2021 부스트캠프 Day 17.
[Day 17] NLP
Basics of Recurrent Neural Networks(RNNs)
Basic structure
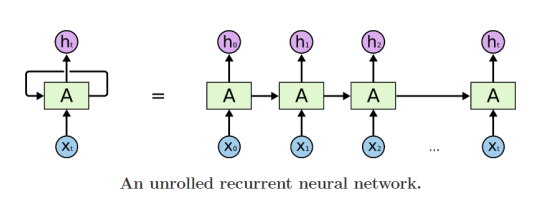
- 서로 다른 time step에서 들어온 입력데이터를 처리할 때, 동일한 파라미터를 통해 매 time step마다 재귀적으로 호출되면서 처리된다.
How to calculate the hidden state of RNNs

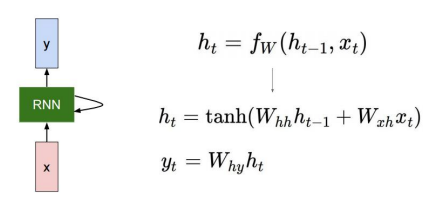
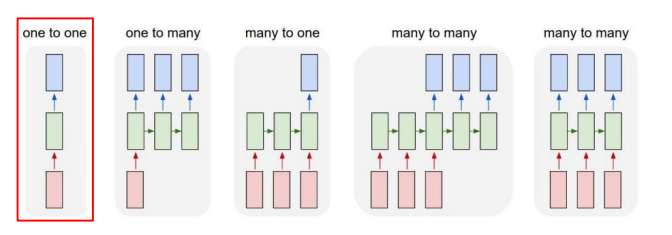
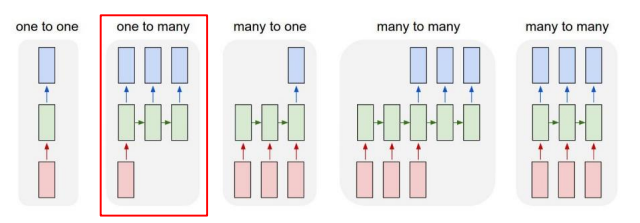
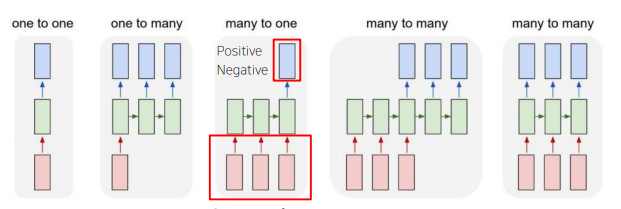
Types of RNNs
One-to-one
- Standard Neural Networks
One-to-many
- Image Captioning
Many-to-one
- Sentiment Classification
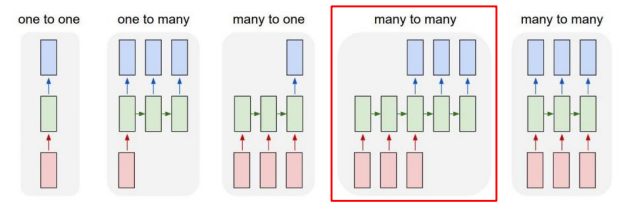
Sequence-to-Sequence
- Machine Translation
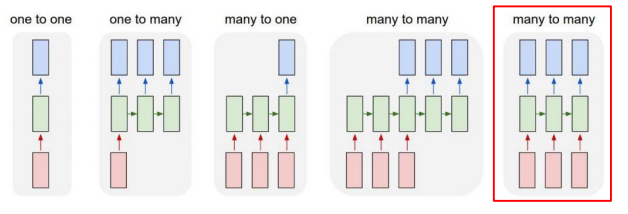
Sequence-to-sequence
- Video classification on frame level
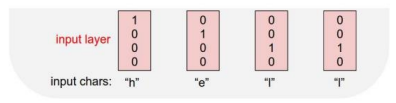
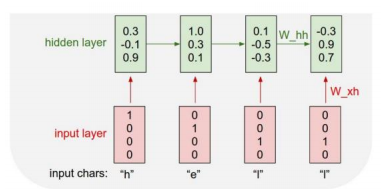
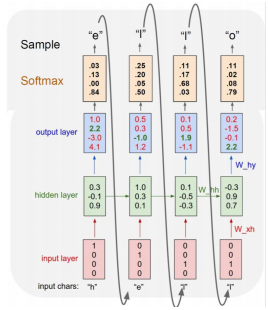
Character-level Language Model
Example of training sequence "hello"
-
Vocabulary : [h, e, l, o]
-
Example training sequence : "hello"

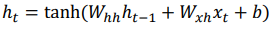
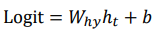
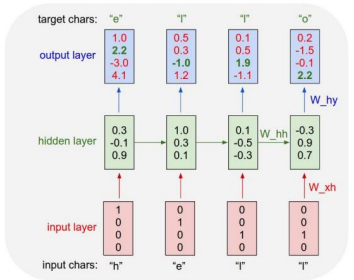
-
첫 번째 output layer vector의 최대값을 보면 'o' 단어를 예측해 내게 된다. 하지만 target char가 'e'이므로 해당값 2.2에 집중하여 이에 맞게 학습이 진행되도록 loss가 계산이 된다.
-
At test-time, sample charactoers one at a time, feed back to model
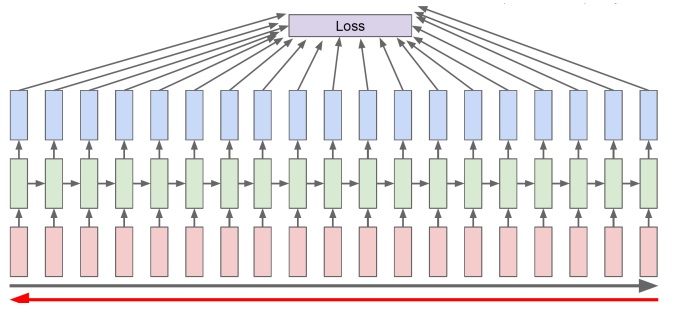
Backpropagation through time(BPTT)
- Forward through entire sequence to compute loss, then backward through entire sequence to comput gradient
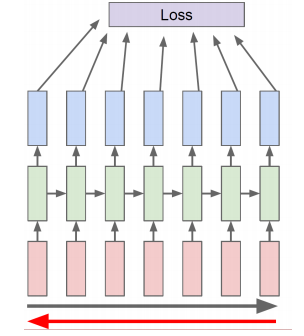
- Run forward and backward through chunks of the sequence instead of whole sequence.
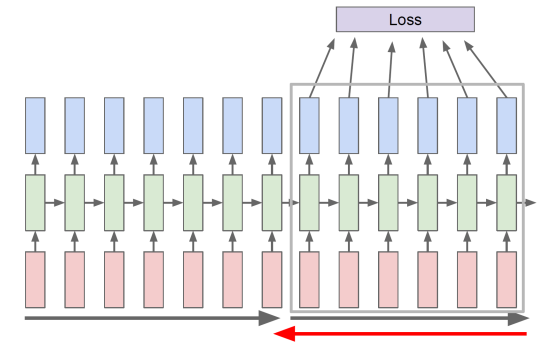
- Carry hidden states forward in time forever, but only backpropagate for som smaller number of steps
Vanishing/Exploding Gradient Problem in RNN
- Multiplying the same matrix at each time step during backpropagation causes gradient vanishing or exploding.
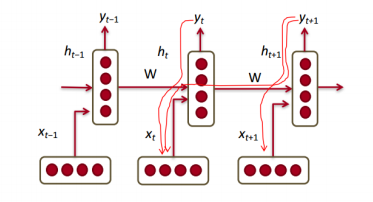
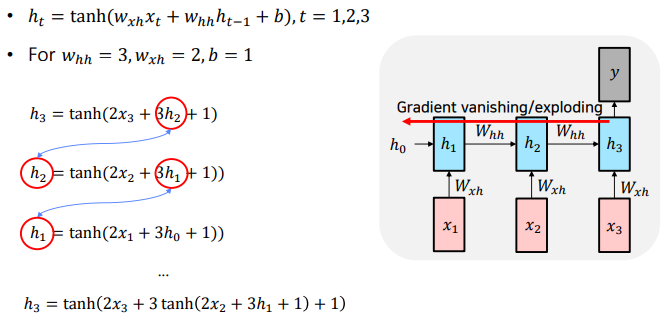
- forward에서 같은 수가 계속적으로 곱하는 것과 같이 backpropagation에서도 같은 수가 계속 곱해지게되면서 등비수열과 유사하게 되며 vanishing/Exploding이 발생하게 된다.
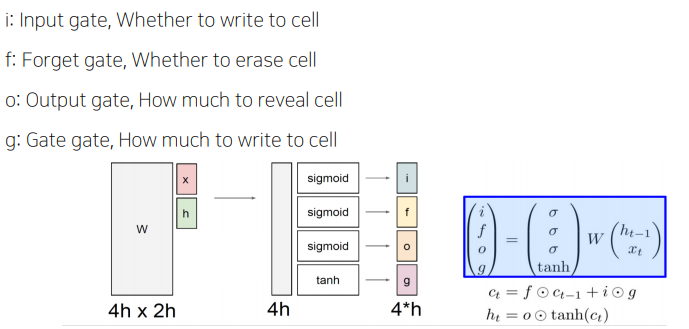
LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory)
이전의 강의에서 깊게 다루었던 내용이라, 다시 복기하는 마음으로 간단하게 정리했다.
Core idea
- pass cell state information straightly without any transformation.
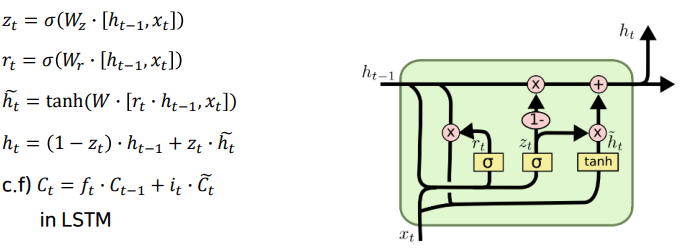
GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit)
adversial attack
defernce against adversarial attack
