
01. 나열된 수에서 최솟값과 최댓값 구하기
여러 개의 수가 배열에 있을 때 그 중 가장 큰 값과 가장 작은 값을 찾는다.
배열의 몇 번째에 있는지 순서를 찾는다.
반복문을 한번만 사용하여 문제를 해결한다.
수의 예 : [10, 55, 23, 2, 79, 101, 16, 82, 30, 45]
// O(n)
public class MinMaxProblem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {10, 55, 23, 2, 79, 101, 16, 82, 30, 45};
int min = numbers[0];
int max = numbers[0];
int minPos = 0;
int maxPos = 0;
for(int i=1; i<numbers.length; i++ ) {
if(min > numbers[i]) {
min = numbers[i];
minPos = i+1;
}
if(max < numbers[i]) {
max = numbers[i];
maxPos = i+1;
}
}
System.out.println("가장 큰 값은 " + max + "이고, 위치는 " + maxPos + "번째 입니다.");
System.out.println("가장 작은 값은 " + min + "이고, 위치는 " + minPos + "번째 입니다.");
}
}02. 정렬된 수에서 하나의 수의 위치 찾기
여러 개의 수가 정렬된 순서로 있을 때 특정한 수를 찾는 방법
단순 반복문을 이용하면 수의 개수에 따라 비교 횟수가 증가하는 O(n)의 수행이 이루어짐
수가 정렬된 상태에서는 이진 탐색(binary search)을 활용하면 매번 비교되는 요소의 수가 절반으로 감소될 수 있으므로 O(logN)의 수행으로 원하는 수를 찾을 수 있음
수의 예 : [12, 25, 31, 48, 54, 66, 70, 83, 95, 108]
83 위치 찾기
package chapter;
public class BinarySearchProblem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {12,25,31,48,54,66,70,83,95,108};
int target = 83;
int left = 0;
int right = numbers.length - 1;
int mid = (left+right) / 2;
int temp = numbers[mid];
boolean find = false;
while(left <= right) {
if(target == temp) {
// 수를 찾은 경우
find = true;
break;
} else if( target > temp) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
mid = (left+right)/2;
temp = numbers[mid];
}
if(find == true) {
mid++;
System.out.println("찾고자하는 숫자는" + mid + "번 째에 있습니다.");
}
else System.out.println("찾는 수가 없습니다. ");
}
}03. 정렬 알고리즘
평균 수행 시간이 O(n^2)인 알고리즘
버블 정렬(Bubble Sort), 삽입 정렬(Insertion Sort), 선택 정렬(Selection Sort)
각 요소가 다른 요소와 평균 한번 이상씩 비교를 하여 정렬 됨
InsertSort 구현해보기
Insertion Sort의 기본 개념은 이미 정렬된 상태의 요소에 새로운 요소를 추가할 때 정렬하여 추가하는 개념이다.(손안의 카드)
두 번째 요소 부터 이전 요소들과 비교하면서 insert 될 위치를 찾아가며 정렬하는 알고리즘
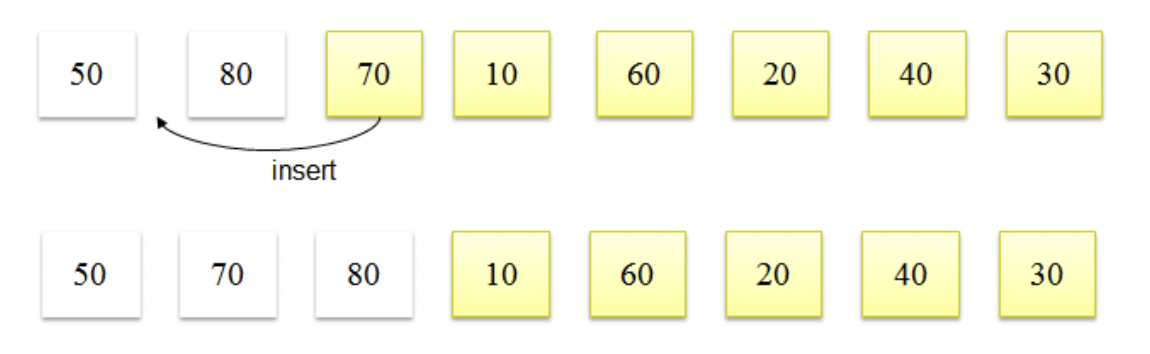
package chapter;
public class InsertionSort {
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr, int count) {
int temp = 0;
int i = 0; int j = 0;
for(i = 1; i < count; i++)
{
temp = arr[i];
j = i;
while((j > 0) && arr[j-1] > temp) {
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
j = j-1;
}
arr[j] = temp;
System.out.println("반복 -" + i);
printSort(arr, count);
}
}
public static void printSort(int value[], int count)
{
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.print(value[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {80, 50, 70, 10, 60, 20, 40, 30 };
insertionSort(arr, 8);
}
}평균 수행 시간이 O(logN)인 알고리즘
- 퀵 정렬(Quick Sort), 병합 정렬(Merge Sort), 힙 정렬(Heap Sort)
- 한번 수행될 때마다 정렬되어야 하는 수의 범위가 1/2로 줄어드는 경우
- 퀵 정렬 이외의 다른 알고리즘은
추가적인 메모리가 필요함
Heap Sort 구현해보기
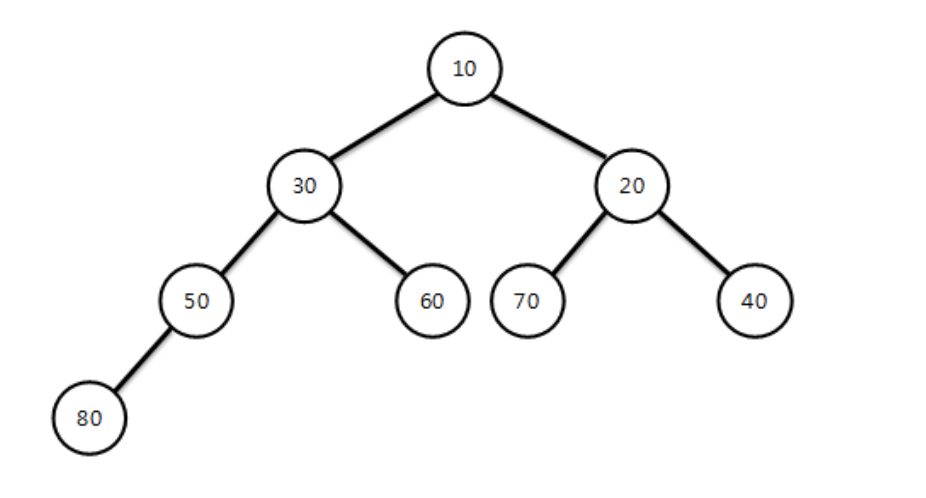
가장 큰놈이 위에 있으면 max heap , 작은 놈이 위에 있으면 min heap
배열로 표현하였을 때 새로운 값을 넣어 reordering 할 시 자기의 parent는 본인 위치 / 2 에 위치한다
package chapter;
public class HeapSort {
private int SIZE;
private int heapArr[];
public HeapSort()
{
SIZE = 0;
heapArr = new int [50];
}
public void insertHeap(int input) {
int i = ++SIZE;
//while((i != 1) && (input < heapArr[i/2])) { // max heap
while((i != 1) && (input < heapArr[i/2])) { // min heap
heapArr[i] = heapArr[i/2];
i = i / 2;
}
heapArr[i] = input;
}
public int getHeapSize() {
return SIZE;
}
public int deleteHeap() {
// 힙은 보통 루트에 있는 값을 제거
int parent,child;
int data, temp;
// 루트에 있는 데이터 대입
data = heapArr[1];
// 맨마지막 element를 temp
temp = heapArr[SIZE];
// 맨 위로 올렸다고 가정
SIZE -= 1;
parent = 1; child = 2;
while(child <= SIZE) {
//if((child < HEAP_SIZE) && (heapArr[child] < heapArr[child+1])) // max heap
//더 작은 자식 값을 찾는 과정.
if((child < SIZE) && (heapArr[child] > heapArr[child + 1])) { // min heap
child ++;
}
//if(temp >= heapArr[child]) break; // max heap
if(temp <= heapArr[child]) break; // min heap
heapArr[parent] = heapArr[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
heapArr[parent] = temp;
return data;
}
public void printHeap() {
//System.out.printf("\n Max Heap: ");
System.out.printf("\n Min Heap");
for(int i=1; i<=SIZE;i++)
System.out.printf("[%d] ", heapArr[i]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapSort h = new HeapSort();
h.insertHeap(80);
h.insertHeap(50);
h.insertHeap(70);
h.insertHeap(10);
h.insertHeap(60);
h.insertHeap(20);
h.printHeap();
int n,data;
n = h.getHeapSize();
for(int i = 1; i<=n; i++) {
data = h.deleteHeap();
System.out.printf("\n 출력 : [%d]", data);
}
}
}04. DFS(Depth - First Search)와 BFS(Breadth - First Search)
그래프 탐색
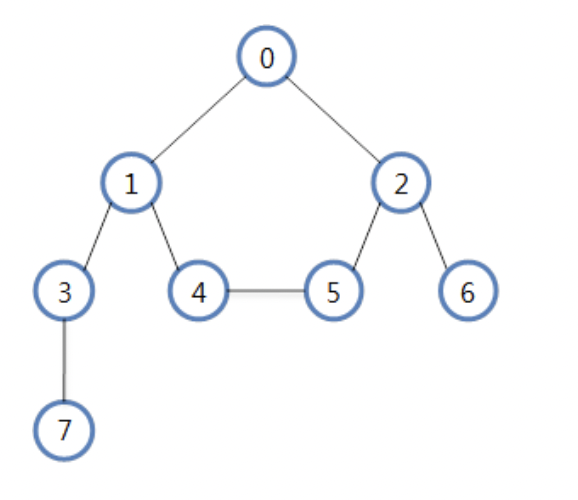
DFS : Stack 이용 , BFS : Queue 이용
그래프를 matrix로 표현하기
package chapter;
public class UndirectedGraph {
private int count; // 노드 개수
private int [] [] vertexMatrix;
public UndirectedGraph(int count) {
this.count = count;
vertexMatrix = new int[count][count]; // count 만큼의 2차원 배열 생성
}
public void addEdges(int from, int to, int weight) {
vertexMatrix[from][to] = weight;
vertexMatrix[to][from] = weight;
}
public int[][] getMatrix(){
return vertexMatrix;
}
}
DFS
인접한 노드를 우선 탐색 하는 방식
스택을 활용하여 구현할 수 있음
DFS 탐색 순서 :
0 - 1 - 3 - 7 - 4 - 5 - 2 - 6 or 0 - 2 - 6 - 5 - 4 - 1 - 3 - 7
package chapter;
import java.util.Stack;
public class DfsSearch {
int count;
boolean[] visited;
Stack<Integer> stack;
int[][] matrix;
public DfsSearch(int count) {
this.count = count;
visited = new boolean[count];
stack = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void dfsTraversal() {
stack.push(0);
visited[0] = true;
while(stack.isEmpty() == false) {
int node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node + " ");
for(int j = 0; j < count; j++) {
if(matrix[node][j] != 0 && !visited[j]) {
stack.push(j);
visited[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 8;
UndirectedGraph graph = new UndirectedGraph(count);
DfsSearch dfsSearch = new DfsSearch(count);
graph.addEdges(0, 1, 1);
graph.addEdges(0, 2, 1);
graph.addEdges(1, 3, 1);
graph.addEdges(1, 4, 1);
graph.addEdges(2, 5, 1);
graph.addEdges(2, 6, 1);
graph.addEdges(4, 5, 1);
graph.addEdges(3, 7, 1);
dfsSearch.matrix = graph.getMatrix();
dfsSearch.dfsTraversal();
}
}BFS
한 노들에 모든 인접한 노드를 탐색하는 방식
큐를 활용하여 구현할 수 있음
BFS 탐색 순서 : 0 - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7
Queue에 인접한 애들 넣으면서 순차적으로 출력 되게끔
public class BfsSearch {
int count;
boolean[] visited;
ArrayList<Integer> queue;
int[][] matrix;
public BfsSearch(int count){
this.count = count;
visited = new boolean[count];
queue = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
public void bfsTraversal() {
queue.add(0);
visited[0] = true;
while(queue.size() != 0) {
int node = queue.remove(0);
System.out.print(node + " ");
for(int j = 0; j<count; j++) {
if(matrix[node][j] != 0 && !visited[j] ) {
queue.add(j);
visited[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 8;
UndirectedGraph graph = new UndirectedGraph(count);
BfsSearch bfsSearch = new BfsSearch(count);
graph.addEdges(0, 1, 1);
graph.addEdges(0, 2, 1);
graph.addEdges(1, 3, 1);
graph.addEdges(1, 4, 1);
graph.addEdges(2, 5, 1);
graph.addEdges(2, 6, 1);
graph.addEdges(4, 5, 1);
graph.addEdges(3, 7, 1);
bfsSearch.matrix = graph.getMatrix();
bfsSearch.bfsTraversal();
}
}
05. 최단거리 구하기 문제
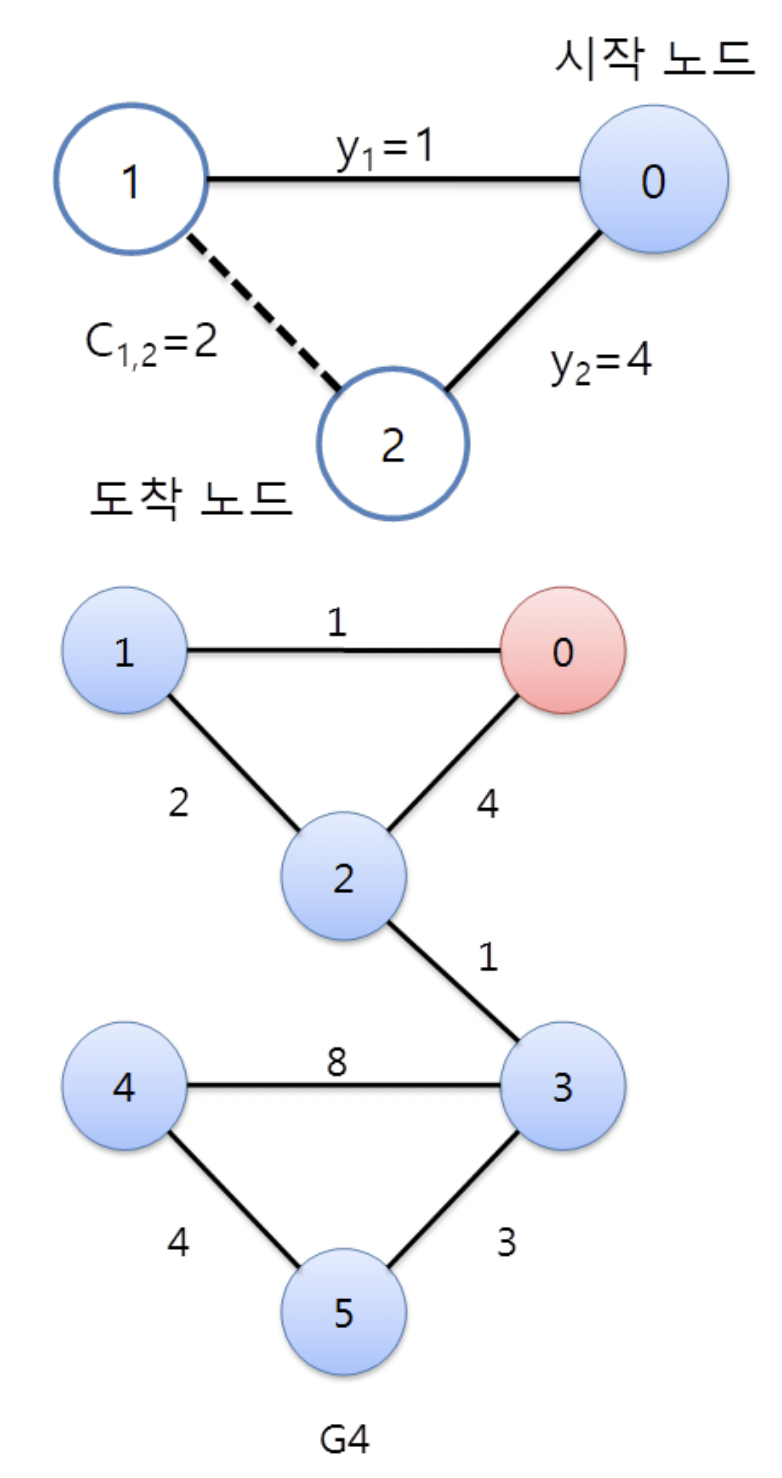
package chapter;
class MyGraph{
private int count; //노드 수
private int[][] vertexMatrix; // matrix로 그래프 표시
private int[] distance; // 특정 노드에 대한 각 노드의 최단 거리
private boolean[] visited; // alread visited???
private static int UNLIMIT = 999999999; // 초기값
public MyGraph(int count){
this.count = count;
vertexMatrix = new int[count][count];
distance = new int[count];
visited = new boolean[count];
}
public void addEdges(int from, int to, int weight){
vertexMatrix[from][to] = weight;
vertexMatrix[to][from] = weight;
}
public void calcShotestPath(int from){
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
distance[i] = UNLIMIT;
}
visited[from] = true;
distance[from] = 0;
//연결노드 distance갱신
for(int i= 0; i<count; i++){
if(visited[from] && vertexMatrix[from][i] !=0){
distance[i] = vertexMatrix[from][i];
}
}
for(int k =0; k<count-1; k++){
int min=UNLIMIT;
int minIndex= -1;
// 거쳐 가지 않았고, 가장 가까운 애를 distance로 선택
for(int i = 0; i< count ;i++){
if(!visited[i] && distance[i]!=UNLIMIT){
if(distance[i] < min ){
min = distance[i];
minIndex = i;
}
}
}
//거쳐 가는 노드
visited[minIndex] = true;
// 다 익스트라 알고리즘
for(int i=0; i<count; i++){
if(!visited[i] && vertexMatrix[minIndex][i]!=0){
// 원래 가는 길이 더 크면 작은 것으로 업데이트 해주자
if(distance[i]>distance[minIndex]+vertexMatrix[minIndex][i]){
distance[i] = distance[minIndex]+vertexMatrix[minIndex][i];
}
}
}
}
}
public void showDistance(int from) {
for(int i = 0; i<count; i++) {
System.out.println(from + " 노드로부터 " + i + " 노드의 최단 거리는 : " + distance[i]);
}
}
}
public class ShortestPath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyGraph graph = new MyGraph(6);
graph.addEdges(0, 1, 1);
graph.addEdges(0, 2, 4);
graph.addEdges(1, 2, 2);
graph.addEdges(2, 3, 1);
graph.addEdges(3, 4, 8);
graph.addEdges(3, 5, 3);
graph.addEdges(4, 5, 4);
// 0노드 부터의 최단 거리
graph.calcShotestPath(0);
graph.showDistance(0);
}
}