let mySet = new Set()
console.log(toString.call(mySet)) // [object Set]set은 set이란 타입이다. 중복없이 유일한 값을 저장할 때, 이미 존재하는지 확인할 때 사용한다.
mySet.add("dongha")
mySet.add("kim")
mySet.add("nana")
mySet.add("dongha")
console.log(mySet) // Set { 'dongha', 'kim', 'nana' }dongha라는 값이 중복되어 set에 담기지 않는다.
console.log(mySet.has("kim")) // truehas로 요소가 있는지 찾을 수 있다. 삭제는 delete 메서드로
WeakSet
weakset은 참조를 가지고 있는 개체만 저장 가능하다. 즉, 가비지 컬렉팅 대상이 되면 weakSet에서도 그 객체가 사라진다. 참조를 계속 모니터링 하는 것
let arr = [1,2,3,4]
let arr2 = [5,6,7,8]
let obj = {arr, arr2}
let ws = new WeakSet()
ws.add(arr)
ws.add(arr2)
ws.add(obj)
console.log(ws)
arr, arr2 arr와 arr2가 키인 객체까지 모두 ws에 넣었다.
arr = nullarr에 null을 주면

arr가 아직 생존한 듯 싶으나
console.log(ws.has(arr)) // false이미 삭제된 상태다.
map 과 WeakMap
Array를 개선한 자료구조가 set이라면 Object를 개선한 것이 map이다.
map은 key, value 구조다.
let wm = new WeakMap()
let func = function(){}
wm.set(func, 0)
console.log(wm)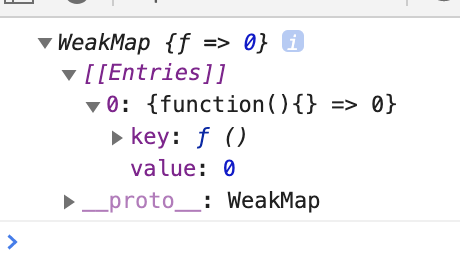
key를 func로 값은 0으로 객체가 만들어졌다.
let cnt = 0;
for(let i =0; i< 10; i++){
cnt = wm.get(func)
cnt++
wm.set(func, cnt)
}
console.log(wm.get(func)) // 10for문을 돌려서 func이 몇 번 실행됐는지 확인해보자. 일단 cnt는 func의 value값으로 지정한다. map에서 get으로 value를 가져올 수 있다. wm.set으로 새로운 cnt를 준다.
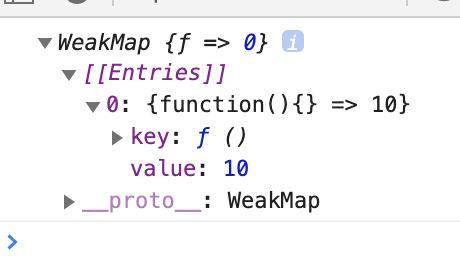
value가 10으로 변했다. 즉, func이 10회 실행됐다.
활용
function Area(height, width){
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
}
Area.prototype.getArea = function(){
return this.height + this.width
}
let myArea = new Area(10,20);
console.log(myArea.getArea()) // 200
console.log(myArea.height) // 10weakMap을 통해 인스턴스 변수를 보호할 수 있다.
const wm = new WeakMap();
function Area(height, width){
wm.set(this, {height, width});
}
Area.prototype.getArea = function(){
const {height, width} = wm.get(this)
return height + width;
}
let myArea = new Area(10,20);
console.log(myArea.getArea()) // 200
console.log(myArea.height) // undefined
일단 WeakMap을 생성하고 wm.set으로 height와 width를 숨긴다. 여기서 this는 Area로 생성하게될 인스턴스다.
그리고 wm.get으로 height랑 width만 뽑아주고 리턴한다. 그러면 외부에서 height로 접근하지 못한다!
로또번호 추첨
const SETTING = {
name: "LUCKY LOTTO",
cnt : 6,
maxNumber:45
}
function getRandomNumber(){
let {cnt, maxNumber} = SETTING
let numSet = new Set()
while(numSet.size < cnt){
let tmp = Math.floor(Math.random() * maxNumber + 1)
if(!numSet.has(tmp)){
numSet.add(tmp)
}
}
return [...Array.from(numSet)]
}
console.log(getRandomNumber())