L->list[i+1] = L->list[i]; //기존의 원소들 한 칸씩 뒤로
L->list[position] = item;
L->length++;
}
}- the add function first checks to see if the array is saturated and the insertion position is within a range
- move the data after the insertion position one space at a time
5. Delete
//position : location to be deleted
//return the element to be deleted
element delete(ArrayListType *L, int position){
int i;
element item;
if(position < 0 || position >= L->length)
error("Position error");
item = L->list[position];
for(i=position; i<(L->length-1); i++) // why '<' not '<='?
L->list[i] = L->list[i+1];
//지워지기 전의 원래의 원소 위치를 i+1로 하니까 그런듯!
L->length--;
return item
}- check the delete position
- move data from deletion position to the end by one space
Linked List
a node consists of data and link, and the link connects nodes
Node: <entry, address>
Node = data field + link field
- data field(entry) - store the data value(element) of the list
- link field(address) - stores the address(pointer) of another node
node is created by allocation dynamic memory whenever necessary
Note)
the physical order of nodes in memory does not need to match the logical order of the list
- physical order : 메모리 안에서의 노드의 주소 순서
- logical order : 리스트 안에서의 노드 순서
이러한 이유로 리스트의 노드들이 연이은 순서로 있어야 할 필요가 없다!
이것도 링크드 리스트의 장점 중 하나!!
그러나 implementation이 어려워 errors are likely to occur라는 단점 또한 지니고 있음
Head pointer
variable that points to the first node in the list
Simple Linked List
Link the data using one link field
→ the value of the last node is NULL
Pseudo Code
1. Insertion
insert_node(L, before, new)
if L == NULL
then L <- new
else new.link <- before.link //before.link == after
before.link <- newelse문의 두 문장은 순서 바뀌면 안 됨
L이 head pointer라면?------녹화강의 보고 이해해보자
2. Deletion
remove_node(L, before, removed)
if L != NULL
then before.link <- removed.link // == after
destroy(removed) //memory disallocationCode
1. 정의
data field is defined as a structure
typedef int element;
typedef struct Listnode{
element data;
struct ListNode *link; //link field uses a pointer
}ListNode;2. 노드 생성
ListNode *p1;
p1 = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
example
Setting data fields and link fields
ListNode *p1;
p1 = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
p1->data = 10;
p1->link = NULL;Creating a second node and connecting it to the first node
ListNode *p2;
p2 = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
p2->data = 20;
p2->link = NULL;
p1->link = p2;Head pointer : a pointer to the fist node in the linked list
3. Insertion
void insert_node(ListNode **phead, ListNode *p, ListNode *new_node)
// phead : pointer to the head pointer of the list
// p : pointer to the preceding node of the location to be inserted
// new_node: pointer to the new node to be insertedSince the head pointer changes inside the function, we need a pointer to the head pointer
Four cases of insertion
- if head is NULL : insert in a blank list
1.1 'new_node' becomes the first node.
→ so only need to change the value of head - insert in the beginning of list
void insert_first(ListNode **phead, ListNode *new_node){
if(*phead == NULL){ //if the list is blank
new_node -> link = NULL;
*phead = new_node;
}
else{
new_node -> link = *phead;
*phead = new_node;
}
}- insert in the middle of list
3.1 copy 'p' -> link to 'new_node' -> link
3.2 let p->link point to new_node
void insert_node(ListNode **phead, ListNode *p, ListNode *new_node){
if(*phead == NULL) { //case1
new_node -> link = NULL;
*phead = new_node;
}
else{ //case3
if(p == NULL){
printf("The preceding node cannot be NULL\n");
exit(1);
}
else{
new_node -> link = p -> link;
p->link = new_node;
}
}
}- insert at the end of list
void insert_last(ListNode **phead, ListNode *new_node){
if(*phead == NULL){ //if the list is blank
new_node -> link = NULL;
*phead = new_node;
}
else{ //Time complexity : O(N)
new_node -> link = NULL; //N = # of nodes
struct ListNode *last = *phead;
while(last -> link != NULL)
last = last->link;
last -> link = new_node
}
}4. Deletion
//phead : pointer to the head pointer
//p : pointer to the preceding node of the node to be deleted
//removed : node to be deleted
void remove_node(ListNode **phead, ListNode *p, ListNode *removed){
if(*phead == NULL){
printf("the list is blank\n")
}
else{
if(p == NULL){
printf("the preceding node cannot be NULL\n");
}
else {
p->link = removed->link;
free(removed);
}
}
}delete the beginning of the list
void remove_node(ListNode **phead, ListNode *removed){
if(*phead == NULL){
printf("the list is blank\n")
}
else{
*phead = (*phead) -> link;
free(removed);
}
}5. Visit operation
- Iteration - more recommended
void display(ListNode *head){
ListNode *p = head;
while (p != NULL){
printf("%d ->", p->data);
p = p->link;
}
printf("\n");
}- Recursion - 굳이 사용하기엔 복잡함
void display_recur(ListNode *head){
ListNode *p = head;
while (p != NULL){
printf("%d ->", p->data);
display_recur(p->link);
}
}6. Search operation
void *search(ListNode *head, int x){
ListNode *p;
p = head;
while (p != NULL){
if(p->data == x) return p;
p = p->link;
}
return p; // return NULL if search fails
}7. Merge operation
ListNode *concat(ListNode *head1, ListNode *head2){
ListNode *p;
if(head1 == NULL) return head1;
else if(head2 == NULL) return head1;
else {
p = head1;
while(p->link != NULL)
p = p->link;
p->link = head2;
return head1;
}
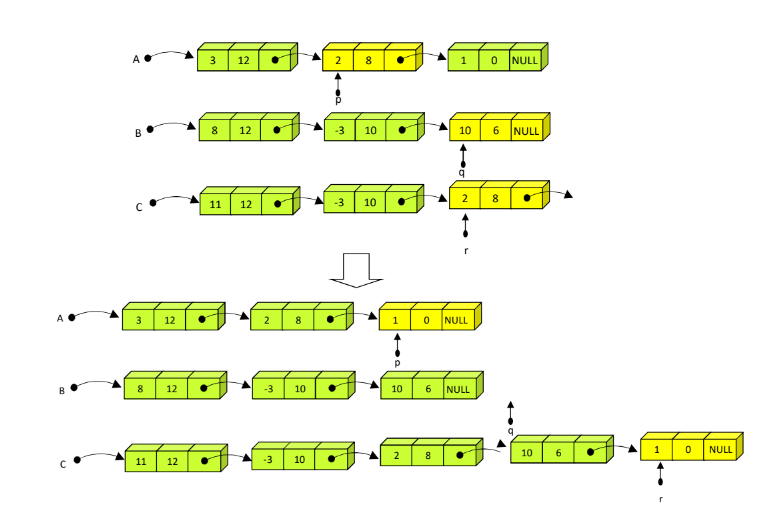
}8. Reverse operation
arrange the nodes of the list in revers order
//g를 return하기 때문에 single pointer
//double pointer를 사용해도 되긴 함
ListNode *reverse(ListNode *head){
ListNode *p, *q, *r;
p = head; //node yet not processed
q = NULL; //node in reverse order
while (p != NULL){
r = q;
q = p;
p = p->link;
q->link = r;
}
return q; //head pointer of the list in reverse order
}Circular Linked List
The link of the last node points to the first node
→ can access from one node to all other nodes
head pointer가 맨마지막 노드를 가리키면, 맨앞 또는 맨마지막 부분에 새 노드를 추가하는 것이 simple linked list보다 간편해짐
Insertion Operation at the Beginning
//phead: pointer of head pointer
//p: preceding node
//node: node to be inserted
void insert_first(ListNode **phead, ListNode *node){
if(*phead == NULL){
*phead = node;
node->link = node; //self connection
}
else{
node->link = (*phead) -> link;
(*phead) -> link = node;
}
}Insertion Operation at the End
void insert_last(ListNode **phead, ListNode *node){
if(*phead == NULL){
*phead = node;
node->link = node; //self connection
}
else{
node->link = (*phead) -> link;
(*phead) -> link = node;
*phead = node;
}
}Time complexity : O(1)
head가 first node address인 경우 마지막 노드까지 하나하나 이동해야 함
→ time complexity = O(N)
그러나 last node address인 경우에는 바로 insertion이 가능하여 time complexity가 감소함
add_first는 둘 다 search를 하지 않아도 되기 때문에 time complexity가 동일함
Doubly Linked List
Problem with the simple linked list
- difficult to find the preceding node
- the preceding node should be defined together when inserting or deleting
Doubly linked list
- a list in which one node has two links to the preceding node and the subsequent node
- pros : a link is bi-directional, so you can search in both directions
- cons : it takes up a lot of space, and the code is complex
Head node
- has no actual data
- is created to simplify insertion and deletion
- is distinguished from head pointer
- in the blank, only the head node exists
void int(DlistNode *phead){
phead->llink = phead;
phead->rlink = phead;
}Structure of a node in a doubly linked list
typedef int element;
typedef struct DlistNode{
element data;
struct DlistNode *llink;
struct DlistNode *rlink;
}DlistNode;Code
1. Insertion
void dinsert_node(DlistNode *before, DlistNode *new_node){
new_node->llink = before;
new_node->rlink = before->rlink;
before->rlink->llink = new_node //before->rlink == after
before->rlink = new_node; //위의 문장과 순서 바꾸면 큰일남
}why we don't have to use head pointer?
-head node를 사용하면 되기 때문 아닐까???
2. Deletion
void dremove_node(DlistNode *before, DlistNode *removed){
if(removed == phead_node) return; //list is blank
removed->llink->rlink = removed->rlink;
removed->rlink->llink = removed->llink;
free(removed);
}- removed->llink == before
- removed->rlink == after
Example
typedef int element;
typedef struct DlistNode{
element data;
struct DlistNode *llink;
struct DlistNode *rlink;
}DlistNode;
void init(DlistNode *phead){
phead->llink = phead;
phead->rlink = phead;
}
void display(DlistNode *phead){
DlistNode *p;
for(p = phead->rlink; p != phead; p = p->rlink){
printf("<--- |%x|%d|%x| --->\n", p->llink, p->data, p->rlink);
}
printf("\n")
}
void dinsert_node(DlistNode *before, DlistNode *new_node){
new_node->llink = before;
new_node->rlink = before->rlink;
before->rlink->llink = new_node
before->rlink = new_node;
}
void dremove_node(DlistNode *before, DlistNode *removed){
if(removed == phead_node) return; //list is blank
removed->llink->rlink = removed->rlink;
removed->rlink->llink = removed->llink;
free(removed);
}case 1
void main(){
DlistNode head_node;
DlistNode *p[10];
init(&head_node);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
p[i] = (DlistNode *)malloc(sizeof(DlistNode));
p[i] -> data = i;
dinsert_node(&head_node, p[i]);
}
dremove_node(&head_node, p[4]);
display(&head_node);
}case 2
void main(){
DlistNode *head_node = (DlistNode *)malloc(sizeof(DlistNode));
DlistNode *p[10];
init(head_node);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
p[i] = (DlistNode *)malloc(sizeof(DlistNode));
p[i] -> data = i;
dinsert_node(head_node, p[i]);
}
dremove_node(head_node, p[4]);
display(head_node);
}//case1
int a1;
init(&a1); //a1 == intiger data
//case2
int *a1 = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
init(a1);
//case3
int a1[1];
init(a1);자세한 설명 영상에서 보기
Linke List Application
1. Polynomial
linked list can be used for processing of polynomials
ex) arithmetic operations of polynomials
representation of a polynomial as a linked list
A = 3x^12 + 2x^8 + 1
B = 8x^12 - 3x^10 + 10^6
code
typedef struct ListNde{
int coef;
int expon;
struct ListNode *link;
}ListNode;
ListNode *A, *B;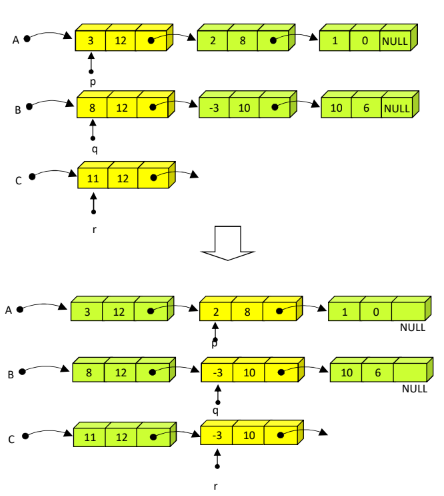
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//Structure of node in the linked list(simple linked list)
typedef struct ListNode{
int coef;
int expon;
struct ListNode *link;
}ListNode;
//Header in the linked list
typedef struct ListHeader{
int length; //number of valid number nodes
ListNode *head; //address of first node
ListNode *tail; //address of last node
}ListHeader;
void error(char *message){
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", message);
exit(1);
}head, tail 사용함으로써
Time complexity of inserting oparation= O(1)
→ 효율적
void init(ListHeader *plist){
plist -> length = 0;
plist->head = plist->tail = NULL;
}
//plist = pointer to point the header of the linked list
//coef = coefficient, expon = exponent
void insert_node_last(ListHeader *plist, int coef, int expon){
ListNode *temp = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (temp == NULL) error("Memory allocation error");
temp->coef = coef;
temp->expon = expon;
temp->link = NULL;
if(plist->tail == NULL){ //빈 리스트인 경우
plist->head = plist->tail = temp;
}
else{
plist->tail->link = temp;
plist->tail = temp;
}
plist->length++;
}
void poly_add(ListHeader *plist1, ListHeader *plist2, ListHeader *plist3){
ListNode *a = plist1->head;
ListNode *b = plist2->head;
int sum;
while(a && b){
if(a->expon == b->expon){
sum = a->coef + b->coef;
if (sum != 0) insert_node_last(plist3, sum, a->expon)
a = a->link; b = b->link
}
else if (a->expon > b->expon){
insert_node_last(plist3, a->coef, a->expon);
a = a->link;
}
else{
insert_node_last(plist3, b->coef, b->expon);
b = b->link;
}
}
for (; a != NULL; a = a->link)
//맨왼쪽 빈칸은 무시하고 조건확인하게 됨(초기화 필요 없으므로)
insert_node_last(plist3, a->coef, a->expon);
for (; b != NULL; b = b->link)
insert_node_last(plist3, b->coef, b->expon);
}
void poly_print(ListHeader *plist){
ListNode *p = plist -> head;
for(; p; p = p->link){
printf("%d %d\n", p->coef, p->expon);
}
}
case 1
void main(){
ListHeader list1, list2, list3;
//initialization of linked list
init(&list1);
init(&list2);
init(&list3);
//generate polynomial 1
insert_node_last(&list1, 3, 12);
insert_node_last(&list1, 2, 8);
insert_node_last(&list1, 1, 0);
//generate polynomial 2
insert_node_last(&list2, 8, 12);
insert_node_last(&list2, -3, 10);
insert_node_last(&list2, 10, 6);
// poly3 = poly1 + poly2
poly_add(&list1, &list2, &list3);
poly_print(&list3);
}case 2
void main(){
ListHeader *list1, *list2, *list3;
list1 = (ListHeader *)malloc(sizeof(ListHeader));
list2 = (ListHeader *)malloc(sizeof(ListHeader));
list3 = (ListHeader *)malloc(sizeof(ListHeader));
//initialization of linked list
init(list1);
init(list2);
init(list3);
//generate polynomial 1
insert_node_last(&list1, 3, 12);
insert_node_last(&list1, 2, 8);
insert_node_last(&list1, 1, 0);
//generate polynomial 2
insert_node_last(&list2, 8, 12);
insert_node_last(&list2, -3, 10);
insert_node_last(&list2, 10, 6);
// poly3 = poly1 + poly2
poly_add(&list1, &list2, &list3);
poly_print(&list3);
}List ADT using Linked List
- the parameter of addition and deletion operation is position
- the parameter of 'insert_node' and 'remove_node' is the node poiner
typedef struct{
ListNode *head; //head pointer to the first node
int length; //number of nodes present in the linked list
}ListType;
ListType list1; //list ADT generationis_empty, get_length
int is_empty(ListType *list){
if(list->head == NULL) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int get_length(ListType *list){
return list->length;
}insertion operation
'get_node_at' : converts a position to node pointer
ListNode *get_node_at(ListType *list, int pos){
int i;
ListNode *tmp_node = list->head;
if(pos < 0) return NULL;
for (i = 0; i<pos; i++) //하나씩 점검하는 방법
tmp_node = tmp_node->link;
return tmp_node
}Insert new data at the 'position'
void add(ListType *list, int position, element data){
ListNode *p;
if((position >= 0) && (position <= list->length)){
ListNode *node = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if(node = NULL) error("Memory allocation arror");
node->data = data;
p = get_node_at(list, position-1); //get preceding node
insert_node(&(list->head), p, node);
//&(list-> head) : first node address
list->length++;
}
}'position <= list->length'
: add the node at last position의 경우까지 고려하여 '<'가 아닌 '<=' 사용
Deletion operation
void delete(ListType *list, int pos){
if (!is_empty(list) && (pos >= 0) && (pos < list->length)){
ListNode *p = get_node_at(list, pos);
ListNode *removed = get_node_at(list,pos);
remove_node(&(list->head), p, removed);
list->length--;
}
}'get_entry' operation
return the data at the 'pos'
void get_entry(ListType *list, int pos){
ListNode *p;
if (pos >= list-> length) error("Position error");
p = get_node_at(list, pos);
return p->data;
}Display operation
display data in the buffer
void display(ListType *list){
int i;
ListNode *node = list->head;
printf("( ");
for (i = 0; i<list->length; i++){
printf("%d", node->data);
node = node -> link;
}
printf(" )\n");
}'is_in_list' operation
find a node whose data = item
int is_in_list(ListType *list, element item){
ListNode *p;
p = list->head;
while((p != NULL)){
if (p->data == item) break;
p = p->link;
}
if(p == NULL) return FALSE;
else return TRUE;
}Example code
int main(){
ListType list1;
init(&list1);
add(&list1, 0, 20);
add_last(&list1, 30);
add_first(&list1, 10);
add_last(&list1, 40);
//list1 = (10,20,30,40)
display(&list1);
delete(&list1, 3); //list1 = (10,20,30)
display(&list1);
delete(&list1, 0); //list1 = (20,30)
display(&list1);
printf("%s\n", is_in_list(&list1, 20) == TRUE? "TRUE": "FALSE");
printf("%d\n", get_entry(&list1, 0));
}