Java 다형성
여러 가지 형태를 가질 수 있는 능력을 의미하며, 자바에서는 한 타입의 참조변수로 여러 타입의 객체를 참조할 수 있도록 했다.
즉, 부모클래스 타입의 참조변수로 자식클래스의 인스턴스를 참조할 수 있다.
자식클래스의 참조변수로 부모클래스의 인스턴스를 참조할 수는 없다.
Parent4 p = new Child4(); // 가능
Child4 c = new Parent4(); // 에러장점
- 다형적 매개변수 같은 타입
- 하나의 배열로 여러 종류 객체 저장
상속관계의 클래스에서는 자식클래스 타입의 인스턴스를 생성할 때, 부모클래스 타입의 참조변수를 사용할 수 있다.
참조변수가 사용할 수 있는 멤버의 개수는 인스턴스 멤버 개수보다 같거나 적어야 한다.
package poly.sample;
public class Parent4 {
protected int num;
public void display() {
System.out.println("부모 클래스 메소드");
}
}package poly.sample;
public class Child4 extends Parent4 {
private int x = 100;
public Child4() {
num = x;
}
public void out() {
System.out.println("부모의 protected num 필드 : " + num);
System.out.println("자식 클래스 메소드");
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println("상속받아 재정의한 메소드");
}
}package test.poly;
import poly.sample.Child4;
import poly.sample.Parent4;
public class TestPolymorphism {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 변수
int a = 30;
int b = 50;
int result = a + b;
System.out.println(result);
// 한 번만 사용할 거면 굳이 15-16 코드 처럼 변수 사용해서 2줄인데, 아래 코드는 1줄로 작성 가능하다.
// Parent4 p1 = new Parent4();
// p1.display();
new Parent4().display();
Child4 c = new Child4();
c.display(); // "상속받아 재정의한 메소드"
c.out(); // 0인데 Child4 기본생성자에 num = x;를 넣어주면 100의 값을 가져올 수 있다.
System.out.println();
// heap에 생성되는 것은 Child 모양으로 생성되고 그 주소를 p에게 전달함.
// p의 자료형은 Parent이므로 p. 으로 접근가능한 범위는 Parent에 있는 field / method 만 가능함
// (접근제한자에 따른 접근도 Parent의 설정에 따름).
Parent4 p = new Child4();
p.display(); // Overriding 된 parent 멤버이므로 접근 가능
// p.out(); 컴파일에러. Parent 타입으로 Child 멤버에 접근할 수 없음.
}
}
// 실행 결과
80
부모 클래스 메소드
상속받아 재정의한 메소드
부모의 protected num 필드 : 100
자식 클래스 메소드
상속받아 재정의한 메소드
참조변수의 형변환
서로 상속관계에 있는 클래스 사이에서만 참조변수의 형변환이 가능하다.
💡 업 캐스팅(Up-casting) : 자식클래스 → 조상클래스 // 형변환 생략가능 다운 캐스팅(Down-casting) : 조상클래스 → 자식클래스 // 형변환 생략불가업 캐스팅(Up-casting)
상속 관계에 있는 부모, 자식 클래스 간에 부모타입의 참조형 변수가 모든 자식 타입의 객체 주소를 받을 수 있음
// Sonata 클래스는 Car 클래스의 후손
Car c = new Sonata();
// Sonata클래스형에서 Car클래스형으로 바뀜(자동 형변환)다운 캐스팅(Down-casting)
자식 객체의 주소를 받은 부모 참조형 변수를 가지고 자식의 멤버를 참조해야 할 경우,
부모 클래스 타입의 참조형 변수를 자식 클래스의 타입으로 형변환 하는 것
반드시 강제 형변환(후손 타입 명시)을 해주어야 한다.
// Sonata 클래스는 Car 클래스의 후손
Car c = new Sonata();
((Sonata)c).moveSonata(); // moveSonata()는 Sonata에만 있는 메소드이다.
// (Sonata)로 강제 형변환/명시적 형변환참조변수의 형변환을 통해서 참조하고 있는 인스턴스에서 사용할 수 있는 멤버의 범위(개수)를 조절한다.
객체배열과 다형성
다형성을 이용하여 상속 관계에 있는 하나의 부모 클래스 타입의 배열 공간에 여러 종류의 자식 클래스 객체 저장 가능
// 방법 1.
Car[] carArr = new Car[5];
carArr[0] = new Sonata();
carArr[1] = new Avante();
carArr[2] = new Grandure();
carArr[3] = new Spark();
carArr[4] = new Morning();
// 방법 2.
Car[] carArr = {
new Sonata(),
new Avante(),
new Grandure(),
new Spark(),
new Morning()
};매개변수와 다형성
다형성을 이용하여 메소드 호출 시 부모타입의 변수 하나만 사용해 자식 타입의 객체를 받을 수 있음
pulbic void execute() {
// 호출
driveCar(new Sonata());
driveCar(new Avante());
driveCar(new Grandure());
}
// 정의
public void driveCar(Car c) {}메소드의 매개변수에 다형성을 적용하면, 동일한 메소드의 오버로딩 개수를 줄일 수 있게 된다.
package test.poly;
public class TestPolyArgument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Buyer b = new Buyer(); // 고객
b.buy(new Chair()); // 고객이 의자하나 구매
b.buy(new Desk()); // 고객이 책상하나 구매
}
}
class Furniture {
private int price; // 제품 가격
public Furniture(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
}
class Chair extends Furniture {
public Chair() {
super(100); // 부모클래스의 생성자 호출
}
public void changeBridge() {
System.out.println("다리바꾸기");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Chair";
}
}
class Desk extends Furniture {
public Desk() {
super(200);
}
public void changeColor() {
System.out.println("색상수정");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Desk";
}
}
class Buyer {
private int money = 500;
public void buy(Furniture f) {
// 만약 Furniture f = new Chair();
if(f instanceof Chair) {
((Chair)f).changeBridge();
}
if(f instanceof Furniture) {
System.out.println("가구");
}
if(f instanceof Object) {
System.out.println("object");
}
// 만약 Furniture f = new Desk();
if(f instanceof Desk) {
((Desk)f).changeColor();
}
if(money < f.getPrice()) {
System.out.println("잔액 부족!");
return;
}
money -= f.getPrice();
System.out.println(f + " 구매성공! 잔액 : " + money + " 만원");
}
}
// 부모타입인 Furniture 덕분에 자식 클래스인 Chair, Desk 모두 하나의 메소드를 사용할 수 있다.
// 만약 Chair, Desk를 매개변수로 받았다면, 아래와 같이 각각 사용할 수 있는 메소드가 필요했을 것이다.
class Buyer2 {
private int money = 500;
// Chair 구매메소드
void buy(Chair c) {
if(money < c.getPrice()) {
System.out.println("잔액부족!");
return;
}
money -= c.getPrice();
System.out.println(c + " 구매성공! 잔액 : " + money + " 만원");
}
// Desk 구매메소드
void buy(Desk d) {
if(money < d.getPrice()) {
System.out.println("잔액부족!");
return;
}
money -= d.getPrice();
System.out.println(d + " 구매성공! 잔액 : " + money + " 만원");
}
public void buy(Furniture f) {
if(money < f.getPrice()) {
System.out.println("잔액 부족!");
return;
}
money -= f.getPrice();
System.out.println(f + " 구매성공! 잔액 : " + money + " 만원");
}
}
// 실행 결과
다리바꾸기
가구
object
Chair 구매성공! 잔액 : 400 만원
가구
object
색상수정
Desk 구매성공! 잔액 : 200 만원instanceof 연산자
현재 참조형 변수가 어떤 클래스 형의 객체 주소를 참조하고 있는지 확인할 때 사용하는 연산자로 클래스 타입이 맞으면 true, 아니면 false 반환
if(레퍼런스 instanceof 클래스타입) {
// true일 때 처리할 내용, 해당 클래스 타입으로 down casting
}
if(c instanceof Sonata) {
((Sonata)c).moveSonata();
} else if(c instanceof Avante) {
((Avante)c).moveAvante();
} else if(c. instanceof Grandure) {
((Grandure)c).moveGrandure();
}instanceof를 이용한 연산 결과로 true를 얻었다는 것은 참조변수가 검사한 타입으로 형변환이 가능하다는 것을 뜻한다.
다형성 실습문제1

Electronic
package com.kh.prac5.model.vo;
public class Electronic {
private String brand; // 펜 유무
private String name; // 기기명
private int price; // 가격
public Electronic() {
super();
}
public Electronic(String brand, String name, int price) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "brand=" + brand + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "원";
}
}Tablet
package com.kh.prac5.model.vo;
public class Tablet extends Electronic {
private boolean penFlag; // 펜 유무
public Tablet() {
super();
}
public Tablet(String brand, String name, int price, boolean penFlag) {
super(brand, name, price);
this.penFlag = penFlag;
}
public boolean isPenFlag() {
return penFlag;
}
public void setPenFlag(boolean penFlag) {
this.penFlag = penFlag;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ", penFlag=" + penFlag;
}
}NoteBook
package com.kh.prac5.model.vo;
public class NoteBook extends Electronic {
private int usbPort; // usb 포트 개수
public NoteBook() {
super();
}
public NoteBook(String brand, String name, int price, int usbPort) {
super(brand, name, price);
this.usbPort = usbPort;
}
public int getUsbPort() {
return usbPort;
}
public void setUsbPort(int usbPort) {
this.usbPort = usbPort;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ", usbPort=" + usbPort;
}
}Desktop
package com.kh.prac5.model.vo;
public class Desktop extends Electronic {
private String graphic; // 그래픽 제조사
public Desktop() {
super();
}
public Desktop(String brand, String name, int price, String graphic) {
super(brand, name, price);
this.graphic = graphic;
}
public String getGraphic() {
return graphic;
}
public void setGraphic(String graphic) {
this.graphic = graphic;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ", graphic=" + graphic;
}
}YoungSan
package com.kh.prac5.controller;
import com.kh.prac5.model.vo.Electronic;
public class YongSan {
private Electronic[] elec = new Electronic[3]; // 전자기기 객체 배열
private int count = 0; // 객체 배열의 인덱스
public YongSan() {
super();
}
public Electronic[] getElec() {
return elec;
}
public void setElec(Electronic[] elec) {
this.elec = elec;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public void insert(Electronic anything) {
elec[count] = anything;
count++;
}
public Electronic[] select() {
return elec;
}
}Run
package com.kh.prac5.run;
import com.kh.prac5.controller.YongSan;
import com.kh.prac5.model.vo.Desktop;
import com.kh.prac5.model.vo.Electronic;
import com.kh.prac5.model.vo.NoteBook;
import com.kh.prac5.model.vo.Tablet;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
YongSan y = new YongSan();
// insert()
y.insert(new Desktop("삼성", "컴퓨터", 1200000, "GeForce"));
y.insert(new NoteBook("LG", "그램", 1500000, 3));
y.insert(new Tablet("애플", "프로3세대", 2500000, true));
// select()
Electronic[] eArr = y.select();
for(int i = 0; i < eArr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(eArr[i]);
}
}
}실행 결과

다형성 실습문제2

Family
package com.kh.prac6.model.vo;
public class Family {
private String name; // 이름
private double weight; // 몸무게
private int health; // 건강도
public Family() {
super();
}
public Family(String name, double weight, int health) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.weight = weight;
this.health = health;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getHealth() {
return health;
}
public void setHealth(int health) {
this.health = health;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name=" + name + ", weight=" + weight + ", health=" + health;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("밥 먹었을 때의 변화");
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("잠을 잤을 때의 변화");
}
}Baby
package com.kh.prac6.model.vo;
public class Baby extends Family {
private String babyBirth; // 아이의 탄생을 나타내는 변수(출산/입양/없음)
public Baby() {
super();
}
public Baby(String name, double weight, int health, String babyBirth) {
super(name, weight, health);
this.babyBirth = babyBirth;
}
public String getBabyBirth() {
return babyBirth;
}
public void setBabyNum(String babyBirth) {
this.babyBirth = babyBirth;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ", babyNum=" + babyBirth;
}
@Override
public void eat() {
setWeight(getWeight() + 3); // 아기는 밥을 먹으면 몸무게 3 증가
setHealth(getHealth() + 1); // 아기는 밥을 먹으면 건강도 1 증가
}
@Override
public void sleep() {
setWeight(getWeight() - 1); // 아기는 잠을 자면 몸무게 1 감소
setHealth(getHealth() + 10); // 아기는 잠을 자면 건강도 10 증가
}
}Mother
package com.kh.prac6.model.vo;
public class Mother extends Family {
private String babyBirth; // 출산 여부
public Mother() {
super();
}
public Mother(String name, double weight, int health, String babyBirth) {
super(name, weight, health);
this.babyBirth = babyBirth;
}
public String getBabyBirth() {
return babyBirth;
}
public void setBabyBirth(String babyBirth) {
this.babyBirth = babyBirth;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ", babyBirth=" + babyBirth;
}
@Override
public void eat() {
setWeight(getWeight() + 8); // 엄마는 밥을 먹으면 몸무게 8 증가
setHealth(getHealth() - 10); // 엄마는 밥을 먹으면 건강도 10 감소
}
@Override
public void sleep() {
setWeight(getWeight() - 8); // 엄마는 잠을 자면 몸무게 8 감소
setHealth(getHealth() + 7); // 엄마는 잠을 자면 건강도 7 증가
}
}Run
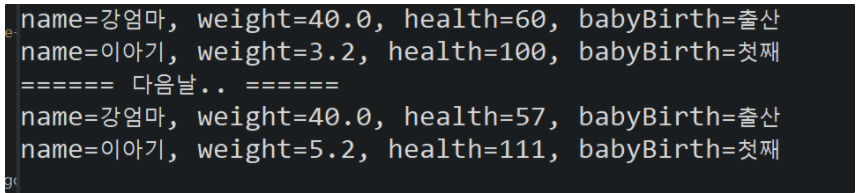
package com.kh.prac6.run;
import com.kh.prac6.model.vo.Baby;
import com.kh.prac6.model.vo.Family;
import com.kh.prac6.model.vo.Mother;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Family f1 = new Mother("강엄마", 40, 60, "출산");
Family f2 = new Baby("이아기", 3.2, 100, "첫째");
System.out.println(f1);
System.out.println(f2);
f1.eat();
f2.eat();
f1.sleep();
f2.sleep();
System.out.println("====== 다음날.. ======");
System.out.println(f1);
System.out.println(f2);
}
}실행 결과