New address in return address
Considerations
- The new address in the return address of function stack should not contain zero in any of its byte, or the badfile will have a zero causing strcpy() to end copying
- e.g., 0xbfffeaf8 + 0x08 = 0xbfffeb00, the last byte contains zero leading to the copy
Execution results
Compiling the vulnerable code with all the countermeasures disabled
- -fno-stack-protector: stack guard(canary) off
- -fcf-protection=none: control flow protection off
- -fno-pie, z-execstack: 실행 가능한 스택, 고정 위치
Executing the exploit code and stack code
- $id 결과, euid=0(root)로 root 쉘을 획득한 상태이다.

A note on countermeasure
- On Ubuntu 16.04,
/bin/shpoints to/bin/dash, which has a countermeasure - It drops privileges when being executed inside a setuid process
1. Point /bin/sh to another shell(simplify the attack)
$sudo ln -sf /bin/zsh /bin/sh
2. Change the shellcode (defeat this countermeasure)
change "\x86""//sh" to "x86""/zsh"- shellcode 내부에서 기본적으로 /bin/sh를 실행하는 부분을 /bin/zsh로 바꿔서 권한이 유지되는 쉘을 띄울 수 있다.
Other methods to defeat the countermeasure will be discussed later
Shellcode
Aim of the malicious code
- Allow to run more commands to gain access of the system
Solution
- Shell program
- 실제 exploit에서는 이 동작을 완전히 binary code로 압축해서 공격한다.

Challenges
- Loader issue
- Zeros in the code
Assembly code (machine instructions) for launching a shell
- Goal Use
execve("/bin/sh", argv, 0)to run shell

- Registers used
- eax = 0x0000000b(11): value of system call execve()
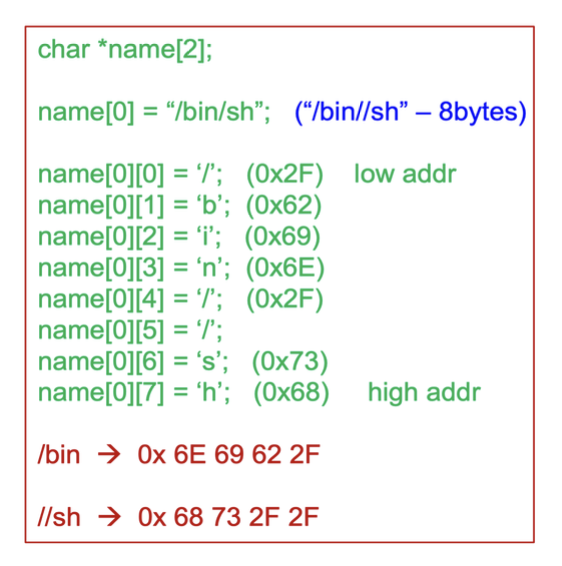
- ebx = address to "/bin/sh": 문자열이 위치한 메모리 주소
- ecx = address of the argument array
- argv[0] = the address of "/bin/sh"
- argv[1] = 0 (i.e., no more argunments)
- edx = zero (no environment variables are passed)
- int 0x80: invoke execve(): 레지스터 값이 준비되면 system call 수행
ebx 안에는 문자열 "/bin/sh"가 시작하는 메모리 위치가 들어있고, ecx 안에는 포인터 배열 'argv'의 시작 주소가 들어있다.
x86-32 registers
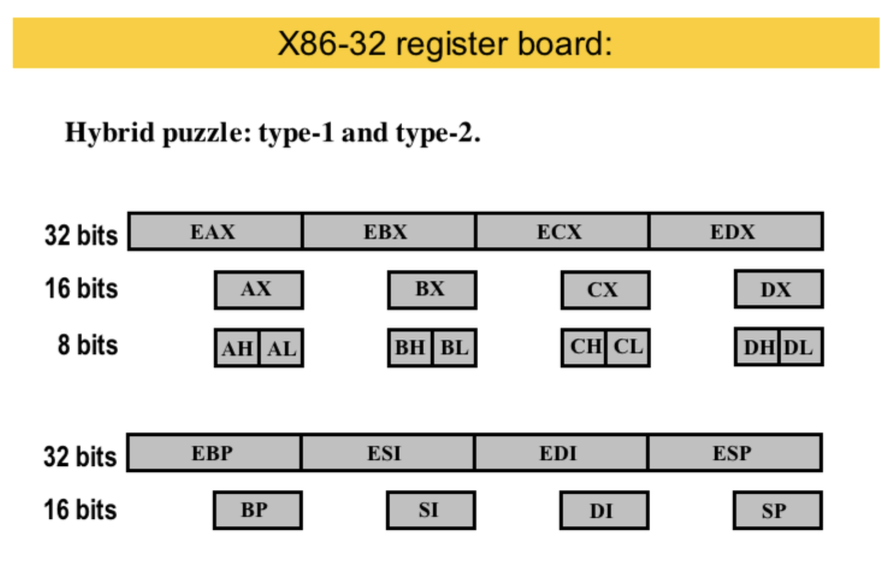
- eax = 32 bits
- ax = 16 bits
- ax = ah + al (high + low)
- ah & al = 8 bits
Byte ordering
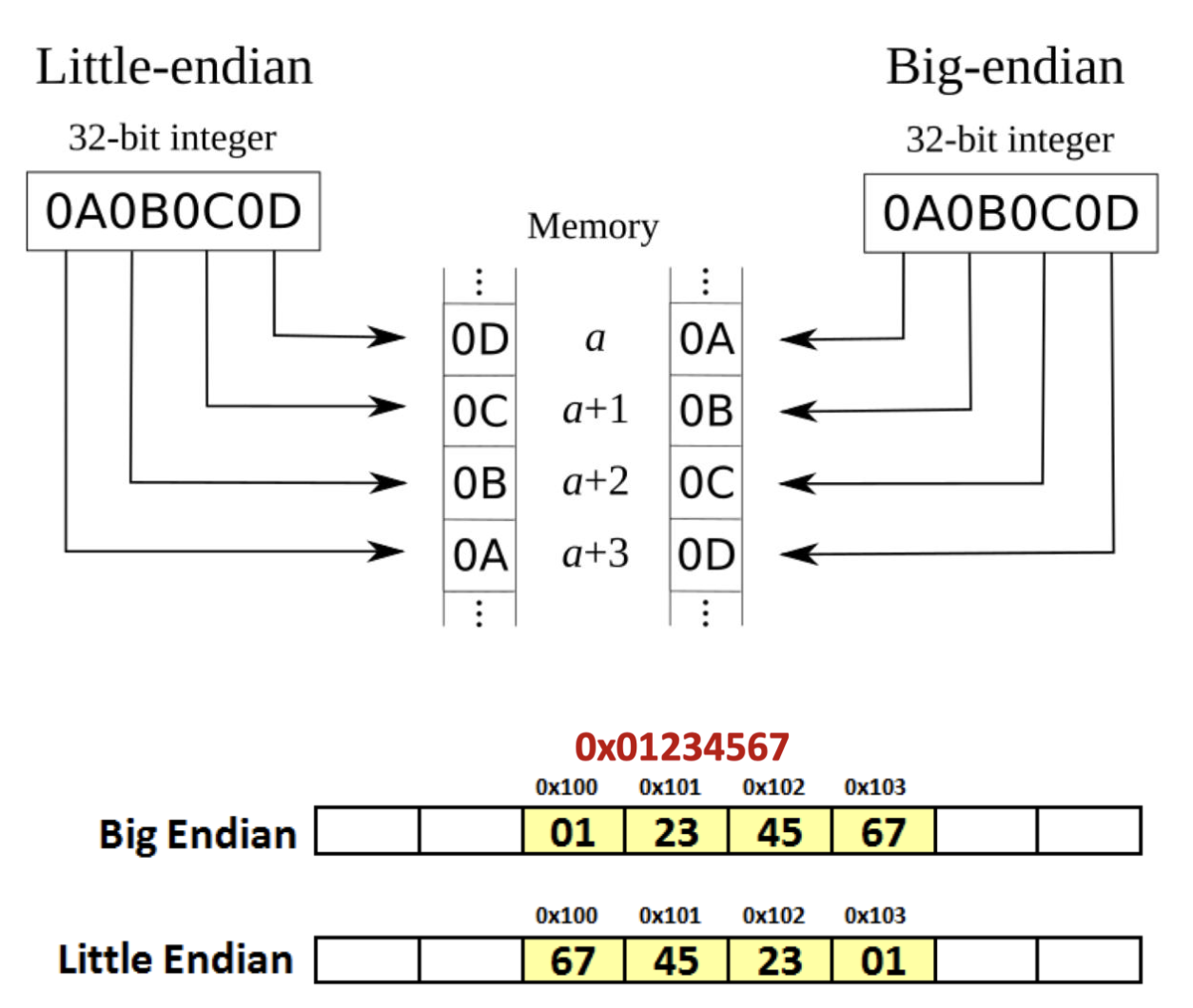
- Big-endian
- 상위 바이트 먼저 저장
- Little-endian
- 하위 바이트 먼저 저장
- 대부분의 x86 system
Shellcode

- 코드 내에 직접 '0x00' byte가 들어가는 부분을 모두 'xorl', 'cdq' 등 명령으로 대신 채워서 null byte가 직접 포함되지 않도록 설계
- 각 명령이 execve()의 인자를 완벽히 준비하고, 최종적으로 system call 실행

- a: ebx를 esp로 옮겨서, ebx가 "/bin//sh" 문자열의 주소를 가지게 만듦
- b: ecx: argv 배열 전체를 가리키는 포인터
Countermeasure
1. Developer approaches
2. OS approaches
- ASLR(Address Space Layout Randomization)
- Shell Program Defense
- Non-Executable Stack(NX bit)
- NX bit를 on하면 stack을 non-executable, stack에 저장된 데이터를 instruction로 실행하는 것을 차단
3. Compiler approches
- StackGuard (Stack canary)
- Compiler adds a random value (canary) below the RET and saves a copy of the random value at a safer place that is off the stack
RT 바로 아래에 임의의 값 canary를 삽입하고, 이 값을 스택 외부의 안전한 곳에 복사해 둔다. 함수가 종료될 때 canary가 변경되었는지 확인하여, stack overflow로 인한 반환 주소 변조 시도를 탐지한다.
Developer's approaches(1): Secure coding
- Check data length
- Don't let user's set the length; set it yourself

Developer's approaches(2)
- Use of safer dynamic link libraries that check the length of the data before copying
- libsafe
- a safer version for the standard unsafe functions(It dose boundary checking)
- libmib
- conceptually supports "limitless" strings instead of fixed length string buffers
- libsafe
- Use safer languages(if you have a choice)
OS approaches(1): ASLR
Principle of ASLR(Address Space Layout Randomization)
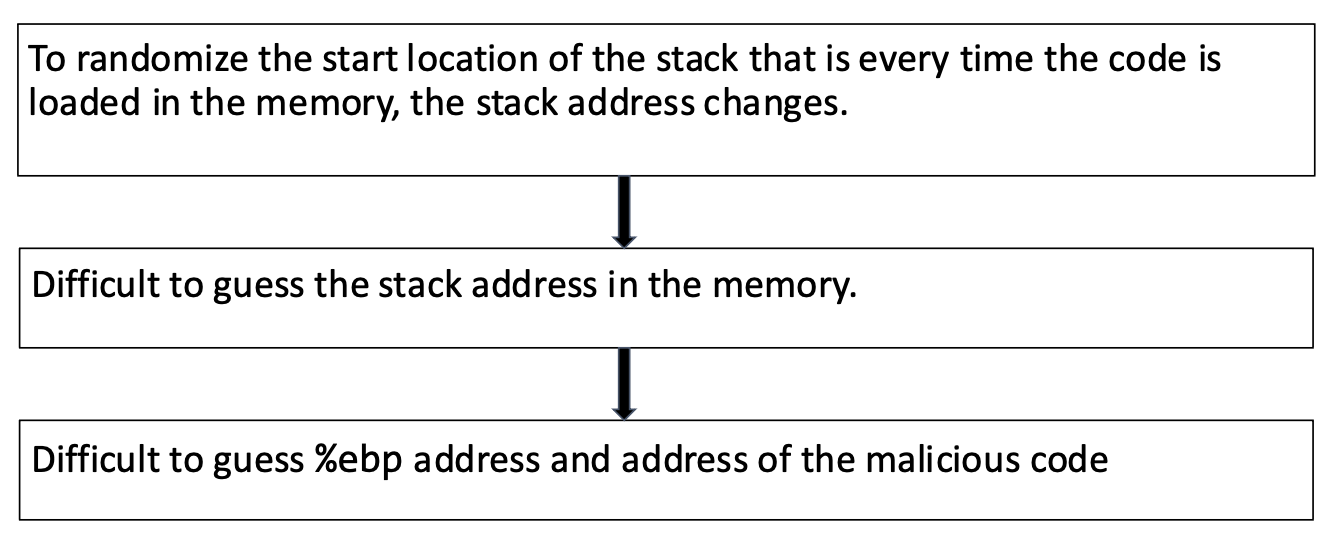
매번 코드가 메모리에 로드될 때마다 스택의 시작 주소를 무작위로 변경하여, 공격자가 메모리 내에서 스택의 정확한 주소를 추측하기 어렵다.
Address space layout randomization

ASLR은 대부분의 최신 OS에서 기본적으로 활성화되어 있으며, 위 코드를 실행하면 stack과 heap에 할당된 메모리 주소가 매번 무작위로 달라지는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 메모리 기반 공격을 방어에 효과적이다.
Address space layout randomization: Working
1. option: 0 (비활성)
- 여러 번 실행해도 stack과 heap 메모리 주소가 항상 동일

2. option: 1 (부분적 비활성)
- stack random, heap 주소는 고정

3. option: 2 (활성)
- stack, heap 둘 다 random이 적용되어 가장 안전함

Address space layout randomization: Defeat it
1. Turn on address randomization(countermeasure)
sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space = 2
2. Compile set-uid root version of stack.c
% gcc -o stack -z execstack -fno-stack-protector stack.c
% sudo chown root stack
% sudo chmod 4755 stack - 일반 사용자가 해당 프로그램을 실행해도 실제 실행 권한은 root로 동작하게 되어, 시스템 보안 실습에 사용된다.
3. Defeat it by running the vulnerable code in an infinite loop

- 반복 실행을 통해 공격자가 한 번이라도 주소 예측에 성공하면 exploit이 가능하다. 32-bit에서는 19-bit의 엔트로피만 존재해, 가능한 값의 가짓수가 개로 제한적이다.
On running the script for about 19 minutes on a 32-bit Linux machine, we got the access to the shell(malicious code got executed)
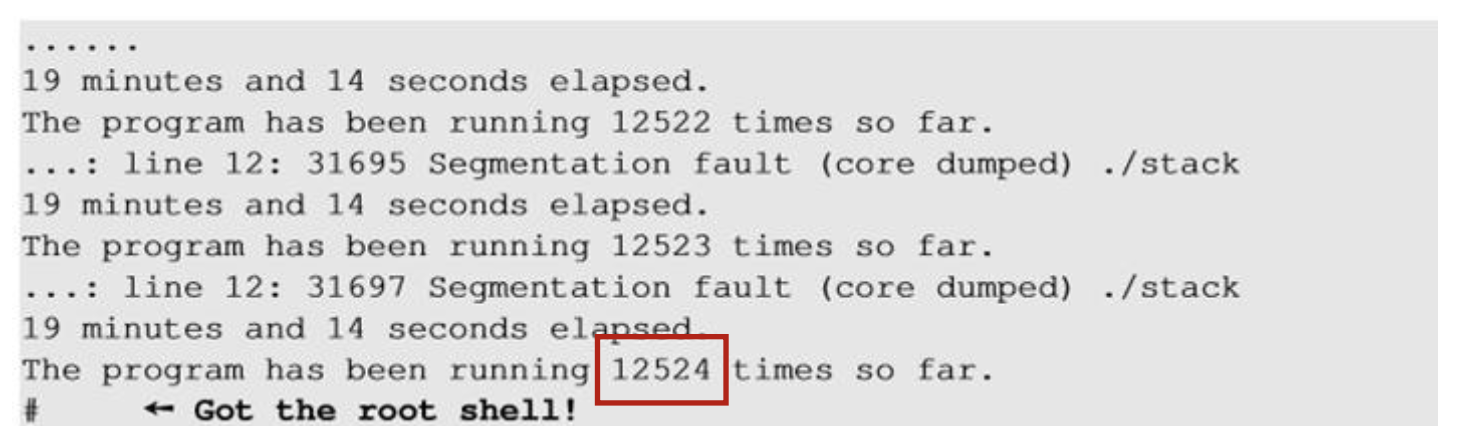
여러 번 프로그램이 비정상 종료(core dumped)되었지만, 반복 시도 끝에 예측이 맞아 exploit이 성공한다. 랜덤이니까 어쩌다 보면 될 수도... 있는 거다.
OS approaches(2): Shell program defense
Copy two shell programs to out current folder, and make them root-owned Set-UID programs
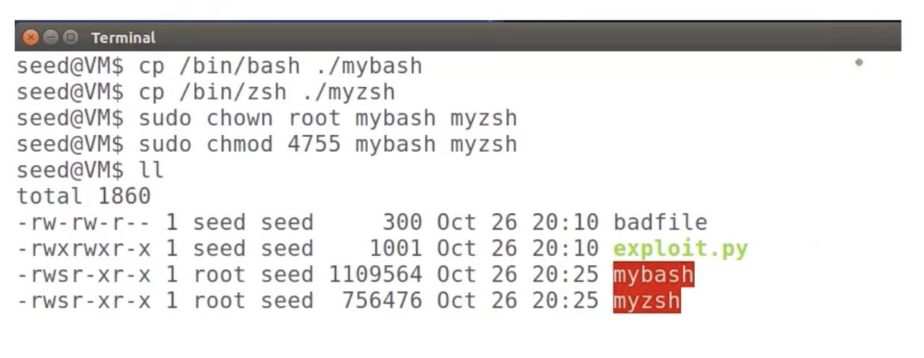
Run them
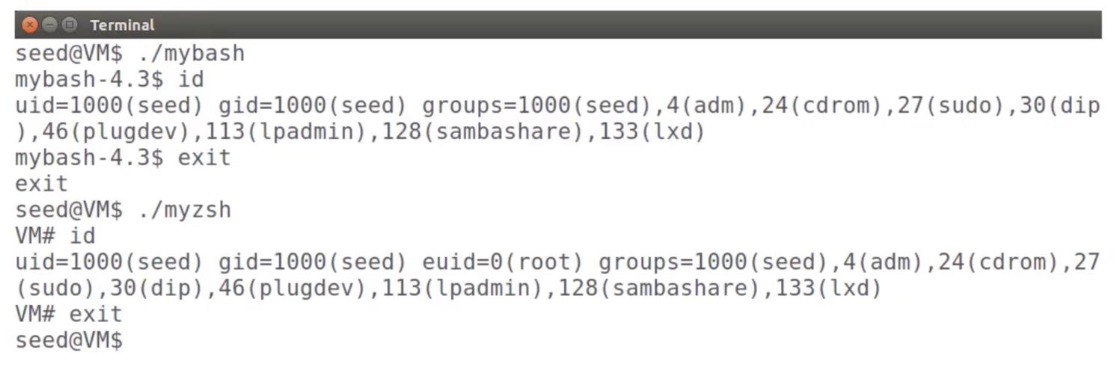
- zsh의 경우, id 명령을 실행하면 UID는 seed이지만, EUID는 root로 변경된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Defeating countermeasure in bash&dash


- The dash shell downgrades the privilege when the EUID RUID
- Dash shell turns the setuid process into a non-setuid process
- It sets the effective user ID to the real user ID, dropping the privilege
- Idea: In order to defeat this countermeasure, before running them, we set the real user ID to 0
- Invoke setuid(0)
- We can do this at the beginning of the shellcode

- setuid(0) shellcode에서도 xorl을 사용해서 역시나 NULL byte 없이 동작하게 만든다.
- eax에 system call number(d5)를 넣고, ebx를 0으로 설정한 뒤 int 0x80을 실행하여 setuid(0) system call 호출
dash나 bash가 고의적으로 완전한 root 권한의 쉘을 막는 대책이 있어서 이를 우회하려면, exploit에서 setuid(0) system call을 먼저 호출해야 한다.
OS approaches(3): Non-executable stack
- NX bit, standing for No-eXecute feature in CPU separates code from data which marks certains areas of the memory as non-executable
- This countermeasure can be defeated using a different technique called Return-to-libc attack(there is a separate chapter on this attack)
이미 실행 가능하도록 OS에 등록된 라이브러리 함수의 주소를 덮어서 프로그램 흐름을 라이브러리 함수로 강제로 반환시킨다.
Non-executable stack: Working
Code on the stack

- Executable stack이 허용된 환경에서는 함수 포인터 형변환을 통해 buffer에 들어있는 shellcode를 함수처럼 호출하여 임의 코드 실행 공격이 성공한다.
- Non-executable stack에서는, buffer에 복사된 shellcode를 실행하려고 할 때 OS가 해당 메모리 영역의 실행을 차단하여 공격이 실패한다.
Execution result

Compiler approach: StackGuard

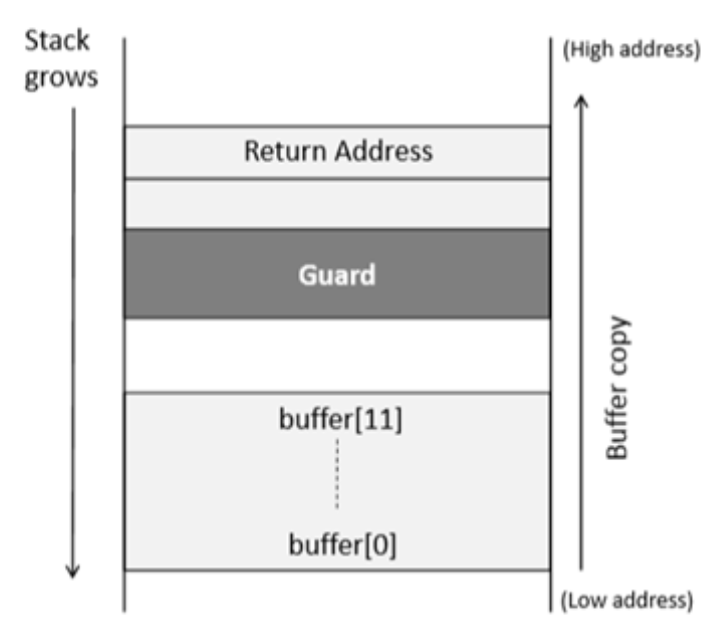
- We may manually add some code and variables to the function
- A random secret value(Guard) is generated and sorted in a memory location (not on stack)
- It is also assigned to a local variable of the function which gets stored in the stack
buffer overflow attack에서는 RET를 덮으려면 그 앞에 있는 stack canary도 함께 덮어쓰게 된다. 함수 종료 직전에, stack에 있는 canary와 프로세스 시작 시 랜덤하게 정해져 전역에 저장된 원래 canary(secret) 값을 비교해서 다르면 즉시 종료한다.
Execution with StackGuard

- strcpy(buffer, str)로 buffer에 데이터가 복사되며, 길이 제한이 없어 overflow 위험 존재
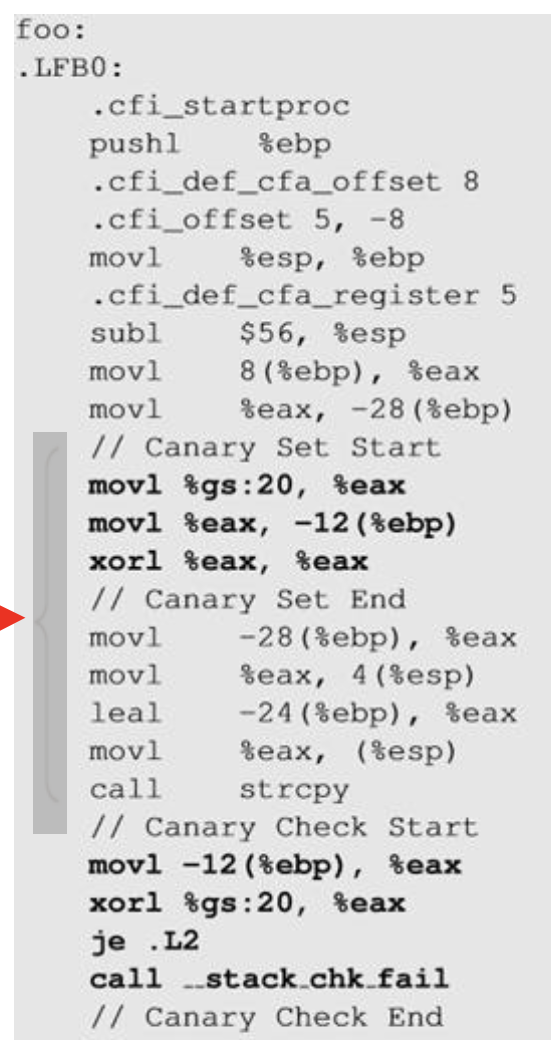
- 컴파일러가 자체적으로 StackGuard 삽입(mov)
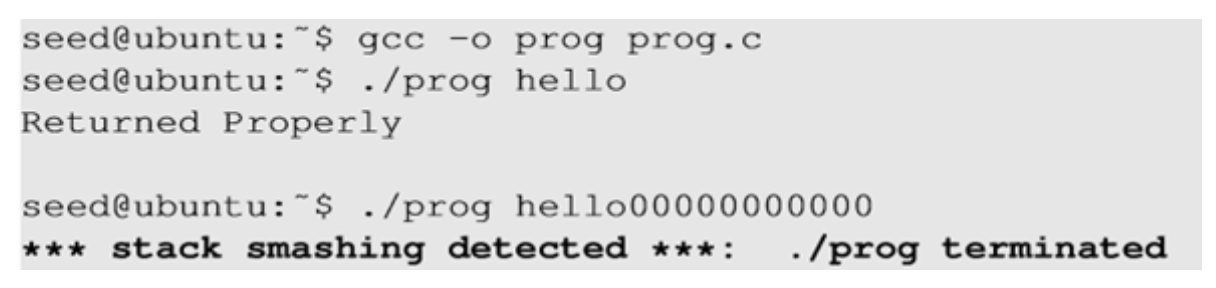
- 함수 종료 직전, 현재 스택에 있는 canary 값과 원래 secret 값을 비교하고 다르면 바로 종료한다.
