1. 트리(Tree)란?
: 계층적인 구조를 표현할 때 사용하는 비선형적 자료구조. 사이클이 없는 하나의 연결 그래프.
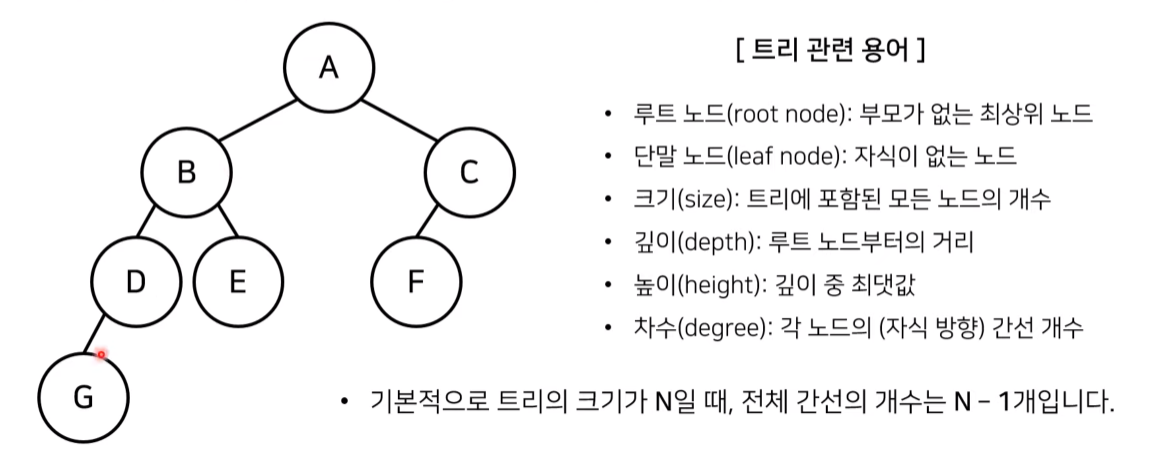
Root Node: ALeaf Node: E, F, GSize: 7- ex.
D의 Depth: 2 Height: 3 (G의 Depth)- ex.
B의 Degree: 2 (D, E)
2. 트리의 특징
1) 트리는 하나의 루트 노드를 가진다.
2) 루트 노드는 0개 이상의 자식 노드를 가진다.
3) 자식 노드 또한 0개 이상의 자식 노드를 가진다.
4) 노드(Node)들과 노드들을 연결하는 간선(Edge)들로 구성된다.
5) 노드가 N개일 때, 항상 N - 1개의 간선을 가진다.
6) 어떤 노드에서 다른 노드로 가는 경로는 유일하다. 즉, 두 정점 사이에 반드시 1개만의 경로를 가진다.
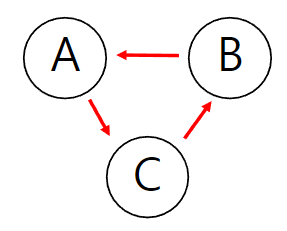
7) 사이클(Cycle)이 존재할 수 없다.
-
사이클(Cycle) : 시작 노드에서 출발해 다른 노드를 거쳐 다시 시작 노드로 돌아오는 것
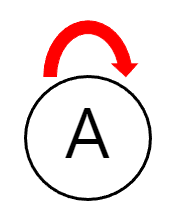
8) self-loop가 존재할 수 없다.
- self-loop : 자기 자신으로 간선을 연결하는 것
9) 루트 노드의 아래로 있는 노드들은 다시 이들끼리 트리를 구성하는데 이를 Sub Tree 라고 한다.

3. 이진 트리 (Binary Tree)
: 모든 노드들이 최대 두 개의 자식을 갖는 트리. 즉, 한 노드의 자식 노드는 0, 1, 2개만 가능하다.
1) 전 이진 트리 (Full Binary Tree)
- 모든 노드가 0개 또는 2개의 자식 노드만을 갖는 트리 (1개이면 안 됨.)

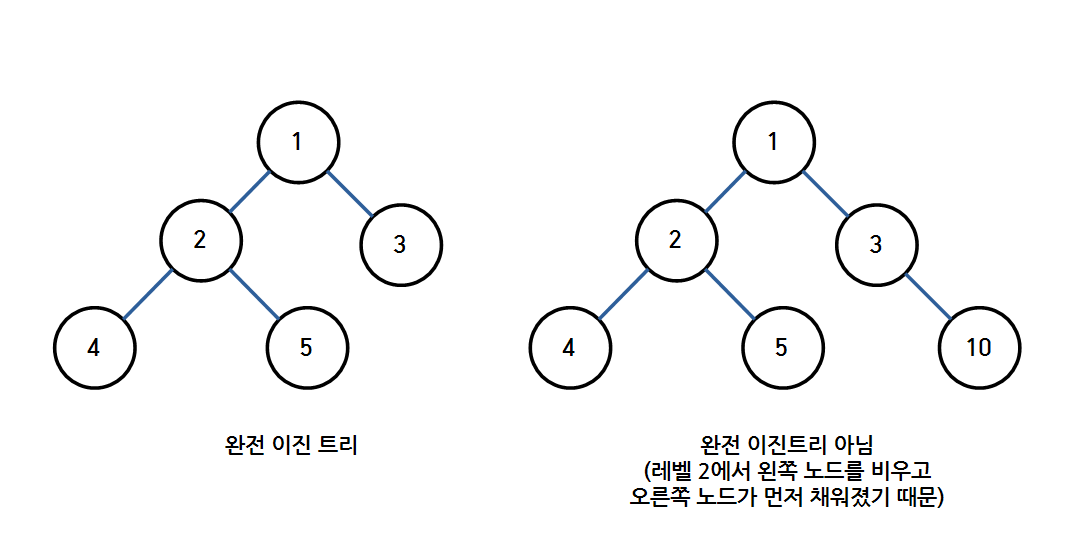
2) 완전 이진 트리 (Complete Binary Tree)
- 마지막 레벨을 제외하고 모든 레벨이 완전히 채워져 있는 트리
- 마지막 레벨은 꽉 차있지 않아도 되지만 왼쪽에서 오른쪽 노드 순서대로 채워져야 함.
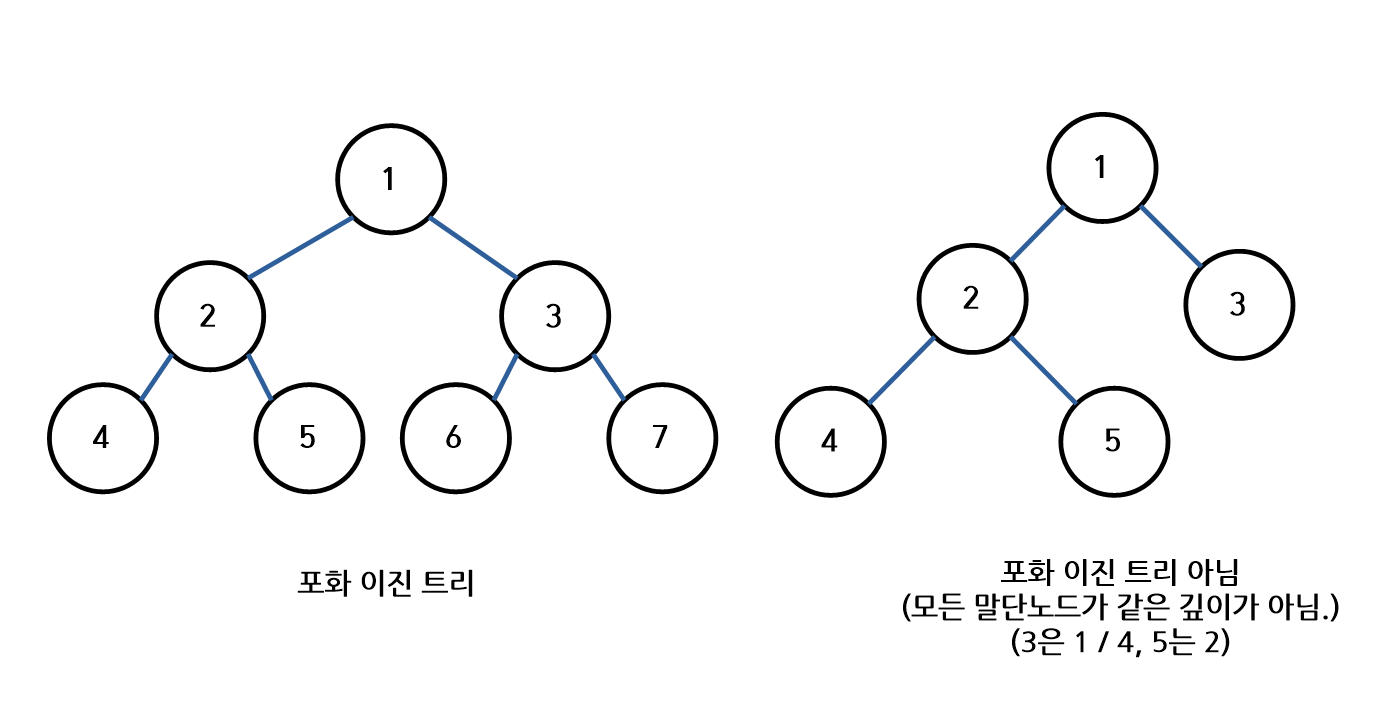
3) 포화 이진 트리 (Perfect Binary Tree)
- 모든 레벨이 노드로 채워져 있는 트리
- 모든 말단 노드(Leaf Node)들은 같은 깊이(Depth)를 가져야 한다.
- 전 이진 트리의 성질을 만족해야 한다. 즉, 모든 노드는 0개 또는 2개의 자식노드만을 가진다.
- 트리의 높이가 h일 때, 모든 노드 개수의 총합은 반드시
2^(h+1) - 1개여야 한다.
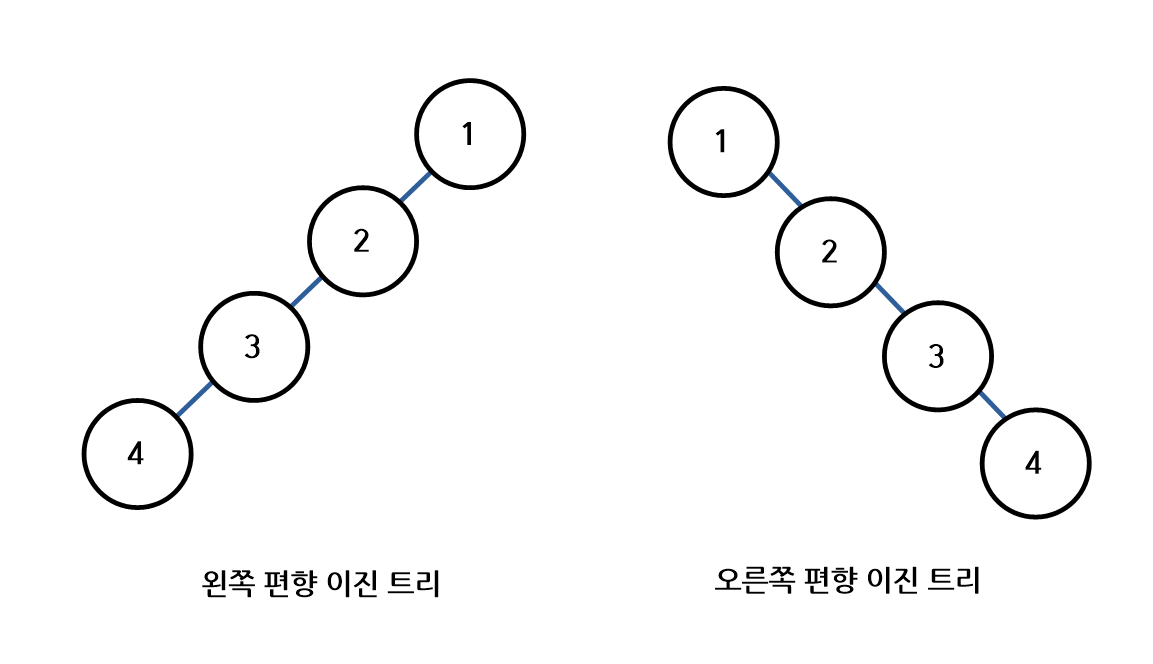
4) 편향 이진 트리 (Skwed Binary Tree)
- 높이 h에 대한 최소 개수의 노드를 가지면서 한 쪽 방향의 자식 노드만을 가지는 이진 트리
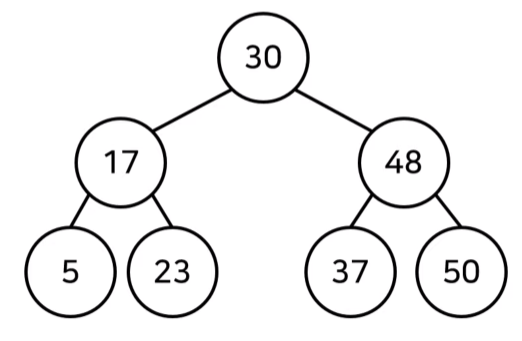
4. 이진 탐색 트리 (Binary Search Tree)
: 이진 탐색이 동작할 수 있도록 고안된 효율적인 탐색이 가능한 자료구조의 일종.
원소의 중복을 허용하지 않는다.
1) 이진 탐색 트리의 특징
- 왼쪽 자식 노드 < 부모 노드 < 오른쪽 자식 노드
- 왼쪽 자식 노드는 부모 노드보다 작다.
- 오른쪽 자식 노드는 부모 노드보다 크다.
2) 이진 탐색 트리의 데이터 탐색 과정

- 루트 노드 30 < 탐색 데이터 37 : 찾는 원소가 더 크므로 오른쪽인 48 방문
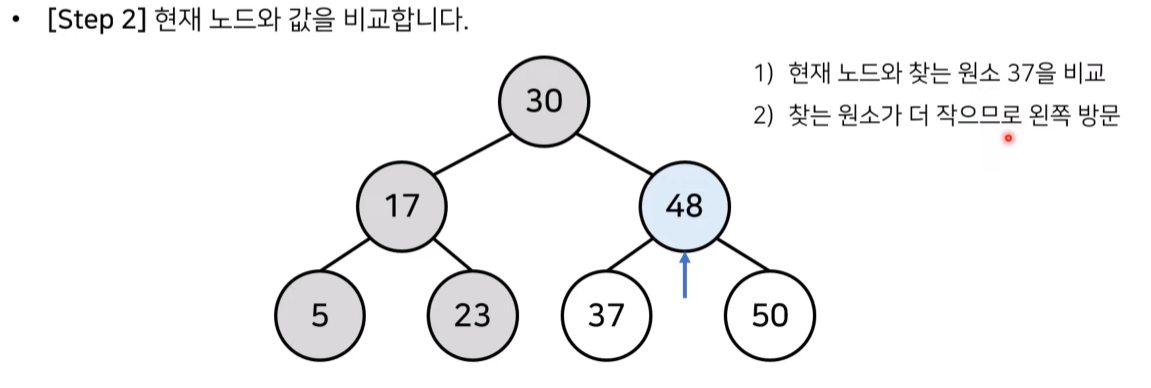
- 현재 노드 48 > 탐색 데이터 37 : 찾는 원소가 더 작으므로 왼쪽인 37 방문
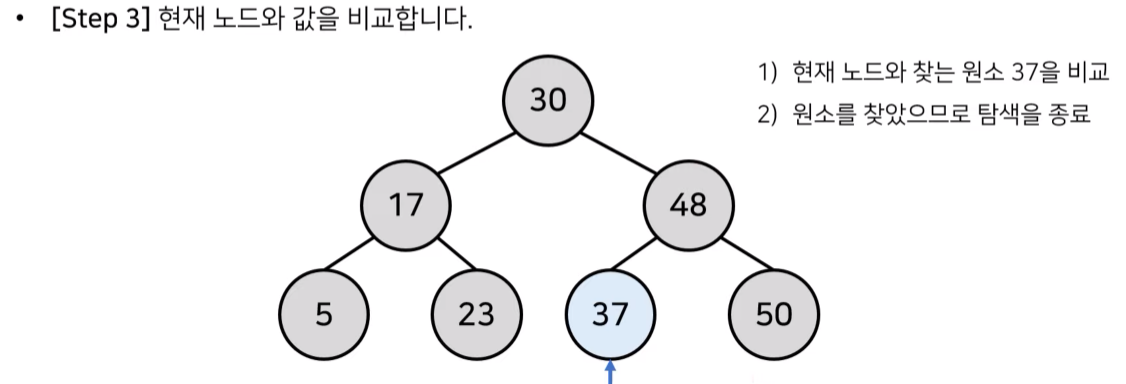
- 현재 노드 37 == 탐색 데이터 37 : 찾는 원소와 같으므로 탐색 종료
❗이진 탐색 트리를 중위 순회하면 오름차순 정렬된 결과값을 얻을 수 있다.
5. 트리의 순회 (Tree Traversal)
: 트리 자료구조에 포함된 노드를 특정 방법으로 한 번씩 방문하는 방법
왼쪽 : L / 루트 방문 : V / 오른쪽 : R이라고 할 때
- 전위 순회(Pre-order Traverse) : 루트를 먼저 방문 (VLR)
- 중위 순회(in-order Traverse) : 왼쪽 자식 방문한 뒤에 루트 방문 (LVR)
- 후위 순회(post-order Traverse) : 오른쪽 자식 방문한 뒤에 루트 방문 (LRV)
1) 각 순회 방식 별 탐색 과정
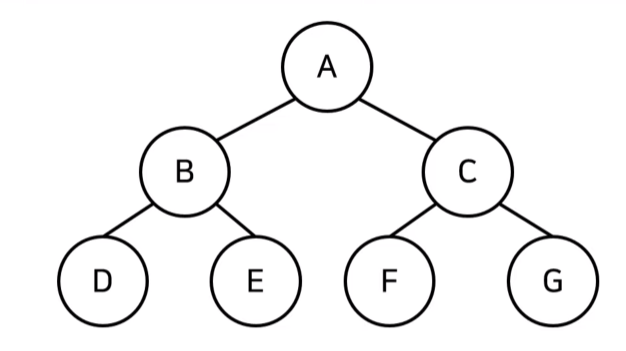
- 전위 순회 : A - B - D - E - C - F - G (루트 - 왼쪽 - 오른쪽)
- 중위 순회 : D - B - E - A - F - C - G (왼쪽 - 루트 - 오른쪽)
- 후위 순회 : D - E - B - F - G - C - A (왼쪽 - 오른쪽 - 루트)
2) 순회 예제 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data; // Node가 저장하는 값
Node* Left; // 해당 노드의 왼쪽 자식 노드
Node* Right; // 해당 노드의 오른쪽 자식 노드
};
void preOrder(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
cout << (node->data) << ' ';
preOrder(node->Left);
preOrder(node->Right);
}
void inOrder(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
inOrder(node->Left);
cout << (node->data) << ' ';
inOrder(node->Right);
}
void postOrder(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
postOrder(node->Left);
postOrder(node->Right);
cout << (node->data) << ' ';
}
Node* insert(Node* node, int data) // 삽입 시에 루트 노드부터 비교
{
if (node == NULL) // 더 이상 비교할 노드가 없으면 새로운 Node 객체를 생성해 삽입한다.
{
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->Left = NULL;
newNode->Right = NULL;
return newNode;
}
if (node->data > data) // 삽입하려는 값이 비교한 노드의 값보다 작으면
node->Left = insert(node->Left, data); // 비교하는 노드의 왼쪽 자식 노드와 비교
else if (node->data < data) // 삽입하려는 값이 비교한 노드의 값보다 크면
node->Right = insert(node->Right, data); // 비교하는 노드의 오른쪽 자식 노드와 비교
else
{
// 비교 노드와 같은 값이면 중복 데이터므로 추가 X
}
return node;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
Node* root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 32);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 13);
root = insert(root, 25);
root = insert(root, 55);
preOrder(root);
cout << endl;
inOrder(root);
cout << endl;
postOrder(root);
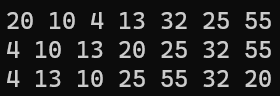
}- 출력 결과
👁️🗨️ 참조
동빈나 유튜브 (https://youtu.be/i5yHkP1jQmo)
https://code-lab1.tistory.com/8
https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/08/12/data-structure-tree.html
https://srdeveloper.tistory.com/m/27
https://jcsites.juniata.edu/faculty/rhodes/dbms/btrees.htm
https://yoongrammer.tistory.com/69
