[CV_논문리뷰]U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
Abstract
we present a network and training strategy that relies on the strong use of data augmentation to use the available annotated samples more efficiently.
해당 논문에서 말하는 Strategy는 다음과 같다.
1. Data Augmentation (Elastic Deformation)
2. Overlap Tile Method
3. Separation of Touching Objects - Weighted 조작
U넷 탄생 배경 설명 -> 극복하기 위한 strategy 설명 → 모델의 구조 설명 → 정리
순으로 논문 리뷰를 진행하겠다.
U넷 탄생 배경
in many visual tasks, especially in biomedical image processing, the desired output should include localization, i.e., a class label is supposed to be assigned to each pixel.
~
Hence, Ciresan et al. [1] trained a network in a sliding window setup to predict the class label of each pixel by providing a local region (patch) around that pixel as input.
Segmentation(각 픽셀별로 Class를 라벨링하는 작업)을 위해 Ciresan이 고안해낸 Sliding window 탐색 방식이 있다. 하지만 이 방식에는 문제가 있다.
Obviously, the strategy in Ciresan et al. [1] has two drawbacks.
- it is quite slow because the network must be run separately for each patch, and there is a lot of redundancy due to overlapping patches.
- Secondly, there is a trade-off between localization accuracy and the use of context.
출처
https://docs.ververica.com/user_guide/sql_development/queries.html
논문에서 말하고 있는 기존 방식의 단점으로는
- windows가 각 Patch마다 모두 훑고 지나가는데 중복되는 부분이 많아 속도가 느리다는 점과
- accuracy ∝
Patch가 커지수록 Accuracy는 줄어든다는 점이었다.
이를 방지하기 위해 U-net에서는 모델 구조 변경 뿐 아니라 여러 Strategy를 적용하였다.
Strategy
- Data Augmentation (Elastic Deformation)

- 변형한 것과 같이 Data Augmentation 기법을 활용하였다. 이는 특히 Biomedical 분야에서 효과를 많이 보곤 한다. (조직의 변형을 현실적이게 시뮬레이션 할 수 있음)
- Overlap Tile Method



- 특징으로는 Unpadded convolution이 사용된다. 그래서 input이미지보다 output이미지가 항상 작아진다. (downsizing)
- 노란색 영역을 Segmentation하기 위해 파란색 영역으로부터 추측한다.
이 때, 파란색 영역은 노란색 영역을 mirroring하여 삽입한 것이다.
출처 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O_7mR4H9WLk
- Separation of Touching Objects - Weighted 조작
 Another challenge in many cell segmentation tasks is the separation of touching objects of the same class
Another challenge in many cell segmentation tasks is the separation of touching objects of the same class
- Cell의 경우 위 그림과 같이 붙어있는 경우가 많다. 이를 사람은 구분할 수 있지만 컴퓨터는 same class로 구분하는 경우가 대다수인데 이를 방지하기 위해 weight값을 조작하여 seperation border을 추출해내게 했다.

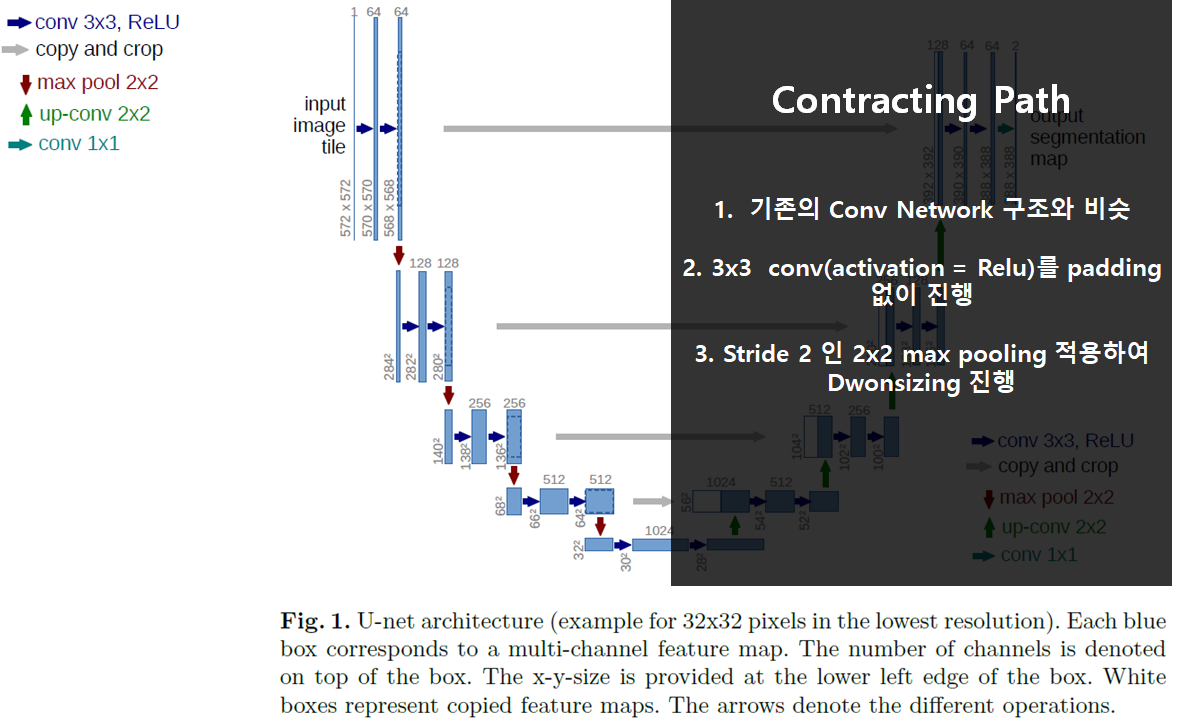
모델 구조
 전체구조는 위와 같이 대칭적인 구조를 보인다.
전체구조는 위와 같이 대칭적인 구조를 보인다.


정리
- 아주 적은 양의 데이터로도 Elastic Deformation Augmentation 기법을 이용하여 좋은 성능을 보여준다.
References
U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
