풀이
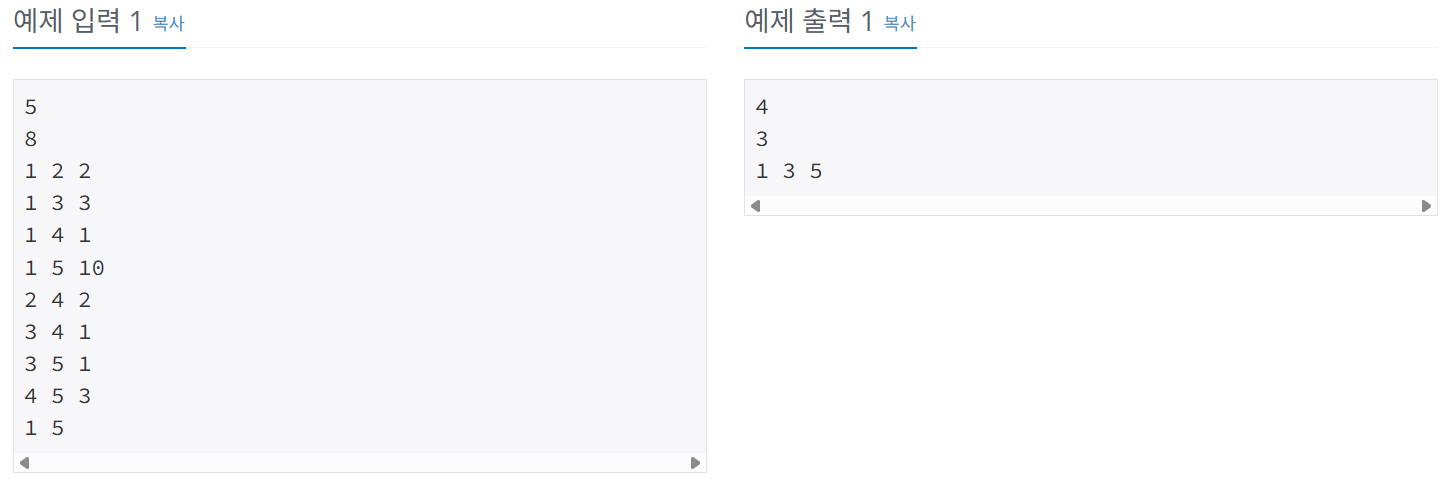
1. 도시 n개가 있고, 각 도시를 잇는 버스(비용)이 있음
2. A에서 B까지 가는데 비용을 최소화 해야함
3. 버스 비용은 무조건 자연수임
위의 조건을 통해서 다익스트라라는 것을 알 수 있다.
한 노드에서 다른 노드로 이동하는데 드는 최소 비용을 구해야하며, 노드 간 이동경로의 비용이 무조건 양수이기 때문에 다익스트라 라는 것을 알 수 있다.(음수면 아님)
해당 문제가 최소 비용 구하기 2 인 이유는 단지 경로도 출력해야 하기 때문이다.
https://velog.io/@dongspam0209/Dijkstra-%EC%95%8C%EA%B3%A0%EB%A6%AC%EC%A6%98 를 참고해서 다익스트라를 일단 구현해보자.
import heapq
import sys
INF=sys.maxsize
input=sys.stdin.readline
N=int(input())
M=int(input())
graph=[[]for _ in range(N+1)]
distance=[INF]*(N+1)
src,dst=map(int,input().split()) # 최종 출발지와 목적지다음 노드로 선택해서 이동할때, distance에서 최소 비용인 노드를 선택해야 하기 때문에 힙 자료구조를 활용한다. (heapq)
def dijkstra(start):
priority_q=[]
heapq.heappush(priority_q,(0,start)) # 시작 노드를 비용 0으로 우선순위 큐에 넣는다.
distance[start]=0 # ditance 맵도 초기화
while priority_q:
# 현재 노드와 (현재 노드까지 드는) 비용 준비.
dist,cur_node=heapq.heappop(priority_q)
# 한 노드로 가는 경우가 여러개 있을 수 있는데 이미 이전에 우선순위 큐로 최소값
# 뽑아진 경우 해당 노드로 가는 다른 길은 볼 필요없어 continue
if dist>distance[cur_node]:
continue
# graph를 통해 현재 노드와 연결된 다음 노드들 검사
for next_node,next_dist in graph[cur_node]:
# 다음 노드로 이동할 때 드는 비용 = 현재까지의 비용 + 다음 노드까지 가는데 드는 비용
cost=next_dist+dist
# 새로운 경로가 더 싸다면 교체해야함 + 해당 경우 우선순위 큐에 추가
# 어차피 heappop으로 경로 비용이 제일 싼 경우가 뽑히기 때문에 상관 x
if cost<distance[next_node]:
distance[next_node]=cost
heapq.heappush(priority_q,(cost,next_node))여기서 경로를 추가해줘야 한다. 최소 비용으로 한 노드까지 가는 경우는 cost를 distance에서 갱신할때마다 next_node의 prev_node(cur_node)를 계속 바꿔주면 된다.
최종적으로 내가 원하는 출발지에서 도착지 까지의 다익스트라 연산이 종료되면, prev_node 배열에는 각 idx에 해당하는 노드의 직전 노드가 저장되는 것이다.
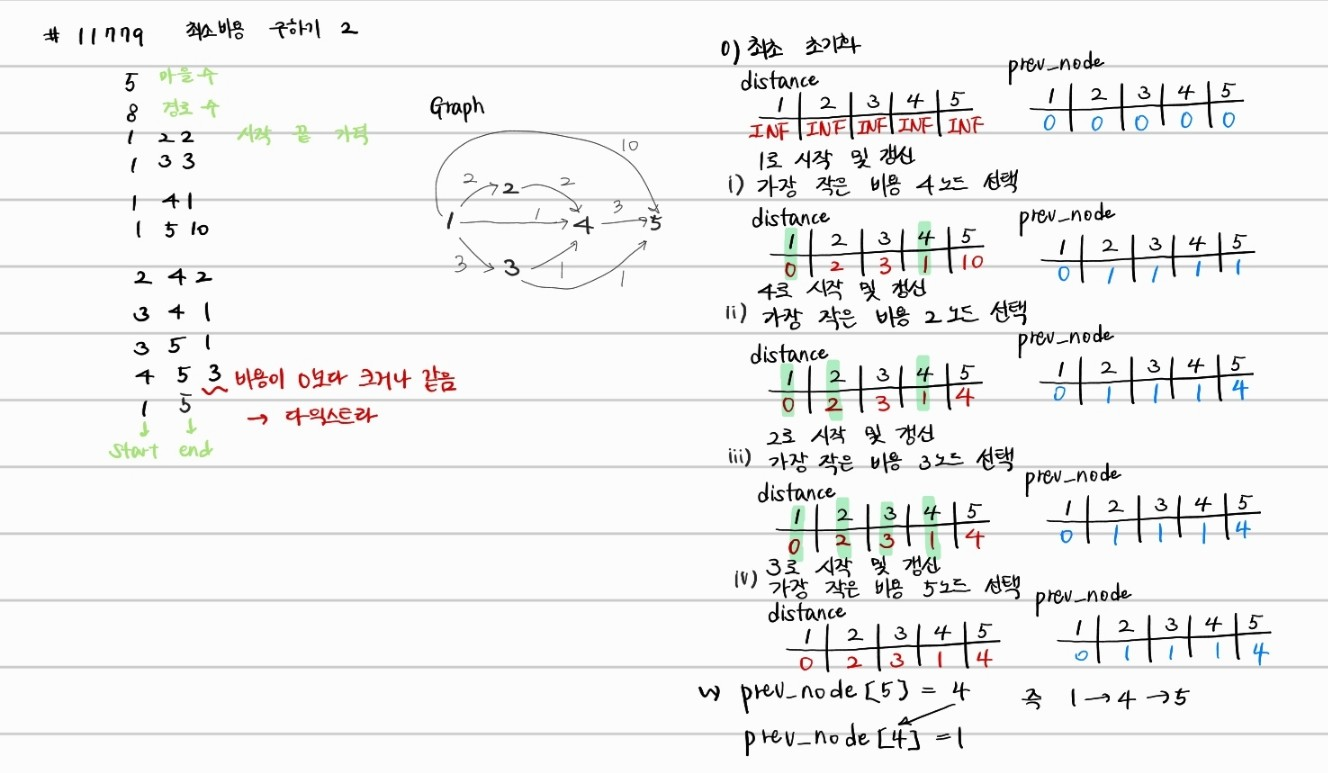
실제로 예시 케이스를 입력하게 되면 위와 같이 동작하게 된다.
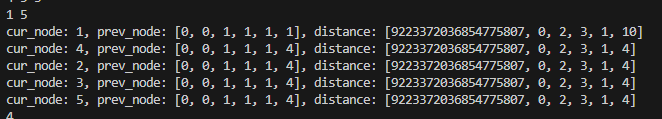
위의 사진 속 prev_node와 distance 배열은 모두 N+1 크기로 선언해서 첫번째 값은 더미값이다.
최종 경로 출력과정은 prev_node배열에서 src까지 역으로 출력하면 된다.
while path_temp!=src:
path_temp=prev_node[path_temp]
path.append(path_temp)
path.reverse()
print(len(path))
print(*path)위와 같이 출력하면 5에서 4, 그리고 1로 가는 경로를 path에 넣을 수 있고 역으로 출력하면 된다.
prev_node를 추가하면 전체 코드는 아래와 같다.
import heapq
import sys
INF=sys.maxsize
input=sys.stdin.readline
N=int(input())
M=int(input())
graph=[[]for _ in range(N+1)]
distance=[INF]*(N+1)
prev_node=[0]*(N+1)
for _ in range(M):
start,end,cost=map(int,input().split())
graph[start].append([end,cost])
# print(graph)
src,dst=map(int,input().split())
def dijkstra(start):
priority_q=[]
heapq.heappush(priority_q,(0,start))
distance[start]=0
while priority_q:
dist,cur_node=heapq.heappop(priority_q)
if dist>distance[cur_node]:
continue
for next_node,next_dist in graph[cur_node]:
cost=next_dist+dist
if cost<distance[next_node]:
distance[next_node]=cost
prev_node[next_node]=cur_node
heapq.heappush(priority_q,(cost,next_node))
# print(f"cur_node: {cur_node}, prev_node: {prev_node}, distance: {distance} ")
dijkstra(start=src)
print(distance[dst])
path=[dst]
path_temp=dst
while path_temp!=src:
path_temp=prev_node[path_temp]
path.append(path_temp)
path.reverse()
print(len(path))
print(*path)