상속
💡 부모 클래스가 가지고 있는 멤버(필드, 메소드)들을 새로 작성할 클래스에서 직접 만들지 않고 상속을 받음으로써 새 클래스가 자신의 멤버처럼 사용할 수 있는 기능 클래스 간의 다중상속은 허용하지 않는다.장점
- 보다 적은 양의 코드로 새로운 클래스 작성 가능
- 코드를 공통적으로 관리하기 때문에 코드의 추가 및 변경 용이
- 코드의 중복을 제거하여 프로그램의 생산성 / 유지보수에 크게 기여
특징
- 모든 클래스는 Object클래스의 후손
- Object클래스가 제공하는 메소드를 오버라이딩하여 메소드 재구현 가능
ex) java.lang.String 클래스의 equals()와 toString()
- Object클래스가 제공하는 메소드를 오버라이딩하여 메소드 재구현 가능
- 부모클래스의 생성자, 초기화 블록은 상속 안 됨
- 자식 클래스 생성 시, 부모 클래스 생성자가 먼저 실행
자식 클래스 생성자 안에 부모 클래스 생성자를 호출하고 싶으면 super() 활용
- 자식 클래스 생성 시, 부모 클래스 생성자가 먼저 실행
- 부모의 private멤버는 상속은 되지만 직접 접근 불가
- 자식 생성자 안에서 부모의 private 필드에 직접 접근하여 대입 불가
super() 이용하여 전달받은 부모 필드 값을 부모 생성자 쪽으로 넘겨 생성하거나 setter, getter 메소드를 이용하여 접근
- 자식 생성자 안에서 부모의 private 필드에 직접 접근하여 대입 불가
상속 지정
// 클래스 간의 상속 시에는 extends 키워드 사용
[접근제한자] class 클래스명 extends 클래스명 {}
public class Academy extends Company {}자바에서는 단일상속만 지원한다.
메소드 오버라이딩
메소드 재정의라고 하고, 부모 클래스로부터 상속받은 메소드를 자식 클래스에서 다시 정의하는 것을 말한다.
@Override 어노테이션을 사용하여 재정의한다는 것을 표시한다.
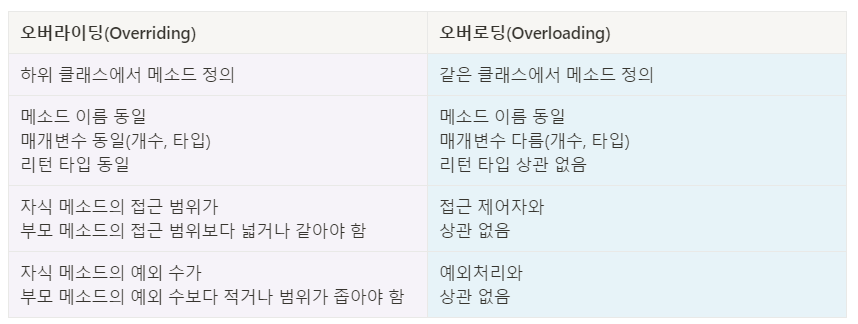
오버라이딩 성립 조건
부모 클래스의 메소드와 자식 클래스의 메소드 비교
- 메소드 이름 동일
- 매개 변수의 개수, 타입 동일 (다르면 overloading)
- 리턴 타입 동일
- private 메소드 오버라이딩 불가
- final 메소드 오버라이딩 불가
// 상속이 불가능한 클래스(종단 클래스)
접근제한자 final class 클래스이름 {...}
public final class FinalClass {}
// 상속 시 오버라이딩이 불가능한 메소드
접근제한자 final 리턴타입 메소드이름(자료형 매개변수) {...}
public final void method() {}오버라이딩과 오버로딩
상속 예시
package inherit.sample;
public class Parent {
private int num;
// public 안붙여주면 default : inherit.sample 안에 든 java 파일에서 가능함.
public void display() {
System.out.println("부모 클래스 메소드");
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
}package inherit.sample;
public class Child extends Parent {
public void out() {
System.out.println("자식 클래스 메소드");
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println("상속받아 재정의한 메소드");
}
}package test.inherit;
import inherit.sample.Child;
import inherit.sample.Parent;
public class TestOverriding {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent p = new Parent();
p.display();
// p.out() // 부모객체는 자식객체의 멤버에 접근할 수 없다.
Child c = new Child();
c.out();
c.display();
}
}
// 실행 결과
부모 클래스 메소드
자식 클래스 메소드
상속받아 재정의한 메소드super()와 super.
자식클래스에서 부모클래스의 생성자나 멤버에 접근하고 싶을 때 super 키워드를 사용한다.
super: 부모 클래스의 멤버를 지칭할 때 사용super(): 부모 클래스의 생성자를 호출할 때 사용.
단, 반드시 후손 생성자 {} 안 첫 줄에 사용해야 한다.
상속 실습문제1

Computer
package com.kh.prac1.parent.model.vo;
public class Computer {
private String cpu; // cpu 사양
private String brand; // 제조사
private int price; // 가격(만원)
public Computer() {
super();
}
public Computer(String cpu, String brand, int price) {
super();
this.cpu = cpu;
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public String getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
public void setCpu(String cpu) {
this.cpu = cpu;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}SmartPhone
package com.kh.prac1.child.model.vo;
import com.kh.prac1.parent.model.vo.Computer;
public class SmartPhone extends Computer{
private String paymentPlan; // 요금제
public SmartPhone() {
super();
}
public String getPaymentPlan() {
return paymentPlan;
}
public void setPaymentPlan(String paymentPlan) {
this.paymentPlan = paymentPlan;
}
}Tablet
package com.kh.prac1.child.model.vo;
import com.kh.prac1.parent.model.vo.Computer;
public class Tablet extends Computer{
private double screenSize; // 스크린 크기
private String pen; // 펜 종류
public Tablet() {
super();
}
public double getScreenSize() {
return screenSize;
}
public void setScreenSize(double screenSize) {
this.screenSize = screenSize;
}
public String getPen() {
return pen;
}
public void setPen(String pen) {
this.pen = pen;
}
}Run
package com.kh.prac1.run;
import com.kh.prac1.child.model.vo.SmartPhone;
import com.kh.prac1.child.model.vo.Tablet;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SmartPhone sp = new SmartPhone();
sp.setCpu("i7-1234");
sp.setBrand("KH");
sp.setPrice(1500);
sp.setPaymentPlan("무제한 요금제");
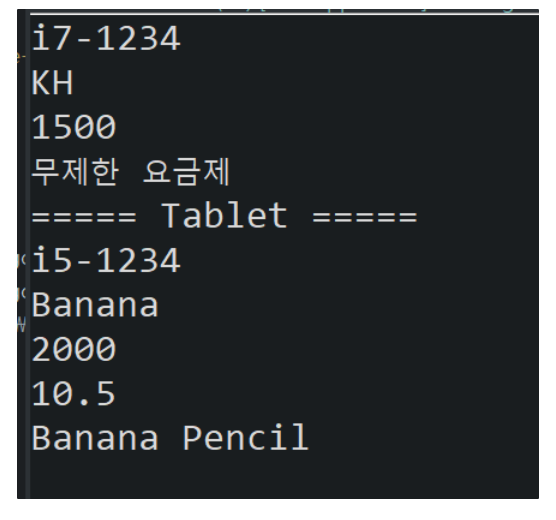
System.out.println("===== SmartPhone =====");
System.out.println(sp.getCpu());
System.out.println(sp.getBrand());
System.out.println(sp.getPrice());
System.out.println(sp.getPaymentPlan());
Tablet tb = new Tablet();
tb.setCpu("i5-1234");
tb.setBrand("Banana");
tb.setPrice(2000);
tb.setScreenSize(10.5);
tb.setPen("Banana Pencil");
System.out.println("===== Tablet =====");
System.out.println(tb.getCpu());
System.out.println(tb.getBrand());
System.out.println(tb.getPrice());
System.out.println(tb.getScreenSize());
System.out.println(tb.getPen());
}
}실행 결과
상속 실습문제2

Circle
package com.kh.prac2.child.model.vo;
import com.kh.prac2.parent.model.vo.Shape;
public class Circle extends Shape {
private int radius; // 반지름
public Circle() {
super();
}
public Circle(int radius) {
// super();
super((int)(radius * radius * Math.PI), (int)(2 * Math.PI * radius));
this.radius = radius;
}
public int getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public String information() {
return super.information() + ", 반지름 : " + radius;
}
}Rectangle
package com.kh.prac2.child.model.vo;
import com.kh.prac2.parent.model.vo.Shape;
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private int width; // 너비
private int height; // 높이
public Rectangle() {
super();
}
public Rectangle(int width, int height) {
// super();
super(width * height, 2 * (width + height));
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public String information() {
return super.information() + ", 너비 : " + width + ", 높이 : " + height;
}
}Shape
package com.kh.prac2.parent.model.vo;
public class Shape {
private int area; // 넓이
private int perimeter; // 둘레
public Shape() {
super();
}
public Shape(int area, int perimeter) {
super();
this.area = area;
this.perimeter = perimeter;
}
public int getArea() {
return area;
}
public void setArea(int area) {
this.area = area;
}
public int getPerimeter() {
return perimeter;
}
public void setPerimeter(int perimeter) {
this.perimeter = perimeter;
}
public String information() {
return "넓이 : " + area + ", 둘레 : " + perimeter;
}
}Run
package com.kh.prac2.run;
import com.kh.prac2.child.model.vo.Circle;
import com.kh.prac2.child.model.vo.Rectangle;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Circle c = new Circle();
// c.setArea(28);
// c.setPerimeter(18);
// c.setRadius(3);
Circle c = new Circle(3);
System.out.println("Circle 관련 : ");
System.out.println(c.information());
// Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
// r.setArea(8);
// r.setPerimeter(12);
// r.setWidth(2);
// r.setHeight(4);
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(2, 4);
System.out.println("Rectangle 관련 : ");
System.out.println(r.information());
}
}실행 결과

오버라이딩 실습문제 1
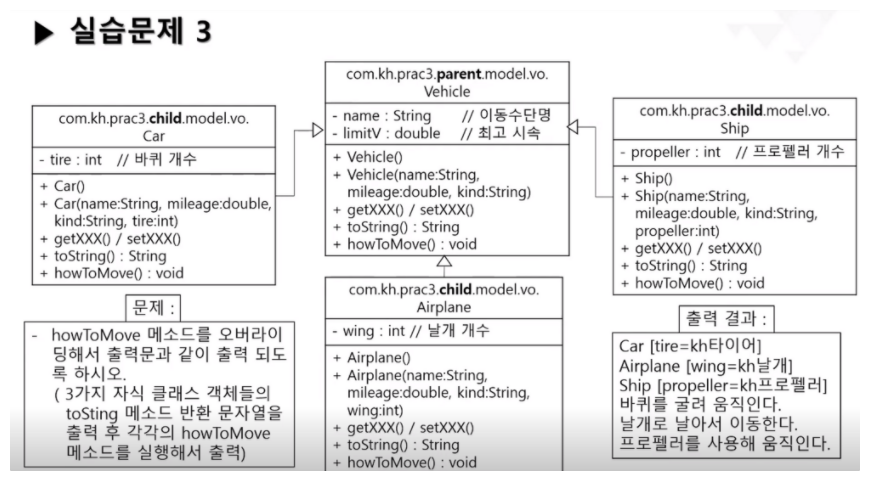
Car
package com.kh.prac3.child.model.vo;
import com.kh.prac3.perent.model.vo.Vehicle;
public class Car extends Vehicle {
private String tire; // 타이어
public Car() {
super();
}
public Car(String tire) {
super();
this.tire = tire;
}
public Car(String name, Double limitV, String tire) {
super(name, limitV);
this.tire = tire;
}
public String getTire() {
return tire;
}
public void setTire(String tire) {
this.tire = tire;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [tire=" + tire + "]";
}
@Override
public void howToMove() {
System.out.println("바퀴를 굴려 움직인다.");
}
}Airplane
package com.kh.prac3.child.model.vo;
import com.kh.prac3.perent.model.vo.Vehicle;
public class Airplane extends Vehicle {
private String wing; // 날개 종류
public Airplane() {
super();
}
public Airplane(String wing) {
super();
this.wing = wing;
}
public Airplane(String name, double limitV, String wing) {
super(name, limitV);
this.wing = wing;
}
public String getWing() {
return wing;
}
public void setWing(String wing) {
this.wing = wing;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Airplane [wing=" + wing + "]";
}
@Override
public void howToMove() {
System.out.println("날개로 날아서 이동한다.");
}
}Ship
package com.kh.prac3.child.model.vo;
import com.kh.prac3.perent.model.vo.Vehicle;
public class Ship extends Vehicle {
private String propeller; // 프로펠러명
public Ship() {
super();
}
public Ship(String propeller) {
super();
this.propeller = propeller;
}
public Ship(String name, double limitV, String propeller) {
super(name, limitV);
this.propeller = propeller;
}
public String getPropeller() {
return propeller;
}
public void setPropeller(String propeller) {
this.propeller = propeller;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Ship [propeller=" + propeller + "]";
}
@Override
public void howToMove() {
System.out.println("프로펠러를 사용해 움직인다.");
}
}Vehicle
package com.kh.prac3.perent.model.vo;
public class Vehicle {
private String name; // 이동수단명
private double limitV; // 최고 시속
public Vehicle() {
super();
}
public Vehicle(String name, double limitV) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.limitV = limitV;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getLimitV() {
return limitV;
}
public void setLimitV(double limitV) {
this.limitV = limitV;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + name + " = " + limitV + "]";
}
public void howToMove() {
System.out.println("움직인다.");
}
}Run
package com.kh.prac3.run;
import com.kh.prac3.child.model.vo.Airplane;
import com.kh.prac3.child.model.vo.Car;
import com.kh.prac3.child.model.vo.Ship;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c = new Car("BMW", 180.5, "kh타이어");
Airplane ap = new Airplane("비행기", 410, "kh날개");
Ship s = new Ship("낚시배", 40, "kh프로펠러");
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(ap);
System.out.println(s);
c.howToMove();
ap.howToMove();
s.howToMove();
}
}실행 결과

오버라이딩 실습문제 2
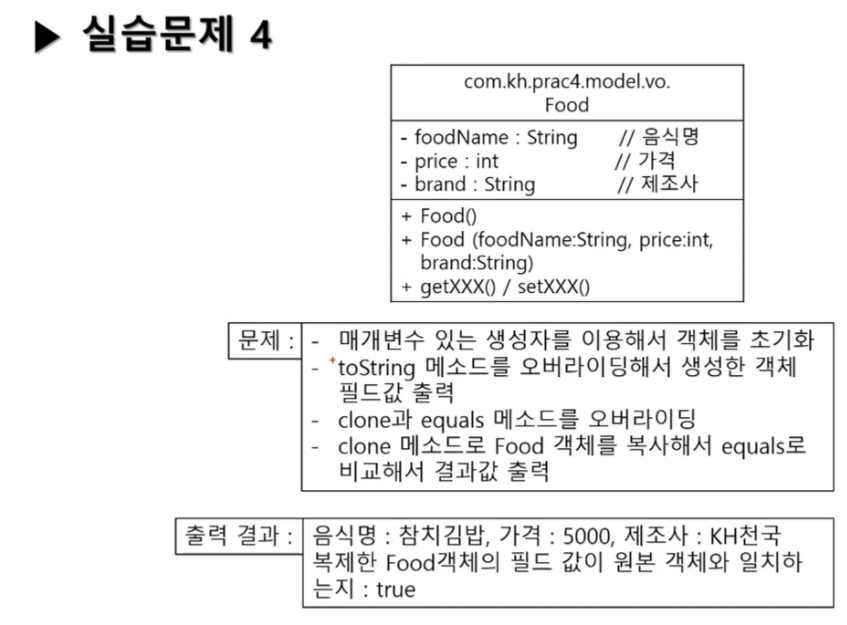
Food
package com.kh.prac4.model.vo;
public class Food {
private String foodName; // 음식명
private int price; // 가격
private String brand; // 제조사
public Food() {
super();
}
public Food(String foodName, int price, String brand) {
super();
this.foodName = foodName;
this.price = price;
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getFoodName() {
return foodName;
}
public void setFoodName(String foodName) {
this.foodName = foodName;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "음식명 : " + foodName + ", 가격 : " + price + ", 제조사 : " + brand;
}
// 지양 하는 방법(clone 오버라이딩)
// @Override
// public Food clone() {
//// return this; // 얕은 복사(원본이 변형됨)
// return new Food(foodName, price, brand); // 깊은 복사(원본은 안전하고 사본만 변형됨)
// }
// 추천하는 방법(새로운 복사 메소드 생성)
public Food cloneFood() {
return new Food(foodName, price, brand);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
Food f = (Food)obj;
return foodName.equals(f.foodName) && price == f.price && brand.equals(f.brand);
}
}Run
package com.kh.prac4.run;
import com.kh.prac4.model.vo.Food;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Food f = new Food("참치김밥", 5000, "KH천국");
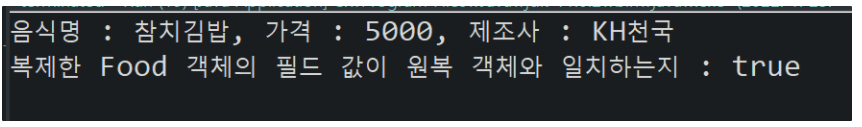
System.out.println(f); // toString();
// Food fCopy = f.clone();
Food fCopy = f.cloneFood();
System.out.println("복제한 Food 객체의 필드 값이 원복 객체와 일치하는지 : " + fCopy.equals(f));
}
}실행 결과