Instruction Types
- Operate instructions: ALU가 계산하는.. (ex. ADD, SUB)
- Data movement instructions: MEM에서 R/W하는.. (ex. LOAD, STORE)
- Control flow instructions: 실행 순서 바꾸는.. (ex. BEQ, BNEQ)
Assembly Language
- The human-readable representation of 'instructions' or 'machine language'
- Has a direct mapping btwn assembly code and instructions (기계어)
von Newmann Model Properties
- Stored Program
Instructions stored in a linear memory array together
Memory is unified between instructions and data
-> Control signal에 따라서 해당 값이 instr인지 data인지 판단
- Sequential instruction processing
PC는 branch 등의 경우를 제외하고는 순서대로 instruction을 실행
Preview(?): ISA specifies..
- Memory organization (메모리가 어떻게 구성되어 있는지)
Address space, Addressability (Word- or Byte- addressable) - The register set (레지스터의 개수)
- The instruction set (instruction의 구성)
Opcodes, Data types, Addressing modes, Length... 등등
Preview(?): Microarchitecture
마이크로아키텍처: 일종의 설계도 느낌!
- Architecture: visible to the software
Address space, addressability, opcode 등.... - Microarchitecture: not visible to the software
cache, instruction cycle, pipelining 등...
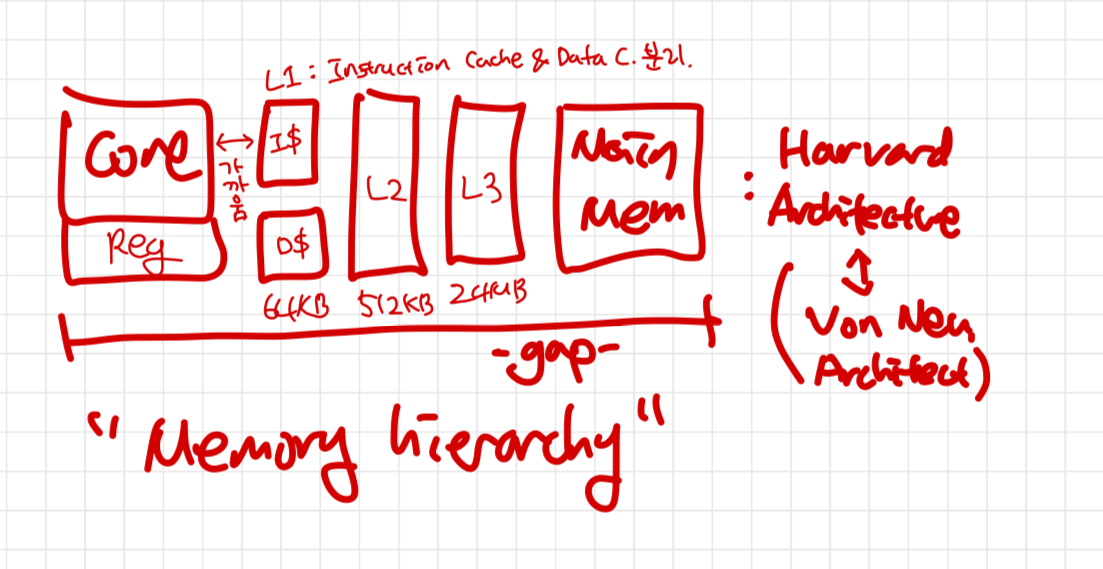
Memory hierarchy
Basic Metrics
Latency or delay (저저익선)
특정 일을 얼마나 빨리 하는 지!
단위: 초 (ms(s), us(s), ns(s), ps(s))
A measured latency is for some particular task!
A CPU doesn't have a latency (CPU는 실행의 '주체'니까)
An application has a latency on a particular CPU
Throughput (고고익선)
같은 시간에 일을 얼마나 많이 하는 지!
단위: 속도(?) (bytes/s, instrs/s, instrs/cycle)
Cost
🤑 ㅋㅋ
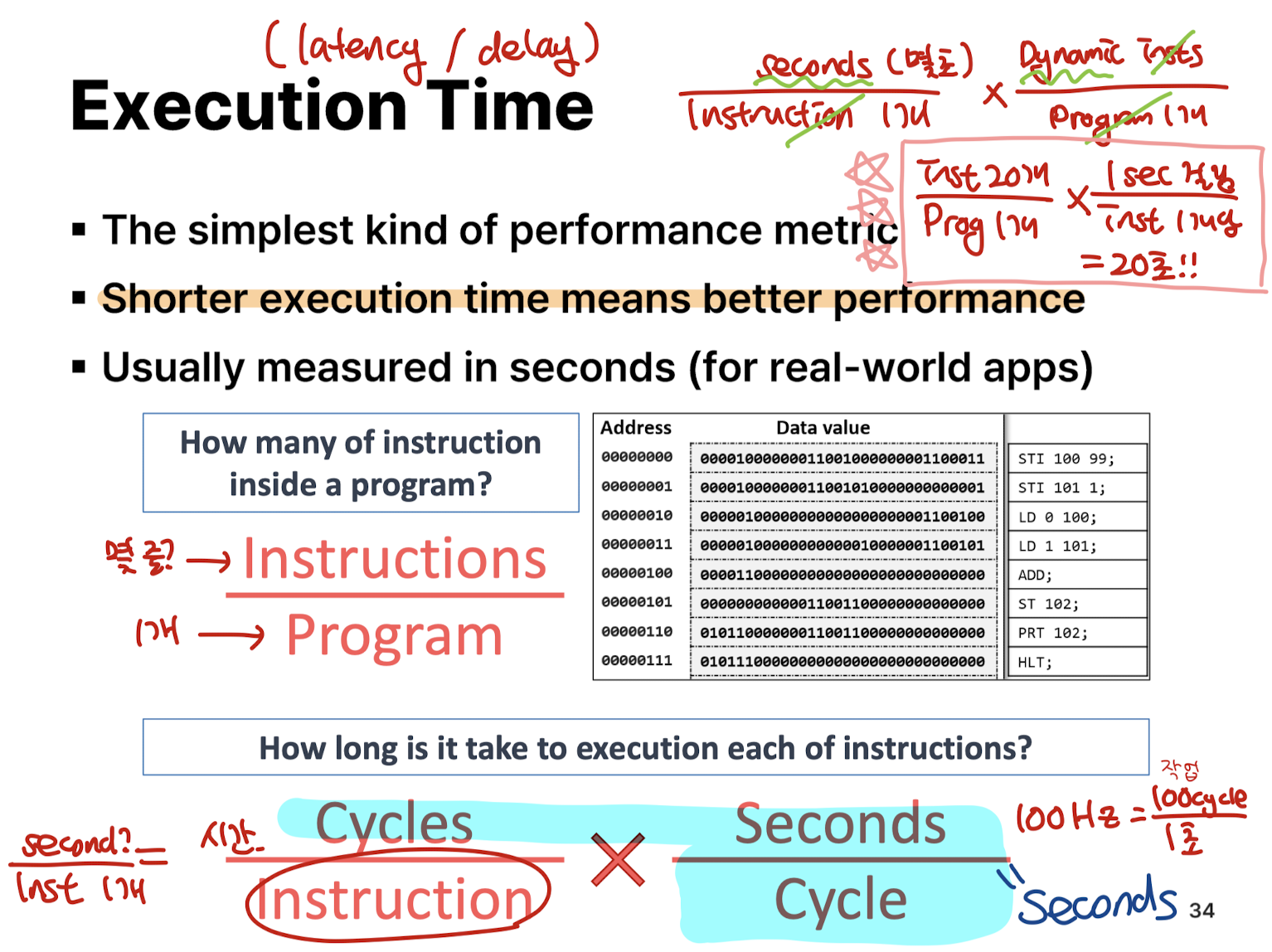
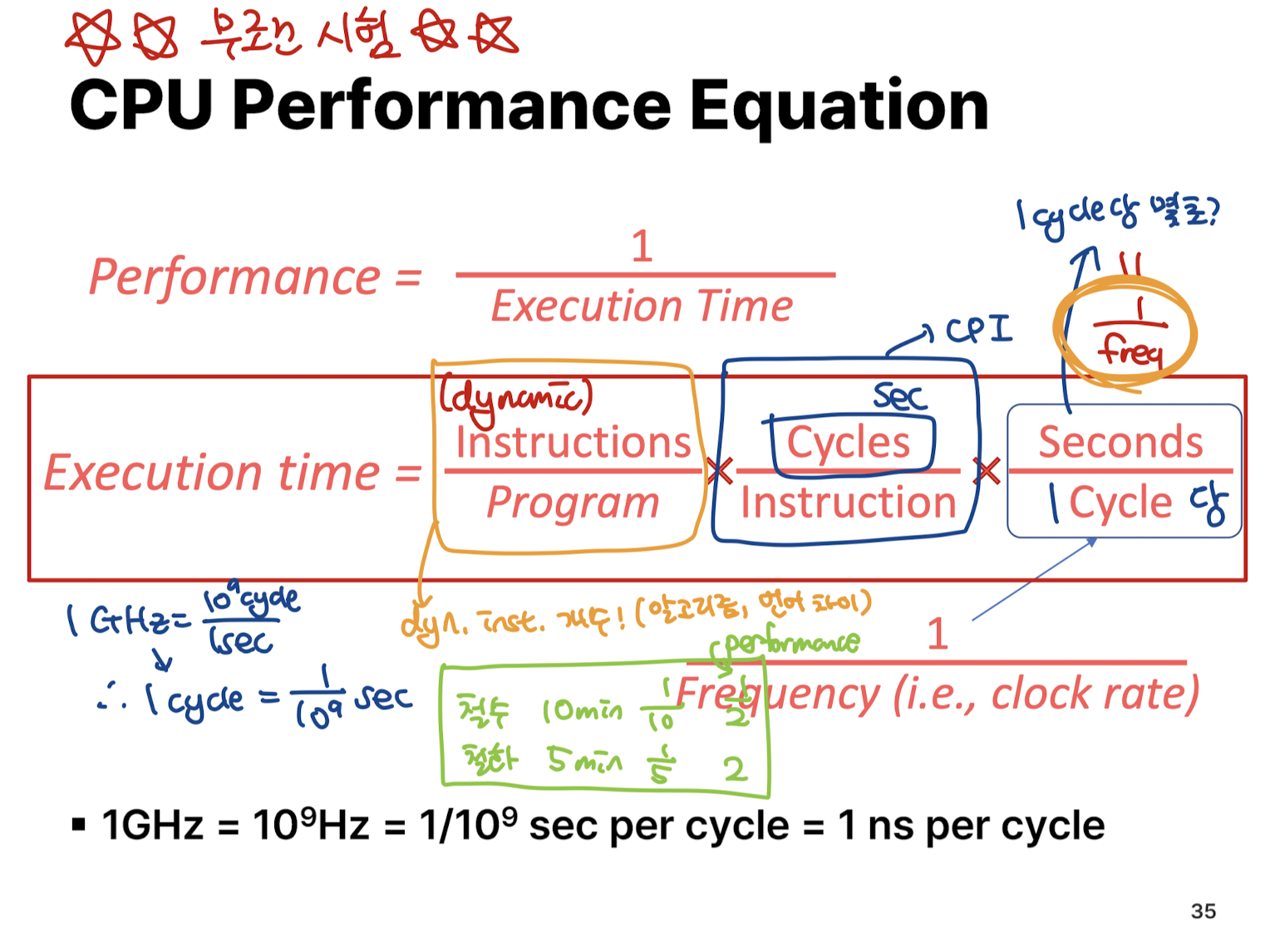
Execution Time (매우 중요!!!)
요건 피피티 필기자료로 대체~! (수식 표현하기 어려워잉..)
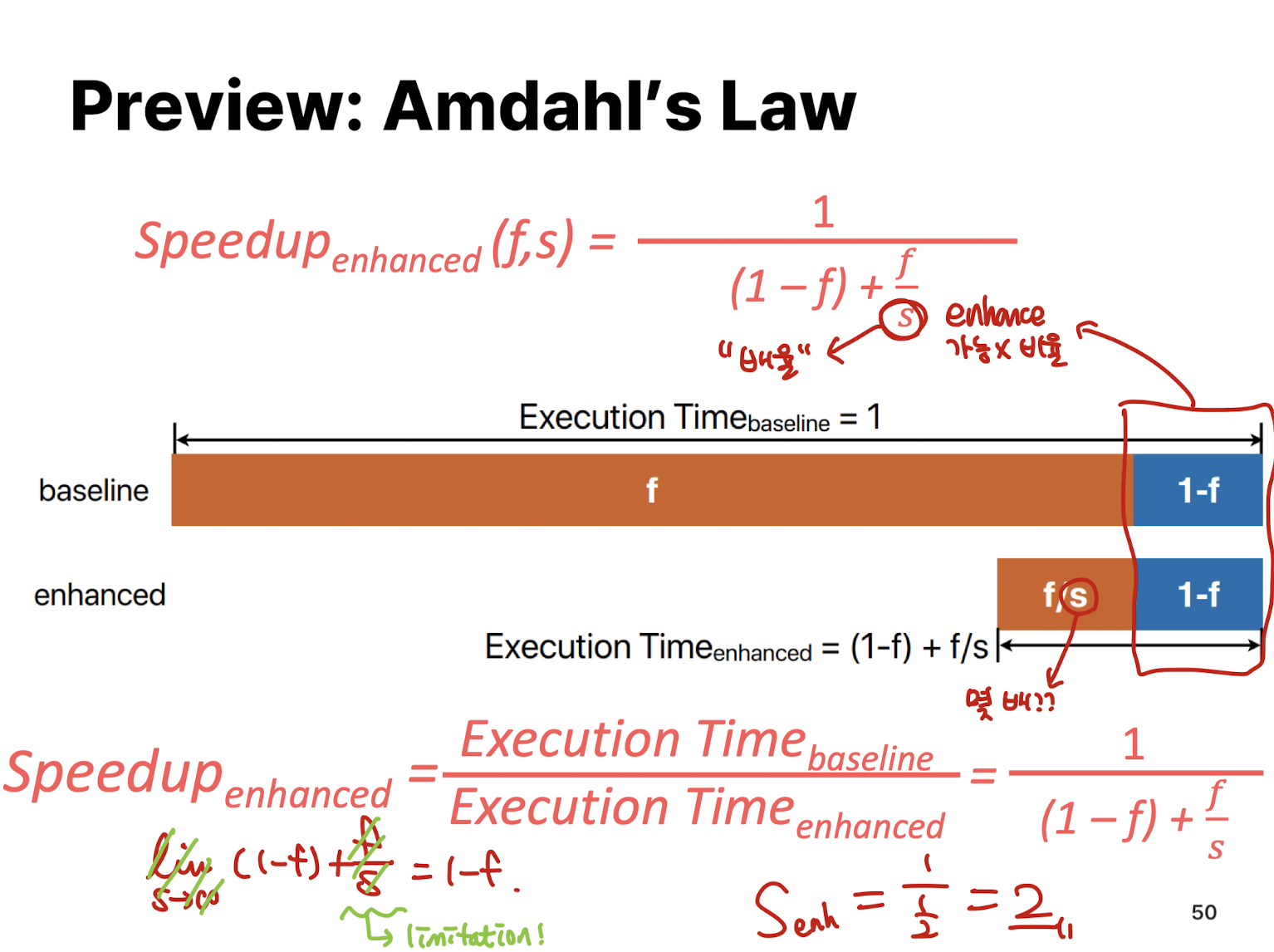
Amdahl's Law
얘도 수식이라서.. 스샷으로 대체
Comparing Performance
- A is X times faster than B if
- Latency(A) = Latency(B) / X- Throughput(A) = Throughput(B) * X
- B is X% faster than B if
- Latency(A) = Latency(B) / (1+X/100)- Throughput(A) = Throughput(B) * (1+X/100)
‼️ 예를 들어서 5배는 500%가 아닌 400%임! 계산할 때 조심하기
Mean (Avg) Performance Numbers
- Arithmetic (산술평균): 우리가 알고있는 그 엔빵 ^^
치명적인 단점은.. 각 배율값(?)을 더해서 나누면 결과 처참해짐 -> 기하 사용 - Harmonic (조화평균): 대역폭이나 성능 구할 때 사용
"For units that are inversely proportional to time (kbps, mbps..)"
뒤집어서 더하고 다시 뒤집기! - Geometric (기하평균): 배율 구할 때 굿 (speedup ratios)
n개의 값을 각각 곱하고 n제곱근 값 구하기
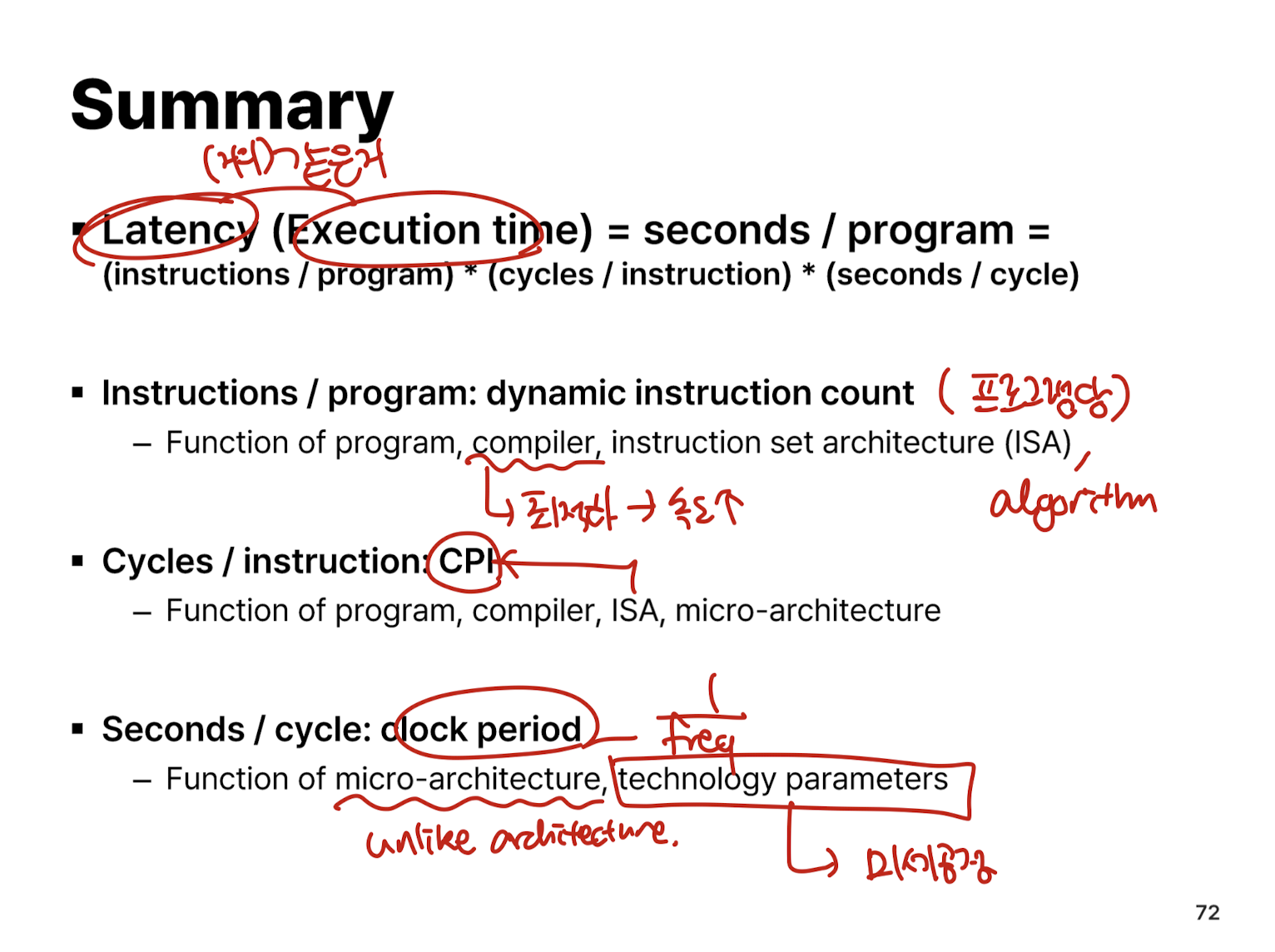
Summary