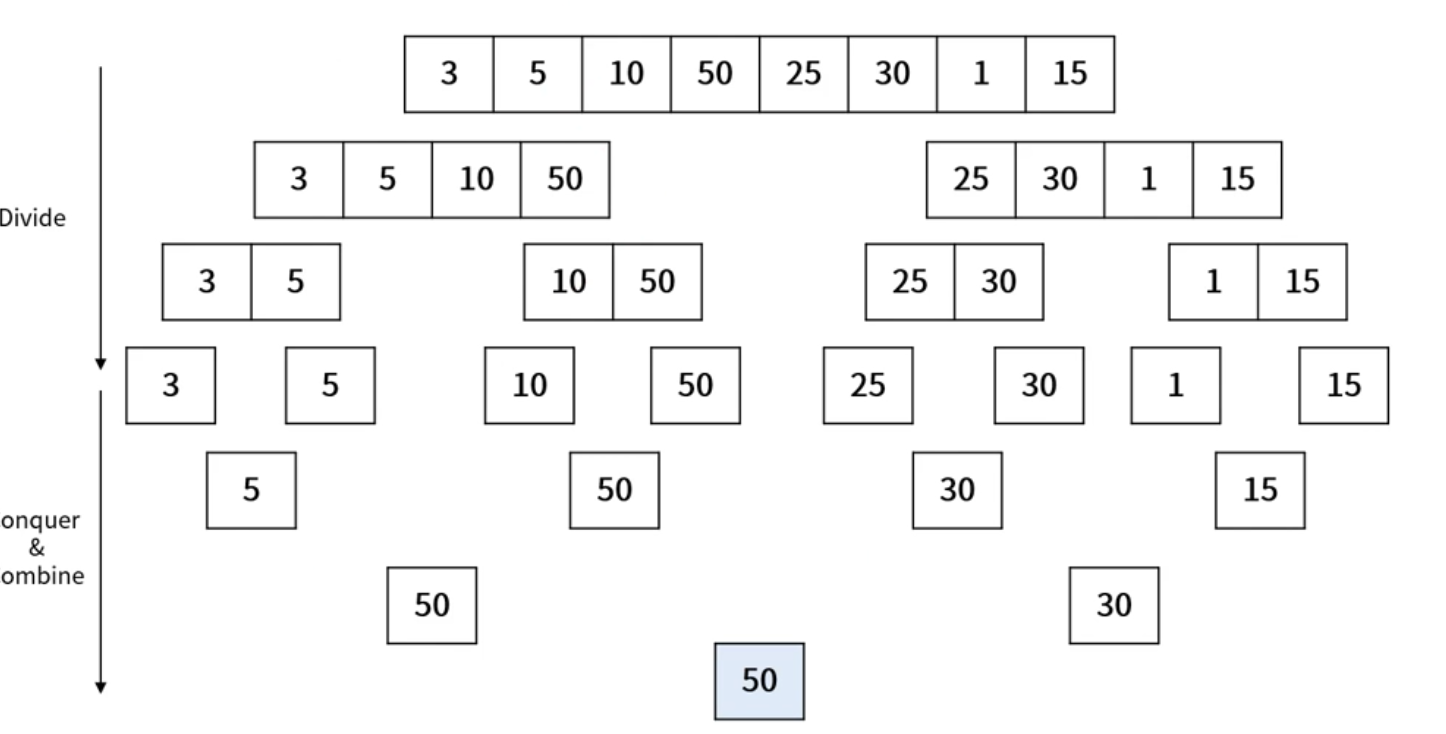
분할 정복(Divide and Conquer)
큰 문제를 작은 부분 문제로 나누어 해결하는 방법
- 합병 정렬, 퀵 정렬, 이진 검색, ...
분할 정복 과정
1. 문제를 하나 이상의 작은 부분들로 분할
2. 부분들을 각각 정복
3. 부분들의 해답을 통합하여 원래 문제의 답을 구함
장점/단점
문제를 나누어 처리하며 어려운 문제 해결 가능
병렬 처리에 이점이 있음
메모리를 많이 사용(재귀 호출 구조)
예시
최대 값 찾기
코드 예시
public static int getMax(int[] arr, int left, int right){
int m = (left+right) / 2;
if(left == right) return arr[left];
left = getMax(arr,left,m);
right = getMax(arr, m+1, right);
return(left> right)? left:right; // conquer
}public class Main {
public static int getMax(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
int m = (left+right) / 2;
if(left == right){
return arr[left];
}
left = getMax(arr, left, m);
right = getMax(arr,m+1,right);
return (left>right)? left:right;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {6, 2, 9, 8, 1, 4, 17, 5};
System.out.println(getMax(arr, 0, arr.length - 1));
}
}연습문제
문제1
// Practice1
// 정수형 배열 nums 가 주어졌다.
// 연속된 부분 배열의 합 중 가장 큰 값을 출력하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// nums: -5, 0, -3, 4, -1, 3, 1, -5, 8
// 출력: 10
// nums: 5, 4, 0, 7, 8
// 출력: 24
// 투 포인터 양끝에 놓는 것도 좋음(이동 조건 잘 세워야, 이 경우엔 분기 조건이 좀 많음)
public class Practice1 {
public static int solution(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return divideSubArray(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
public static int divideSubArray(int[] nums, int left, int right){
if(left == right){
return nums[left];
}
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
int maxLeft = divideSubArray(nums,left,mid);
int maxRight = divideSubArray(nums,mid+1,right);
int maxArr = getMaxSubArray(nums,left,mid,right);
return Math.max(maxLeft, Math.max(maxRight, maxArr));
}
public static int getMaxSubArray(int[] nums, int left, int mid, int right){
int sumLeft = 0;
int maxLeft = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = mid; i >= left; i--) {
sumLeft += nums[i];
maxLeft = Math.max(maxLeft, sumLeft);
}
int sumRight = 0;
int maxRight = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = mid+1; i <= right; i++) {
sumRight += nums[i];
maxRight = Math.max(maxRight, sumRight);
}
return maxLeft + maxRight;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] nums = {-5, 0, -3, 4, -1, 3, 1, -5, 8};
System.out.println(solution(nums));
nums = new int[]{5, 4, 0, 7, 8};
System.out.println(solution(nums));
}
}문제 2
// Practice2
// 2차원 정수형 배열 lists 가 주어졌다.
// lists[i] 에는 각 링크드 리스트의 원소 정보가 들어 있고,
// 원소들은 오름차순 정렬된 상태이다.
// 모든 링크드 리스트를 하나의 정렬된 링크드 리스트로 합병하세요.
// 입출력 예시
// lists: {{2, 3, 9}, {1, 5, 7}, {3, 6, 7, 11}}
// 출력: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 3 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 7 -> 9 -> 11
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static Node solution(Node[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return divideList(lists, 0, lists.length-1);
}
public static Node divideList(Node[] lists, int left, int right){
if(left == right){
return lists[left];
}
int mid = left + (right-left) / 2;
Node l1 = divideList(lists,left,mid);
Node l2 = divideList(lists,mid+1,right);
return mergeList(l1, l2);
}
public static Node mergeList(Node l1, Node l2){
if(l1 == null){
return l2;
}
if(l2 == null){
return l1;
}
Node merge = new Node(0);
Node cur = merge;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val < l2.val){
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(l1 != null){
cur.next = l1;
}
if(l2 != null){
cur.next = l2;
}
return merge.next;
}
// 문제에 주어진 2차원 배열을 링크드 리스트로 구성
public static void setUpLinkedList(Node[] node, int[][] lists) {
for (int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
node[i] = new Node(lists[i][0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
Node cur = node[i];
for (int j = 1; j < lists[i].length; j++) {
cur.next = new Node(lists[i][j]);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
// 결과 출력 부분
public static void printList(Node node) {
Node cur = node;
while (cur.next != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " -> ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println(cur.val);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[][] lists = {{2, 3, 9}, {1, 5, 7}, {3, 6, 7, 11}};
Node[] node = new Node[lists.length];
setUpLinkedList(node, lists);
Node combinedNode = solution(node);
printList(combinedNode);
}
}
