백트래킹
모든 경우의 수를 탐색하며 최적해를 구하는 과정에서 유망하지 않은 쪽은 더 이상 구하지 않는 방법
-> 돌 다리도 두드려 보고 가는 느낌!
Promising : 해가 될 가능성이 있는 경우 유망하다고 함
Pruning(가지치기) : 해가 될 가능성이 없는 경우 해당 노드를 제외 하는 것
BackTracking : 유망하지 않은 쪽으로 가지 않고 되돌아 오는 것
기본적으로 재귀함수 및 DFS를 자유자재로 구현할 줄 알아야 함!
N-Queen 문제
N x N 체스판에서 퀸 N개를 서로 공격할 수 없도록 배치하는 경우의 수
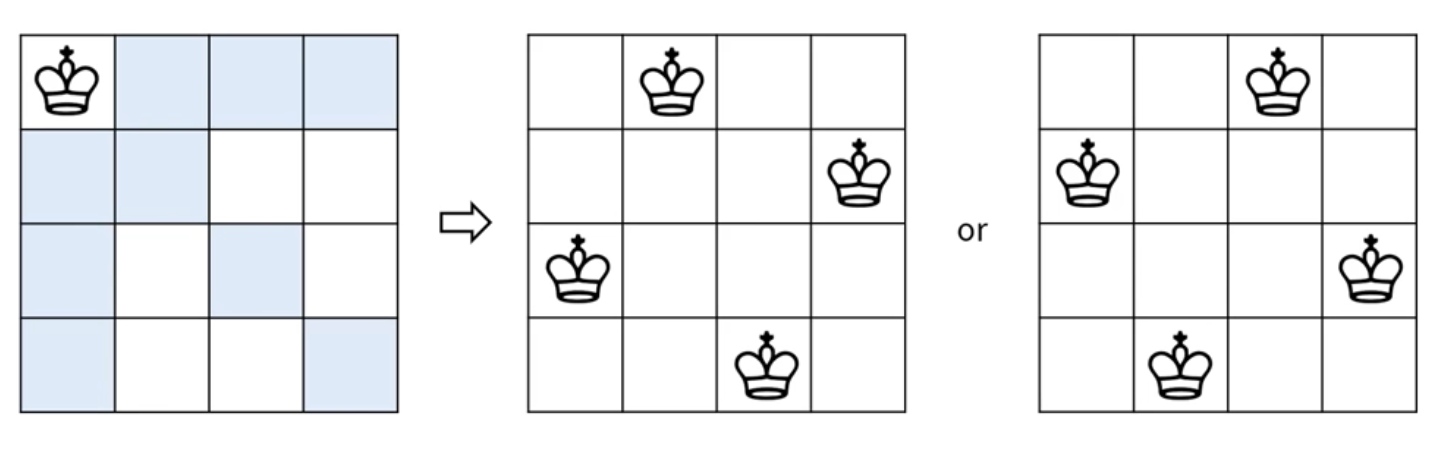
위 경우 퀸을 4 x 4에서 4개 배치
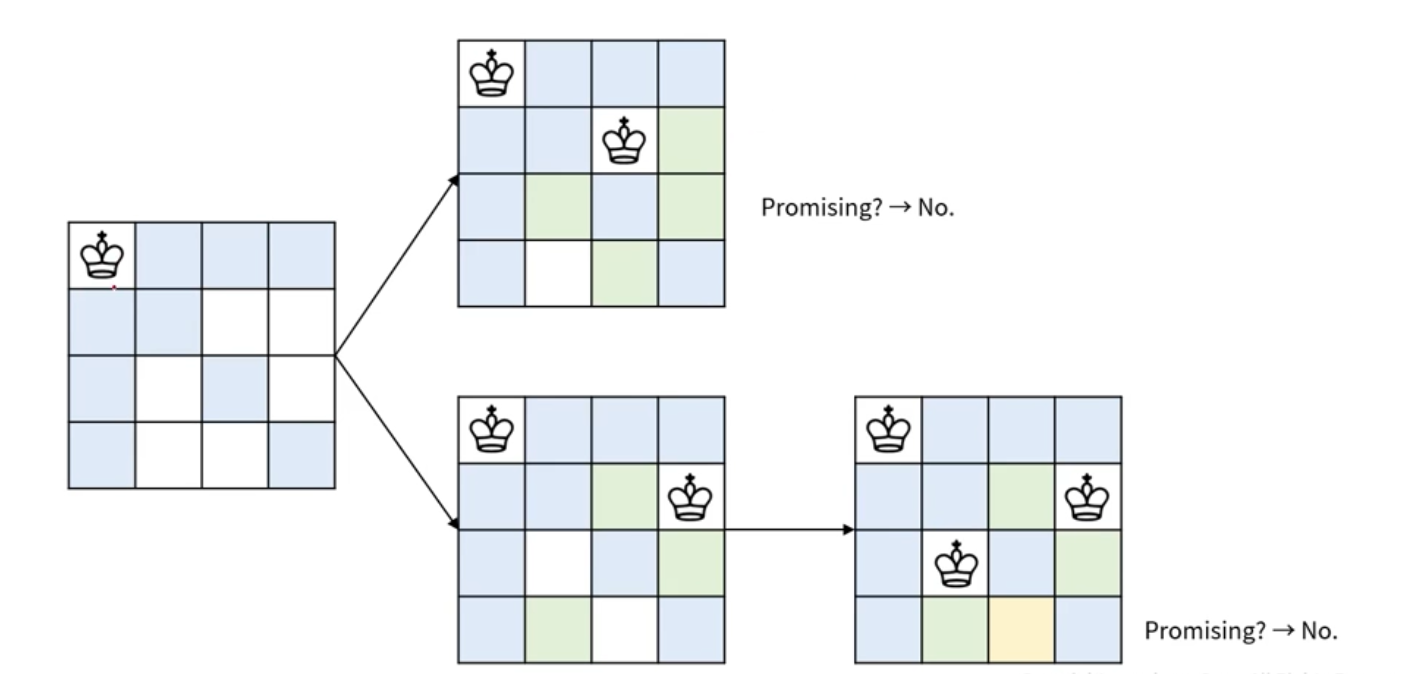
처음에 퀸을 둔 후 다음 퀸을 배치(이동 방향에 걸리지 않는 곳에)할 때
이후 두번째 퀸을 배치함으로써 두면 안되는 곳을 초록색으로(가지치기) .....
-> 위와 같은 로직 반복
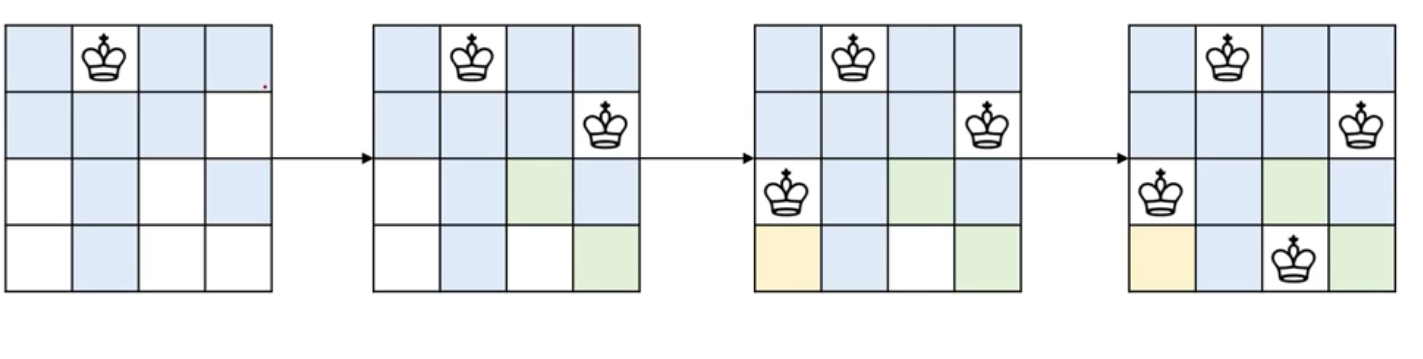
구현 예시
// 알고리즘 - 백트래킹
public class Main {
static int n = 4;
static int[] board = new int[n]; // 이 행에 몇번째의 퀸을 두었는지 기록할 배열
static int cnt;
public static int nQueen(int row) {
if(row == n ){
// 모든 퀸을 놓은 경우
cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(board[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return cnt;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
board[row] = i;
// promising
if(isPromising(row)){
nQueen(row + 1);
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static boolean isPromising(int row){
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
if(board[row] == board[i] || row - i == Math.abs(board[row] - board[i])){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
Arrays.fill(board,-1); // 혹시나 해서 내가 추가함
System.out.println("경우의 수: " + nQueen(0)); // 2
}
}
연습 문제
문제 1
// Practice1
// 정수형 n과 m이 주어졌을 때,
// 1 부터 n 까지의 정수 중에서 중복 없이 m 개를 고른 수열을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// n: 3
// m: 2
// 출력: [1, 2], [1, 3], [2, 1], [2, 3], [3, 1], [3, 2]
// Permutation 문제
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Practice1 {
public static boolean[] visited;
public static int[] out;
public static void solution(int n, int m) {
visited = new boolean[n];
out = new int[m];
permutation(n,m,0);
}
public static void permutation(int n, int m, int depth){
if(depth == m){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(out));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(!visited[i]){
visited[i] = true; // 가지치기
out[depth] = i + 1;
permutation(n,m,depth+1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
solution(3, 2);
System.out.println();
solution(4, 3);
}
}문제 2
// Practice2
// 숫자 7193 은 7193 도 소수이고,
// 719, 71, 7 도 각각 소수이다.
// n 이 주어졌을 때, n 자리 수 중에 위와 같은 소수를 찾는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// 입력 n: 3
// 출력: 233, 239, 293, 311, 313, 317, 373, 379, 593, 599, 719, 733, 739, 797
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Practice2 {
public static ArrayList<Integer> result;
public static ArrayList<Integer> solution(int n) {
result = new ArrayList<>();
// 첫째자리에 올수 있는 숫자 2___, 3____, 5___, 7____
// 이후 뒤의 숫자에는 0,2,4,6,8,5 중 하나라도 오면 백트래킹 시킴
int[] primeNum = {2,3,5,7};
for (int i = 0; i < primeNum.length; i++) {
// backTracking()
backTracking(primeNum[i], 1, n);
}
return result;
}
public static void backTracking(int prime, int len, int n){
if(len >= n){
result.add(prime);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if(i % 2 != 0 || i != 5){
int primeCandidate = prime * 10 + i;
if(isPrimeNumber(primeCandidate)){
backTracking(primeCandidate, len + 1, n);
}
}
}
}
public static boolean isPrimeNumber(int num){
for(int i = 2; i <= num/2; i++){
if(num % i == 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(solution(3));
System.out.println();
System.out.println(solution(4));
}
}문제 3
// Practice3
// sols 배열에 5지 선다 문제의 정답들이 적혀있다.
// 3번 연속 해서 같은 정답이 있는 경우가 없다는 것을 알아낸 후,
// 문제를 찍어서 푼다고 할 때, 5점 이상을 받을 경우의 수를 출력하세요.
// 문제는 총 10문제이며 각 문제당 1점이다.
// 입출력 예시
// sols: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
// 결과: 261622
public class Practice3 {
final static int numOfProblems = 10;
static int cnt;
public static void solution(int[] sols) {
if (sols == null || sols.length != numOfProblems) {
return;
}
cnt = 0;
int[] submit = new int[numOfProblems]; // 내가 푼 값들
// backTracking
backTracking(sols,submit, 0, 0);
System.out.println(cnt);
}
public static void backTracking(int[] sols, int[] submit, int correctCnt, int idx){
if(numOfProblems - idx + correctCnt < 5){
return;
}
if(idx == numOfProblems){
// 10번 까지 푼 경우
if(correctCnt >= 5){
cnt += 1;
}
}else{
int twoInRow = 0; // 3연속 정답인 케이스 없음
if(idx >= 2){
if(submit[idx-1] == submit[idx - 2]){
twoInRow = submit[idx - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
if(i == twoInRow){
continue;
}
submit[idx] = i;
if(sols[idx] == i){
backTracking(sols, submit, correctCnt + 1, idx + 1);
}else{
backTracking(sols, submit, correctCnt, idx+1);
}
submit[idx] = 0;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] sols = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
solution(sols);
sols = new int[] {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5};
solution(sols);
}
}문제 4
// Practice4
// 2차원 배열 board 가 주어졌다.
// 해당 배열 데이터에는 'o', '#', '.' 의 정보가 기입되어 있다.
// 'o': 동전을 의미
// '#': 벽을 의미
// '.': 빈칸을 의미
// 동전은 항상 두개가 주어진다.
// 두 동전이 함께 이동하다가 하나가 보드에서 떨어지는 경우의 최소 이동 횟수를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
// 단, 이동 규칙은 다음과 같다.
// 동전은 좌, 우, 위, 아래로 이동 가능하며 같은 방향으로 함께 이동
// 빈칸이나 동전이 있는 칸으로는 이동 가능
// 벽일 때는 이동 불가
// 이동 횟수가 10번을 넘으면 중지하고 -1 반환
// 입출력 예시
// board: {{'.', '#'}, {'.', '#'}, {'.', '#'}, {'o', '#'}, {'o', '#'}, {'#', '#'}}
// 결과: 4
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Practice4 {
final static int[][] dirs = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
static int cnt;
static class Coin {
int x;
int y;
public Coin(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static void solution(char[][] board) {
if (board == null || board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0) {
return;
}
int n = board.length;
int m = board[0].length;
cnt = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
ArrayList<Coin> coins = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// 동전 2개 찾아서 coins 에 추가
if (board[i][j] == 'o') {
coins.add(new Coin(j, i));
}
}
}
Coin coin1 = coins.get(0);
Coin coin2 = coins.get(1);
backTracking(board, m, n, coin1.x, coin1.y, coin2.x, coin2.y, 0);
System.out.println(cnt == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : cnt);
}
public static void backTracking(char[][] board, int m, int n, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int moveCnt) {
// 10번 이상 이동하는 경우 return
if (moveCnt >= 10) {
return;
}
// 두 동전은 같은 방향으로 함께 이동
for (int[] dir: dirs) {
// 1번 동전 다음 위치
int x1Next = x1 + dir[0];
int y1Next = y1 + dir[1];
// 2번 동전 다음 위치
int x2Next = x2 + dir[0];
int y2Next = y2 + dir[1];
// 밖으로 떨어진 동전 개수 세는 용
int dropCnt = 0;
// 떨어졌는지 확인
if (x1Next < 0 || x1Next >= m || y1Next < 0 || y1Next >= n) {
dropCnt += 1;
}
if (x2Next < 0 || x2Next >= m || y2Next < 0 || y2Next >= n) {
dropCnt += 1;
}
// 두 동전 중 하나만 떨어뜨려야 하므로 이 경로는 continue 처리
if (dropCnt == 2) {
continue;
}
// 하나 떨어졌으면 cnt 반환
if (dropCnt == 1) {
cnt = Math.min(cnt, moveCnt + 1);
return;
}
// 벽이면 제자리로 두고 다음 진행
if (board[y1Next][x1Next] == '#') {
x1Next = x1;
y1Next = y1;
}
// 벽이면 제자리로 두고 다음 진행
if (board[y2Next][x2Next] == '#') {
x2Next = x2;
y2Next = y2;
}
backTracking(board, m, n, x1Next, y1Next, x2Next, y2Next, moveCnt + 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
char[][] board = {{'.', '#'}, {'.', '#'}, {'.', '#'}, {'o', '#'}, {'o', '#'}, {'#', '#'}};
solution(board);
board = new char[][] {{'#', '#', '#'}, {'.', 'o', '.'}, {'#', '.', '#'}, {'.', 'o', '.'}, {'#', '#', '#'}};
solution(board);
board = new char[][] {{'#', '#', '#'}, {'.', 'o', '.'}, {'#', '#', '#'}, {'.', 'o', '.'}, {'#', '#', '#'}};
solution(board);
}
}