2. Protection & Security
Operating System Services
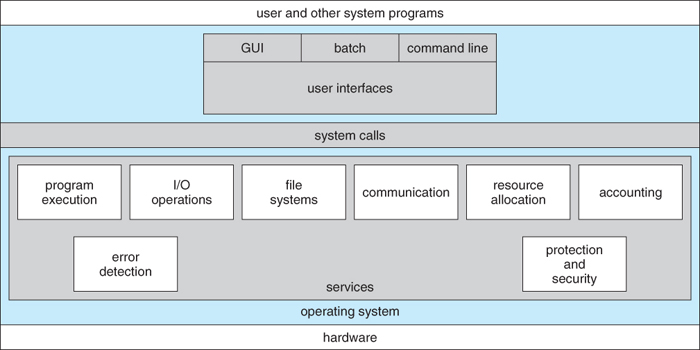
Protection and Security
핵심 서비스가 존재하는 커널 안에 protection and security라는 영역이 존재한다.
- Authentication, ownership, restriced access
- Logging and Security regulations
- 보안이 매우 중요한 시스템에서는 모든 프로세스 활동을 기록
Protection & Security
1. Protection
- Controlling access of processes or users to resources defined by the OS
- Internal to the OS
- Virtual address space
- File permission modes: rwx
2. Security
- Defense of OS against internal and external attacks(e.g. malware)
- it must also consider external environment
Protection은 올바른 사용에 초점을 맞추고, security는 시스템을 나쁜 의도로부터 지키는 방어의 의미에 가깝다.
Two Key Concepts
Linux에서는 모든 resource를 file로 칭한다.
Protection
mechanisms used to control access to the valued resources
- Referring to specific mechanisms used by OS to safeguard information
- Usually accompanied by detection and response mechanisms
- We can refer to protection as a subset of security
Goals of Protection
- Computer consists of a collection of objects, h/w or s/w
- Each object has a unique name and can be accessed through a well-defined set of operations
- Protection problem: ensure that each object is accessed correctly and only by those processes that are allowed to do so
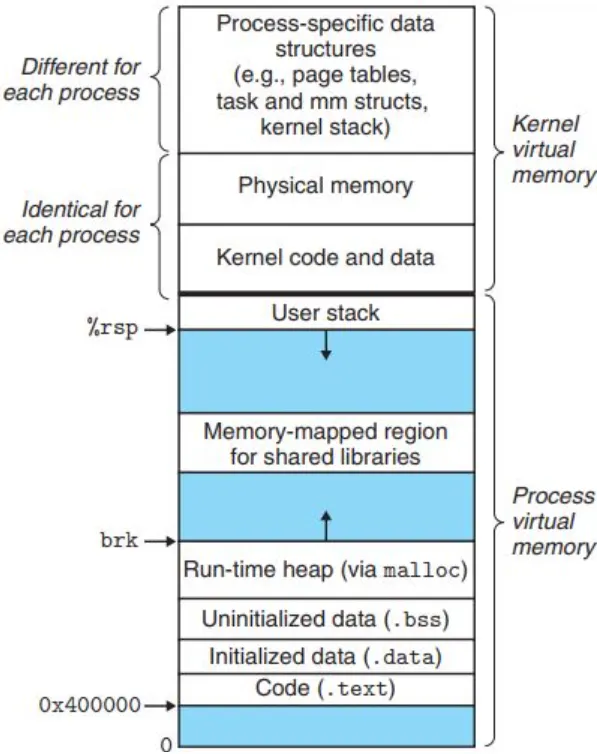
Virtual Address Space of a Linux Process
32-bit 시스템에서는 프로세스마다 4GB의 virtual memory를 할당받는다. 4GB의 메모리 영역 중 대략 1GB는 커널 영역에 해당하고 메모리 내에는 여러 partition이 존재한다.
- Identical space: 프로세스끼리 share하는 영역
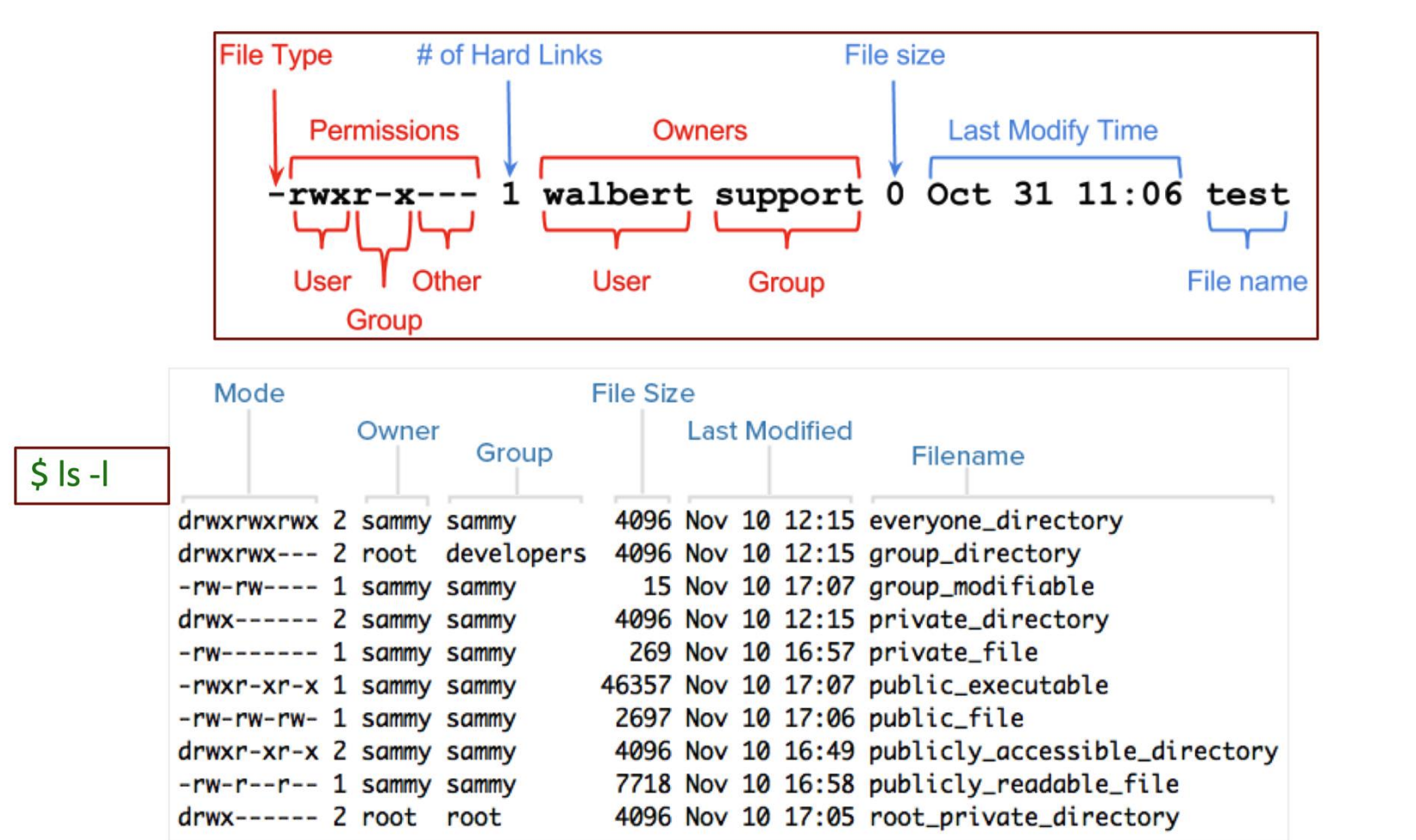
Access Control
- User는 Group안에 속함
- Dir이면 d, file이면 -
Protection: abstract concept
- Running code can access some set of data
- Code == program, module, component instance
- Data == objects, state, files, VM segments
- We call that set a Domain or Protection domain
- Determined by context and indentity
- Protection domains may overlap
protection domain은 이 코드는 이런 데이터들에만 접근할 수 있다는 보안 울타리를 논리적으로 정의한 개념이다.
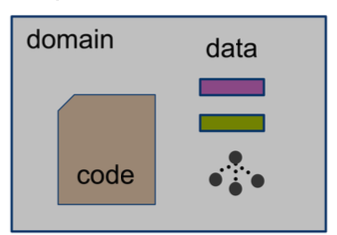
Examples
- Unix(VM/VAS)
- The machine checks address references against the VAS maps
- The kernel checks references to files, ports, etc
- program이 Virtual Address Space에 접근하려고 할 때마다 h/w가 체크
- Web script
- Browser checks access to data, cookies, server, URLs
- Java procedure
- JVM+ libs check all accesses
- 모든 access를 확인하기 때문에 안전하지만 그만큼 느리다.
- Java Security Architecture
- JVM+ libs check all accesses
Java는 Type-safe 언어로 c언어처럼 메모리 주소를 직접 조작할 수 없기 때문에 메모리가 안전하다. java는 프로그래밍 언어 자체가 안전 장치 역할을 한다.
Protection
1. Isolation
- partition, operate separately from each other is the physical sense
2. Share all or nothing
3. Share via access limitation
- different entities enjoy different levels of access to an object(by owner)
- OS acts as a guard
4. Limit use of an object
- 접근 뿐만 아니라 어떻게 사용할 수 있는가도 제한, 같은 객체라도 사용자에 따라 용도가 달라진다.
Sandboxes
an environments where the program can execute but can't affect the rest of the machine
- Strong isolation is conceptually pretty easy
- e.g. VMware, run the program on a separate machine
- More elegant mechanism
- Emulator for malware analysis
- Android app has a unique UID and plays in its own sandbox
- 각 앱마다 unique한 사용자 ID를 할당하여 서로의 데이터 폴더에 접근 불가
sandbox는 안전하게 위험한 것을 다루는 기술의 핵심이다. 코드가 실행되지만, 시스템의 다른 부분에는 영향을 줄 수 없는 격리된 환경을 뜻한다. 완벽한 격리와 실용적 기능 사이의 절묘한 균형을 찾는 것이 가장 어려운 과제이다.
OS Protection Principles
- All objects need protection, but in particular those that are shareable, e.g.,
- Memory
- I/O devices(disks, printers, tape drives, etc.)
- data
- The basis of OS protection is separation
- Kernel space vs. User space, Normal users vs. Root user
- Disk partitioning, Separation of home dir
- Sperate the address space for each process
공유 가능한 객체들은 여러 프로그램이 동시에 접근할 수 있기 때문에 충돌이나 악용이 일어날 수 있다.
OS protection의 기본은 separation이다. kernel과 user 공간을 분리하고, Normal user와 Root user 구분 , Disk partitioning 등을 예로 들 수 있다.
1. CPU & Memory Protection
2. Fundamental problem
- How to keep users/processes separate?
3. Separation
- Physical separation
- Separate devices
- Temporal separation
- One at a time
- Logical separation
- Address space separation, Sandboxing
- Cryptographic separation
- Make information unintelligible to outsider
- Page level encryption, Column-level encryption in DB
- Or any combination of the above
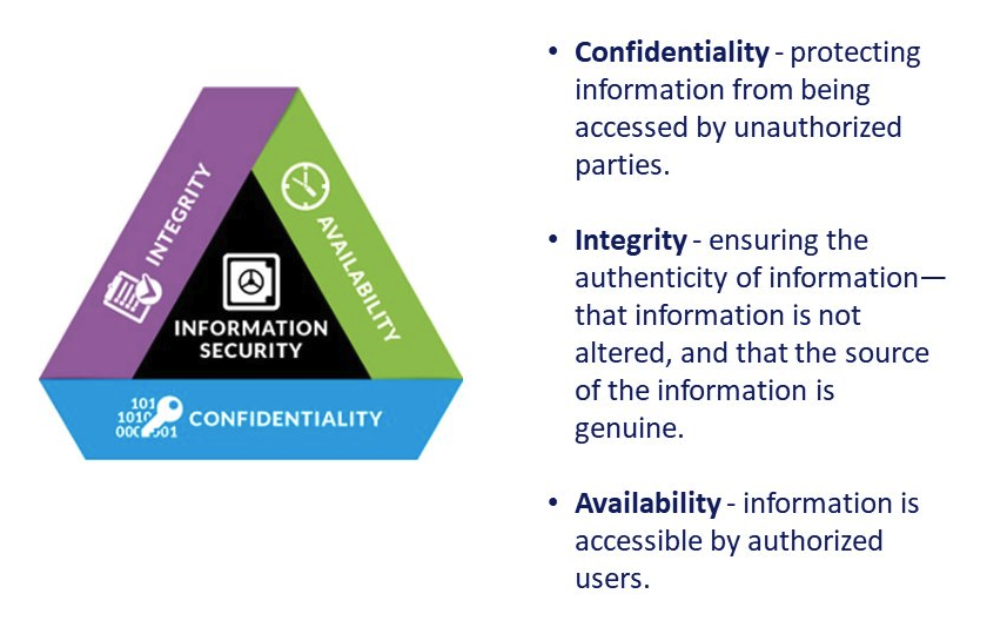
Security
Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability
1. Confidentiality 기밀성
- 의도된 사람만 정보를 볼 수 있다.
2. Integrity 무결성
- 정보가 변조되지 않았음을 보장
- Hash function(one-way): 1 bit라도 틀어지면 hash 값이 달라진다.
3. Availability 가용성
- 정보, 시스템, 서비스가 필요할 때 접근 가능한 상태를 유지한다.
- DoS 공격은 시스템을 압도적인 요청으로 마비시켜 정당한 사용자들이 서비스를 이용할 수 없게 만드는 공격이다.
System Security는 의도적인 공격으로부터 시스템을 보호하는 것을 다루며, 이러한 공격은 내부 또는 외부에서 올 수 있고 정보를 훔치거나, 정보를 손상시키거나, 또는 다른 방식으로 의도적으로 큰 파괴와 혼란을 야기하려고 시도하는 개인들로부터 온다.
- 내부, 외부의 고의적 공격으로부터 보호하기 위해서는 protection만으로는 불충분하며, 외부 환경까지 포괄적으로 고려해야 한다.
- Security must considers the external environment in which the system operates
- Refers to providing a protection system to system resources
- Unauthorized access
- Malicious access to system memory
- Malware
- Protecting information/systems/assets against various threats
What is Security?
Security = State of being secure, free from threat/risk/vulnerability
- Confidentiality
- Encryption
- Integrity
- Cryptographic hash functions
- Availability
- Filtering, Mirroring, Backup
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Auditing
Authentication(인증)은 누구인지 증명하는 과정이고, Authorization(인가)는 무엇에 접근할 수 있는지 허용하는 과정이다.
Security in OS
The OS must protect itself from security breaches, such as
- Runaway processes(Denial of Service)
- Memory-aceess violations
- Stack overflow violations
- buffer overflow(허용 범위를 벗어남)의 대표적인 유형으로 악성 코드 실행이나 시스템 제어권 탈취에 악용된다.
- Launching programs with excessive privileges
- 필요 이상의 높은 권한으로 프로그램을 실행하는 것으로 권한 상승 공격의 일종이다.
stack 영역은 함수호출을 할 때 사용하는 파라미터들을 저장하고, 끝나면 공간을 회수한다.
DoS(Denial of Service, 서비스 거부)
- 컴퓨터 시스템이나 네트워크를 공격해서 정상적인 사용자가 서비스를 사용할 수 없게 만드는 행위
- 일반적으로 공격자는 서버에 과도한 요청을 보내서 시스템 자원을 소진시킨다.
The Security Problem
모든 상황에서 시스템 자원이 의도된 대로만 사용되고 접근될 때 시스템이 안전하다고 할 수 있지만, 이는 달성 불가능하다. 현대 시스템은 너무 복잡해서 모든 경우의 수를 예측할 수 없고, 완벽한 보안 시스템은 존재하지 않는다.
- Intuders(crackers) attempt to breach security
- Threat is potential security violation
- Attack is attempt to breach security
- accidental or malicious
위협은 잠재적인 보안 위반, 공격은 실제로 보안 위반을 시도하는 행위이다.
Intruders(Attackers, Crackers)
- Masquerader 신분 위장자
- unauthorized individual이 시스템에 침투하여 정당한 사용자의 계정을 악용
- Misfeasor 불법 행위자
- a legitimate user who accesses resources to which they are not privileged, or who abuse such priviliege
- Clandestine user 은밀한 사용자
- 시스템의 통제권을 장악하여 감사 통제를 회피하거나 감사 기록 수집을 억제하는 개인
- 직접적인 해를 끼치는 것은 아닌데, 주고 받는 데이터를 염탐하는 것이다.
Methods of obtaining passwords
- trying default pw
- exhausively testing short pw
- trying words from a dictionary, or from a list of common pw
- collecting personal information about users
- using a Trojan horse
- 정당한 프로그램으로 위장하여 사용자를 속여 설치하게 만든 후, 악의적인 행동을 수행하는 악성 코드
- eavesdropping on communication lines
Security Threats
1. Interruption
- 정상적인 통신을 완전히 차단하거나 시스템 마비
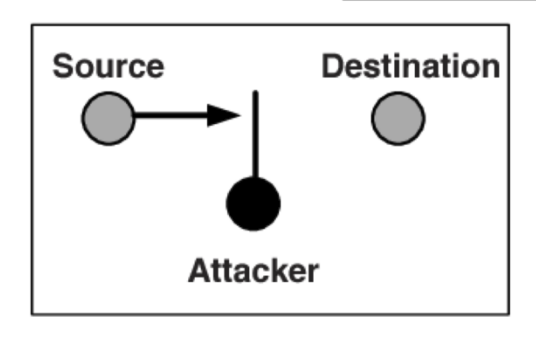
2. Interception
- 송신자와 수신자 사이의 통신을 몰래 감청하거나 도청
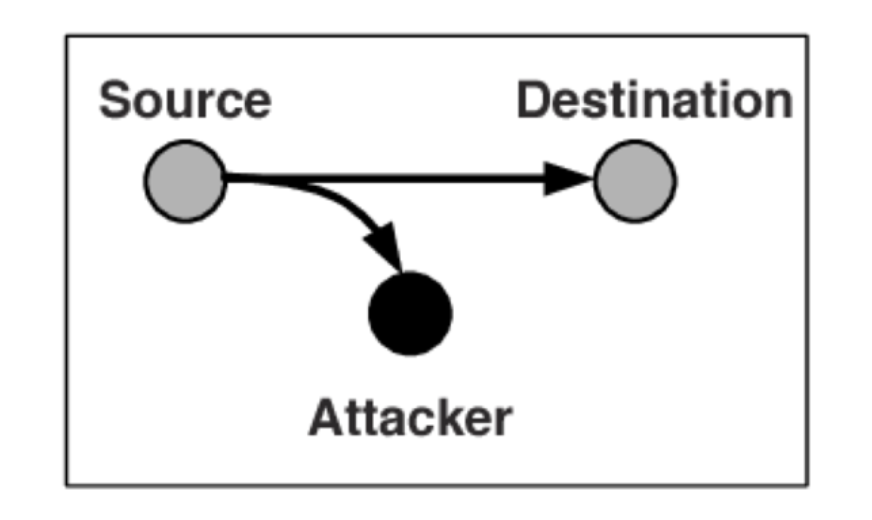
3. Modification 변조
- 전송 중인 데이터를 중간에서 변경하거나 조작
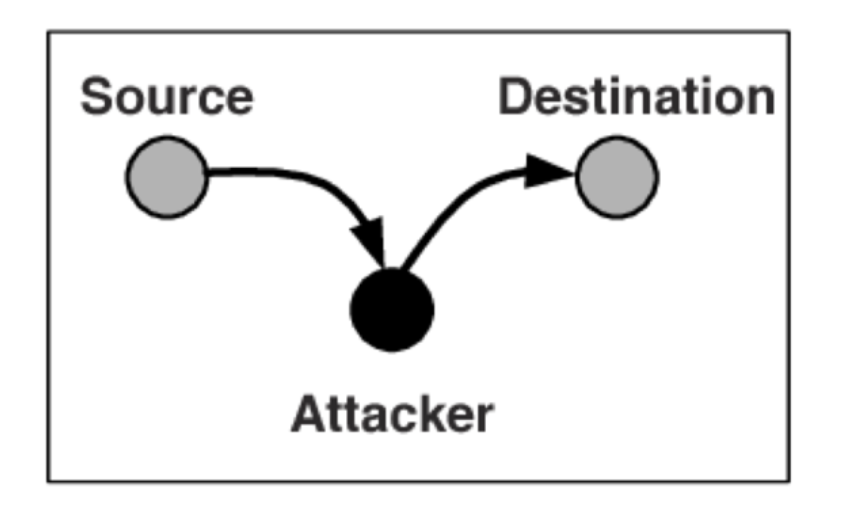
4. Fabrication 위조
- 존재하지 않던 가짜 데이터나 허위 정보를 새로 생성해서 주입
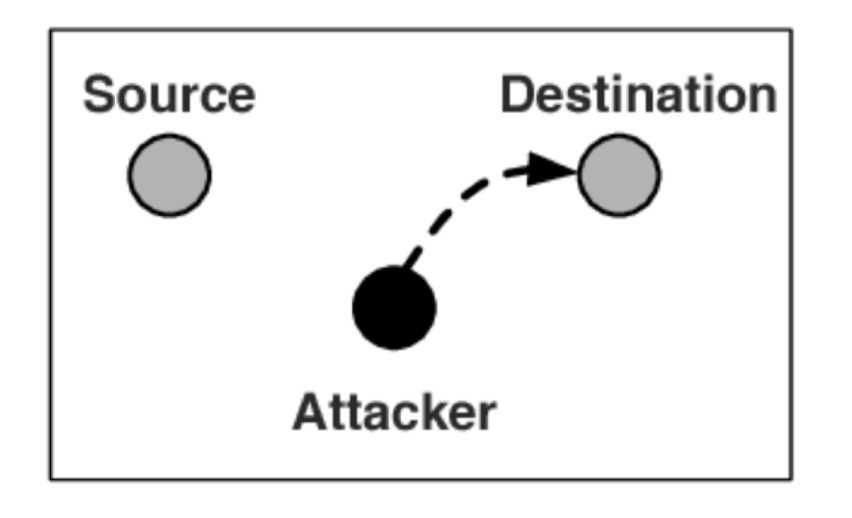
Security Violation Categories
- Breach of confidentiality
- Unauthorized reading of data
- Breach of integrity
- Unauthorized modification of data
- Breach of availability
- Unauthorized destruction of data
- Theft of sevice
- Unauthorized use of resources
- Denial of service (DoS)
- Prevention of ligitimate use
Security Violation Methods
- Masquerading
- 인증 과정을 우회하거나 침해하여 권한이 없는 사용자가 승인된 사용자로 가정하는 행위를 의미
- Replay attack
- 인증 과정이나 메시지 전달에서 정상 매세지를 위조하는 공격
- Main-in-the-middle attack (중간자 공격)
- 공격자가 데이터 흐름의 중간에 끼어 송신자와 수신자 사이에서 데이터를 가로채거나 변경
- Session hijacking
- already-established session을 탈취하여 추가 인증 절차를 우회
- Privilege escalation
- 사용자가 원래 가져야 하는 권한보다 더 높은 권한을 얻는 공격
Session
TCP Connection: 컴퓨터 네트워크에서 두 통신 주체 사이에 이루어지는 가상의 논리적 연결
네트워크 세션은 TCP 연결과 같이, 핸드셰이크로 연결을 만들고 데이터를 주고 받다가 연결을 종료하는 기간
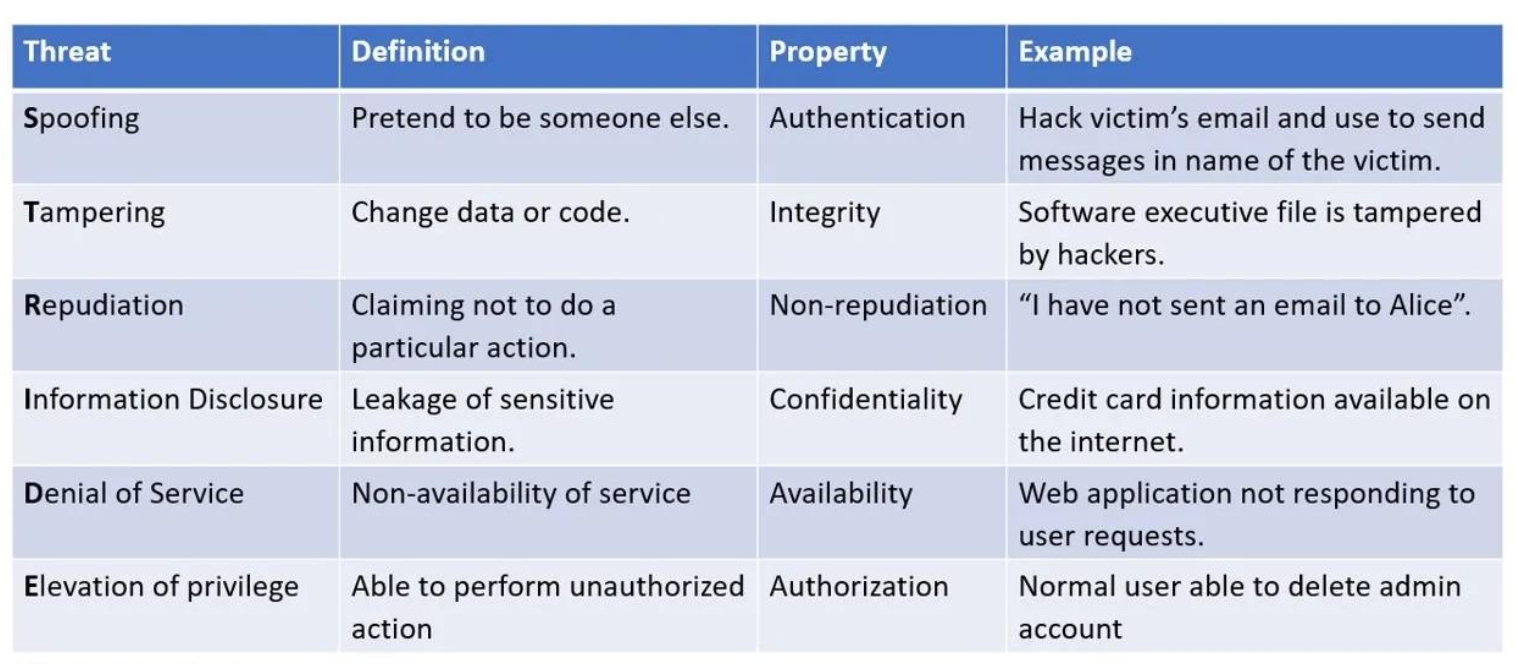
Microsoft STRIDE
보안 위협을 6가지 카테고리로 분류해 체계적으로 분석하는 데 사용하는 방법론이다.
Elements of security
- Isolation/Protection
- 보안 경계를 통해 내부 자원을 외부로부터 보호한다.
- Integrity
- Authentication
- Identity and attributes
- Authorization == access control
- 접근 정책에 따라 사용자의 자격을 검사해서 접근 허용/차단을 결정한다.
The First Axiom of Security
- Security is at least as much a social problem as it is a technical problem
- human are the weak link
기술적인 보안 뿐만 아니라 사회적 요소를 항상 고려해야 한다.
- Keys left in the lock
- Phishing
- Executable attachments
- Trojan software
- Post-it password
- Bribes, torture, etc
- 뇌물이나 협박으로 비밀을 빼내는 행위를 뜻한다.
Summary: Protection vs Security
Protection
- Control the access of users and processes to resources
- Ensure that no process access or interfere with resources to which they are not entitled, either by design or by accident.
Security
protection보다 넓은 범위로 고의적인 공격으로부터 시스템을 방어한다.
사용자가 공격자나 비인가 접근이나 권한 상승, 데이터 탈취 등을 시도할 때 이에 대응하는 기능을 포함한다.
- Malware threat
- Unauthorized access
Protection은 실수나 구조적인 문제로부터 자원을 보호하는 기본적인 접근 제어이고, Security는 악의적인 공격이나 해킹 시도까지 포함해 더 넓은 범위의 보호 개념이다.
