https://youtube.com/watch?v=_i8O_o2ozlE&feature=share&utm_source=EKLEiJECCKjOmKnC5IiRI
https://securitymax.tistory.com/87 을 루트로 이것 저것 자료 정리한 글입니다.
개인 공부용으로 작성한 글이니 원본 링크만 참고하시고 제 글은 무시하시는 것이 좋습니다
패킷의 생성 원리
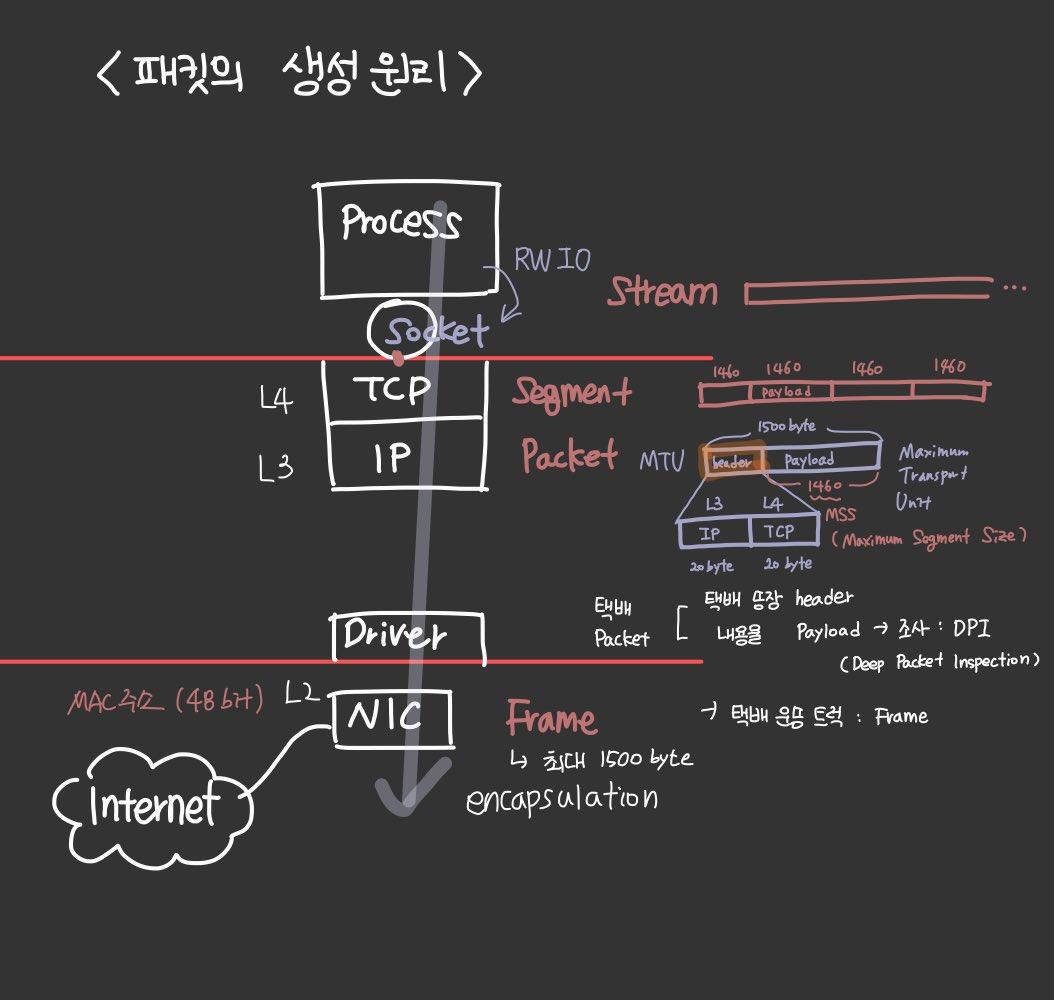
stream 단위의 파일을 TCP에서 segment (MSS + TCP header) -> UPD는 segment라고 안하고 datagram이라고 함(참고)
IP 레이어에서 packet (MSS + TCP header + IP header) = MTU
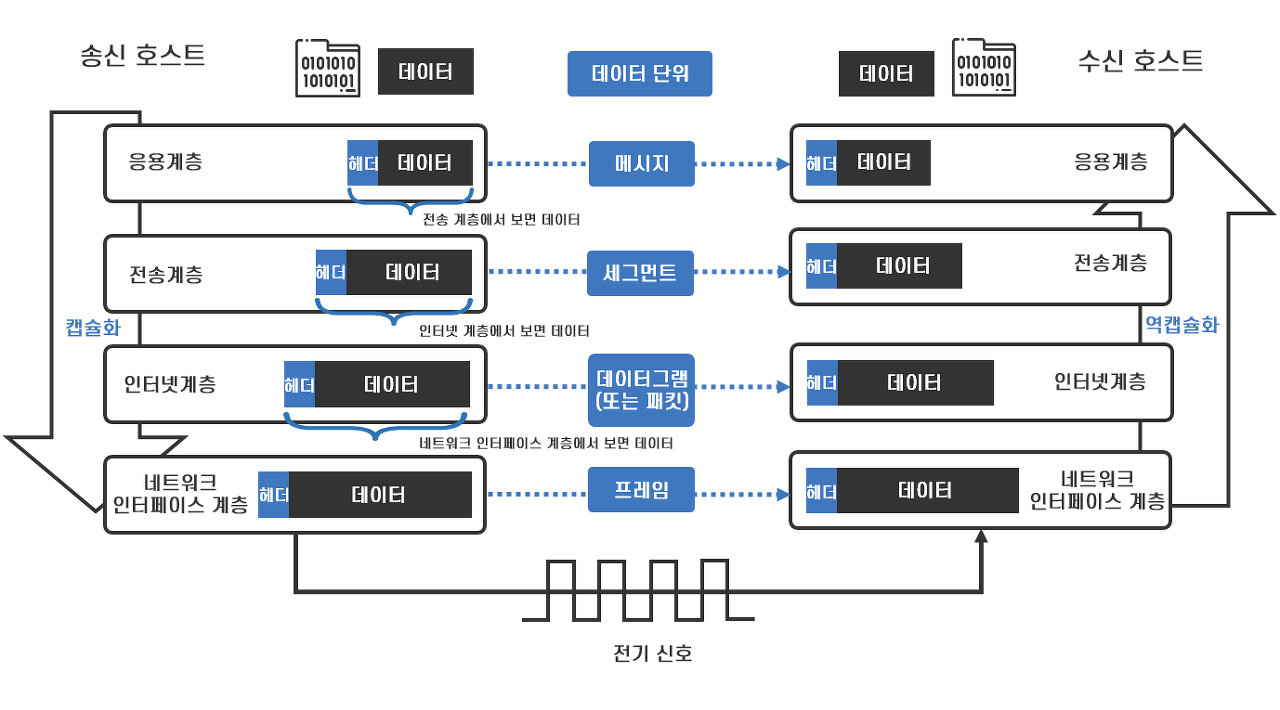
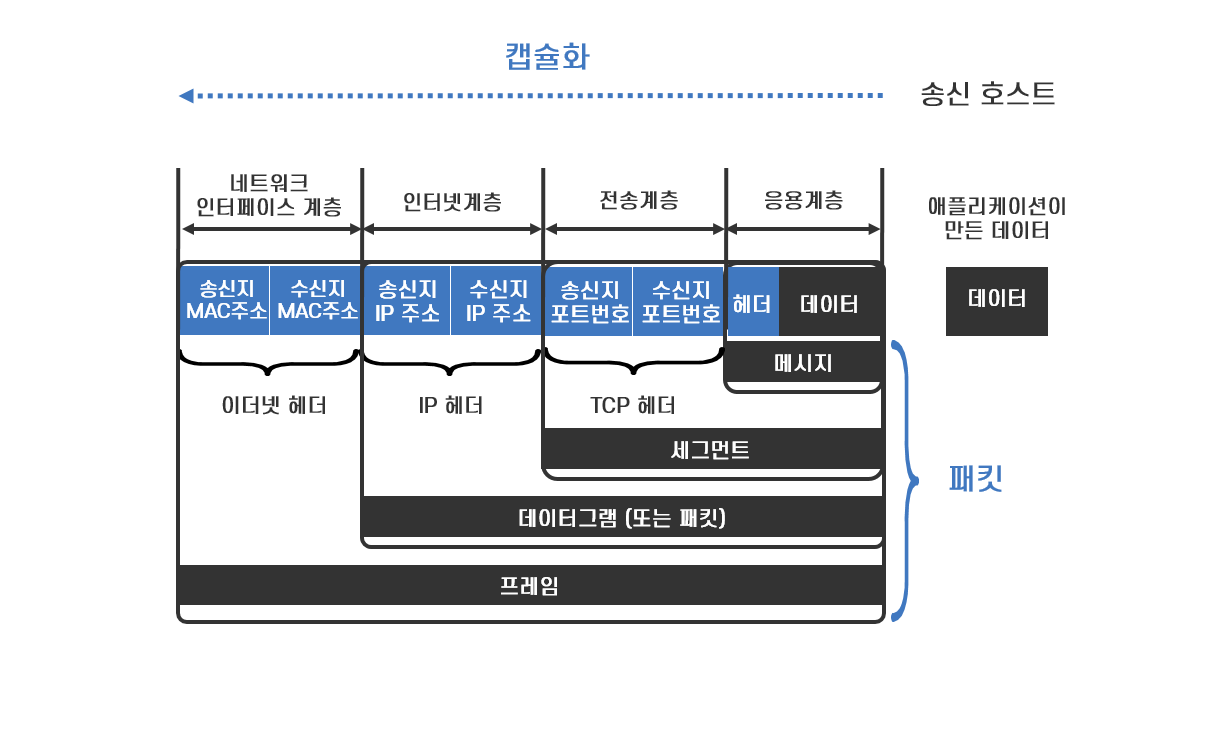
Frame: MTU 1500 byte + 이더넷 헤더 14byte
- Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU)
MTU is the largest packet or frame size, specified in octets (eight-bit bytes) that can be sent in a packet- or frame-based network. The internet’s transmission control protocol (TCP) uses the MTU to determine the maximum size of each packet in any transmission.
MTU is usually associated with the Ethernet protocol, where a 1500-byte packet is the largest allowed.
Ip header
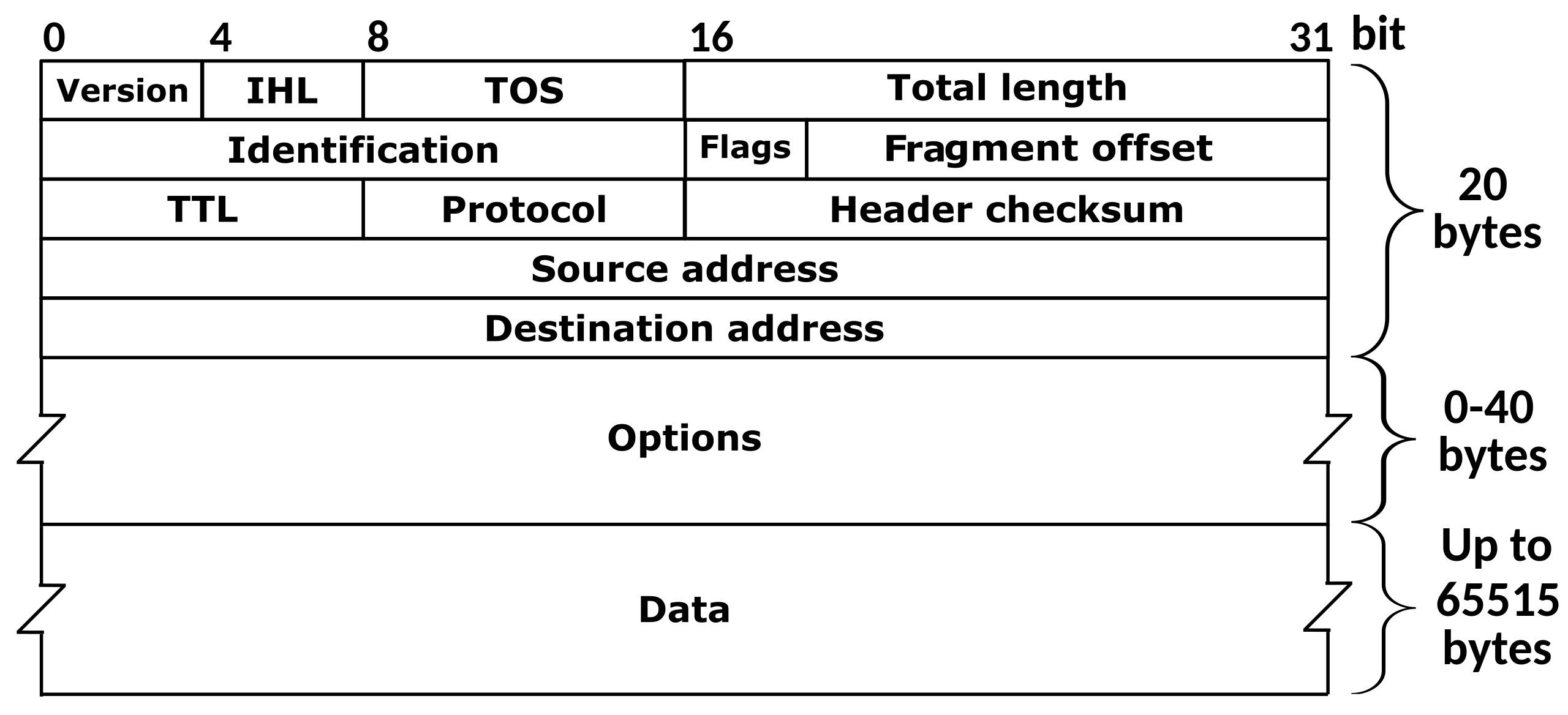
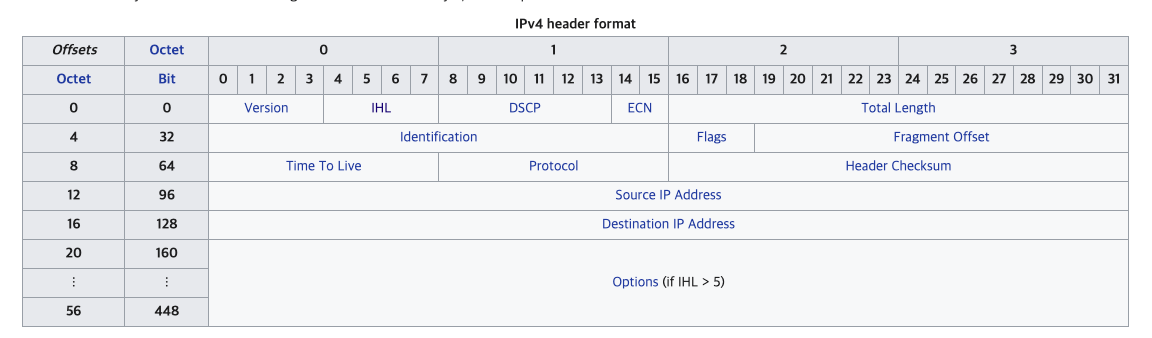
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv4 에 가서 보면 프로토콜에 대해 자세히 설명되어있다.
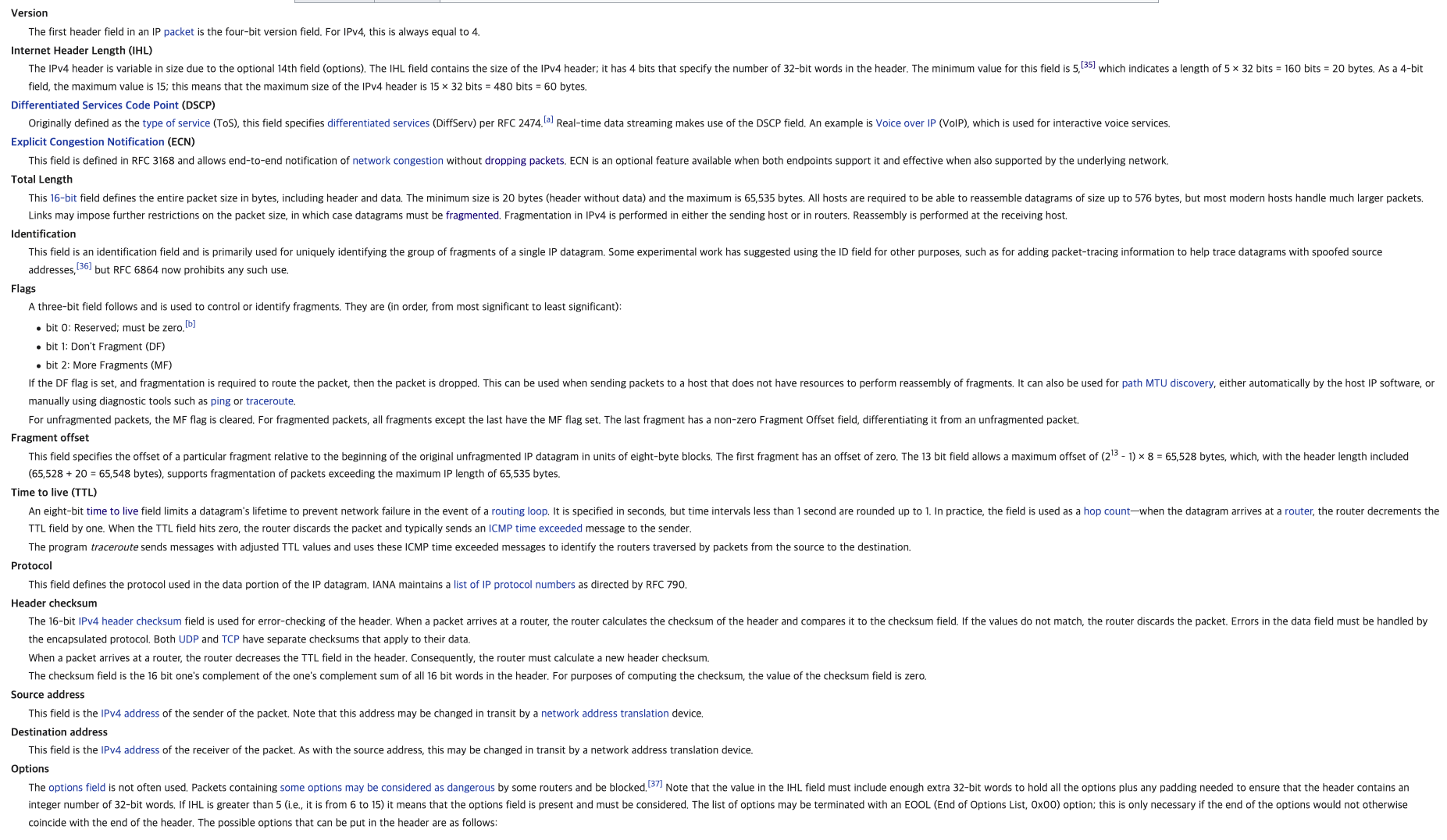
글씨 잘 안보이네... 가서 읽으면 됨 대충 인상 깊거나 체크할 부분..
- Internet Header Length (IHL)
The IPv4 header is variable in size due to the optional 14th field (options). The IHL field contains the size of the IPv4 header; it has 4 bits that specify the number of 32-bit words in the header.
The minimum value for this field is 5,[35] which indicates a length of 5 × 32 bits = 160 bits = 20 bytes. As a 4-bit field,
the maximum value is 15; this means that the maximum size of the IPv4 header is 15 × 32 bits = 480 bits = 60 bytes. => 전체 헤더길이 / 4 해주면 됨
- Fragment
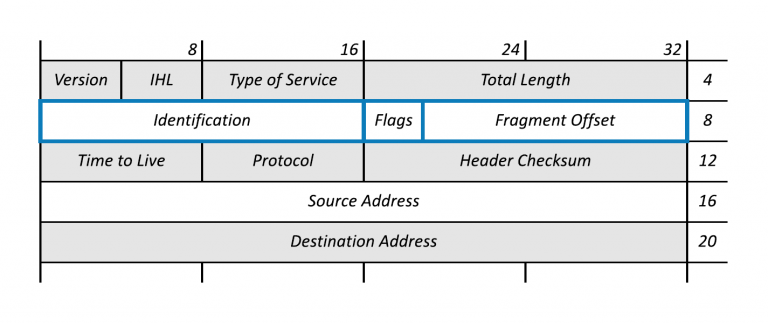
재조립은 항상 최종 수신지에서만 가능함
IPv4: 발신지 뿐만아니라 중간 라우터에서도 조각화 가능
IPv6: 발신지에서만 가능
https://packetpushers.net/ip-fragmentation-in-detail/
Flags field (3 bits) will be 0 (unset) and the second bit, Don’t Fragment (DF), will also be unset. Unlike the original packet, all but the last fragment will have the third bit of the field, More Fragments (MF), set to 1.
기준으로 얼마나 떨어져있느냐 ~ 잘라놓은 조각들 길이들
출처 http://users.cis.fiu.edu/~vince/cgs4285/class13.html
If any fragment of a packet is lost, the reassembly will timeout and the entire set of fragments needs to be sent again. Timeouts vary, 15 seconds is suggested to start with.
- Key things to remember:
-
IP fragmentation is done when a station needs to send a IP packet that is larger than the MTU of the Layer 2 (MAC) medium it wants to send it on.
-
The original packet will be divided into smaller packets, on a 8 byte boundary.
-
Each fragment contains information letting the receiving station know where it fits in the original datagram.
- First fragment has MF bit set (=1) and Fragment offset=0
- Middle fragments have MF bit set and Fragment offset != 0
- Last fragment has MF bit clear (=0) and frag offset !=0
-
Receiving station will start a timer upon receiving a fragment. If the timer expires before all the fragments arrive, then the original packet is declared lost. The station that was receiving and trying to re-assemble the packet would then send an ICMP TTL exceeded (type=11) fragmentation reassembly time exceeded (code=1).
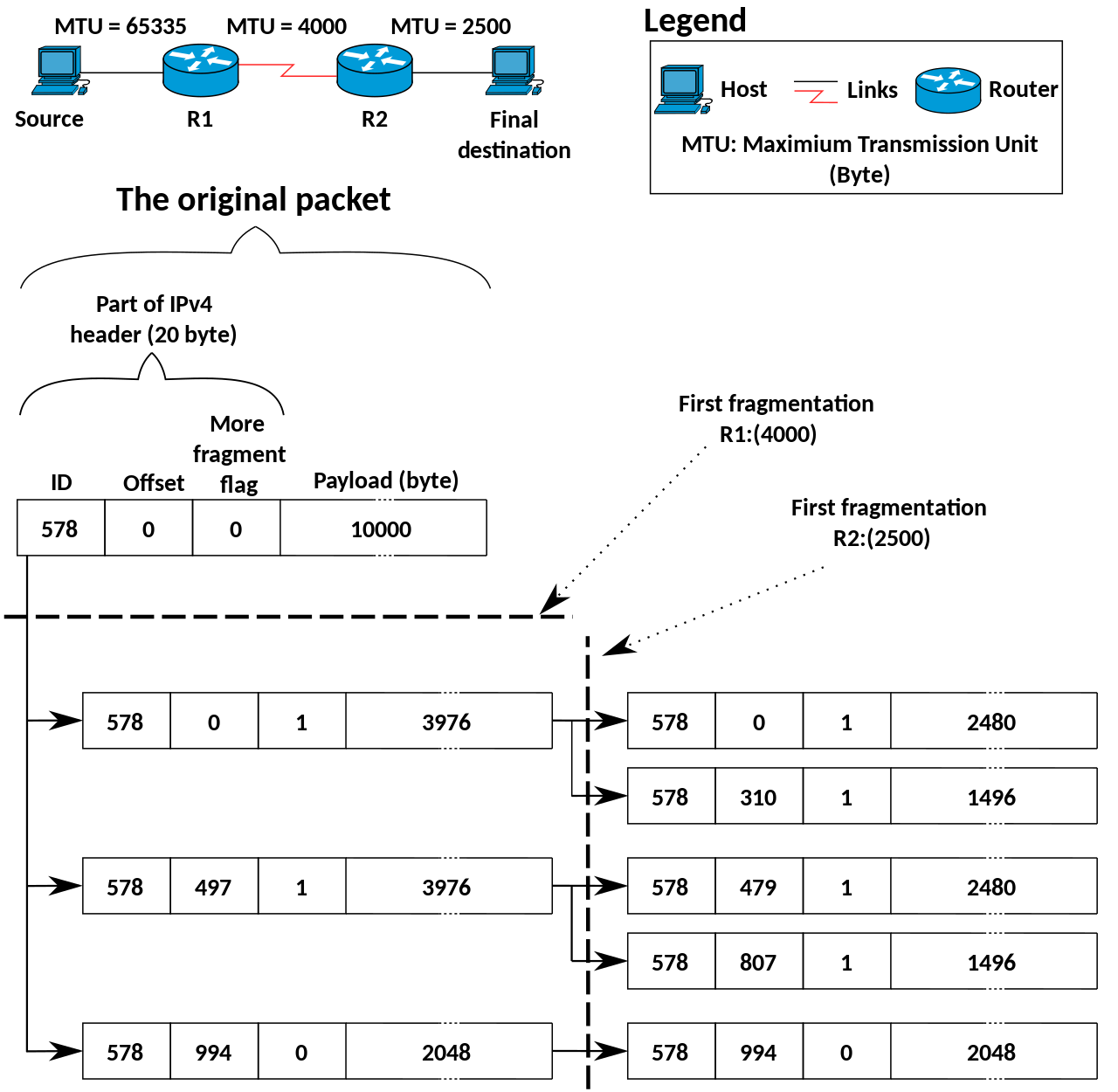
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv4#Fragmentation_and_reassembly
An example of IPv4 multiple fragmentation. The fragmentation takes place on two levels: in the first one the maximum transmission unit is 4000 bytes, and in the second it is 2500 bytes.
- fragment offset 관련 추가 문서
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IP_fragmentation
What is an IP/ICMP Fragmentation DDoS Attack?
이걸로 DDos 공격도 한다고...
https://www.netscout.com/what-is-ddos/ip-icmp-fragmentation
When a packet is too large, it must be sliced into smaller fragments in order to be transmitted successfully. This leads to several packets being sent, one which contains all the info about the packet, including the source/destination ports, length, etc. This is the initial fragment.
The remaining fragments are “naked” in the sense that they simply consist of an IP header plus a data payload. These fragments contain no information on protocol, size or ports
The attacker can employ IP fragmentation to target communications systems, as well as security components. ICMP-based fragmentation attacks typically submit fake fragments that cannot be defragmented. This in turn causes the fragments to be placed in temporary storage, taking up memory and in some cases exhausting all available memory resources.
-
UDP and ICMP fragmentation DDoS attacks – In this type of DDoS attack, fake UDP or ICMP packets are transmitted. These packets are designed to look like they are larger than the network’s MTU, but only parts of the packets are actually sent. Since the packets are fake and can’t be reassembled, the server’s resources are quickly consumed, which ultimately renders it unavailable to legitimate traffic.
-
Why Are IP/ICMP Fragmentation DDoS Attacks Dangerous?
IP/ICMP fragmentation DDoS attacks, like many other DDoS attacks, will overwhelm the destination resources due to the massive traffic volumes. However, this DDoS attack will also force the destination to use resources to attempt to reassemble the packets which will often result in network devices and servers crashing. Lastly, as the non-initial fragments do not contain any information about which service they belong to, it is difficult to decide which packets are safe to drop and which are not.
- How to Prevent an IP/ICMP Fragmentation DDoS Attack?
패킷 규칙을 지키는지 검사하기
첫번째 분할 조각 외 일괄적으로 거부하는 법 -> 별로 안좋음
속도 제한을 걸기 (장단점 둘 다 있음)
원문
inspecting incoming packets to determine if they breach fragmentation rules.
One possible denial of service mitigation approach is to block all non-initial fragments, but this will result in an issue with legitimate traffic, which relies on those fragments.
A better solution is to use rate-limiting, which will not block anything during peacetime, but will drop the majority of packets (both good and bad because rate-limiting has no idea what is what) and the destination under attack will be unaffected. This approach does risk creating issues with legitimate services which rely on fragments, but this trade off may be deemed worthwhile when under attack. No method will result in 100% success.
If you are using services which rely on fragments, for example DNS, you can whitelist the specific servers you rely on and use rate-limiting for the rest.
추가 찾아봄 (MSS조절 TCP/IP 통신해서 조절)
https://www.imperva.com/learn/application-security/what-is-mtu-mss/
l2 계층 이더넷은 1500바이트 밖에 못봄
ip 계층에서 MTU에서 tcp ip 헤더를 각 20바이트씩 붙이니까
MSS 는 페이로드를 1460만큼 가져옴
근데!! 만약에 GRE 프로토콜을 가져와다 쓴다! 그러면 1500 바이트가 넘어버림
그러면?? 뭘 줄이냐면~~ TCP MSS 를 줄입니다~ (기본 사이즈가 1470인데 1436 바이트로 줄임
그 용량 타협보는걸 MSS announcement (= negotiation) 이라하는데 three handshake 라고 함
https://learn.microsoft.com/ko-kr/troubleshoot/windows-server/networking/three-way-handshake-via-tcpip
What Is an MSS Announcement?
During the three-way TCP handshake, the receiving party sends an “MSS announcement”. This announcement declares what is the maximum size of the TCP segment the receiving party can accept. MSS can be used independently in each direction of data flow.
Since the end device will not always know about high level protocols that will be added to this packet along the way, it often won’t adjust the TCP MSS value. To compensate for this, network devices have the option of rewriting the value of TCP MSS packets that are processed through them.
For example, in a Cisco Router the command ip tcp mss-adjust 1436 at the interface level will rewrite the value of the TCP MSS of any SYN packet that passes through this interface.
클라이언트 - 서버간 MTU가 다르면 악수할 때 서로 MSS값을 TCP 헤더 옵션필드에 넣어서 서로 보고 세션 성립하면! 그때 패킷을 나누어서 잘라서 보내는 것
또 TCP 프로토콜로 통신하면 3-way handshake 때 MSS를 협상하고 거기에 맞춰서 세그먼트를 만들지만 UDP 프로토콜은 그런 과정이 없어서 패킷으로 만들 때 파편화함.
(대충 지정된 MTU값보다 크게 잘려서 오면 fragmentation이 일어나고, MTU값을 정하는 과정은 TCP/IP 3 way handshaking 때 일어난다 이해함)
ICMP protocol (ICMP, 인터넷 제어 메시지 프로토콜)
참고 페이지
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Control_Message_Protocol
ICMP 란 신뢰성 없는 IP 를 대신해 통신의 이상 유무를 알리기 위해 네트워크의 에러 메시지를 전송하거나 네트워크의 흐름을 통제하기 위한 프로토콜로 ICMP 메시지를 사용하여 타깃의 라우팅 경로를 변경하여 패킷의 흐름을 조정한다.
한 네트워크에 여러 개의 라우터가 있는 경우 좀 더 효율적인 경로라고 판단되는 특정 라우터의 IP 주소를 ICMP Redirect 를 통해 보낼 수 있다. ICMP Redirect 를 받은 클라이언트는 패킷의 내용대로 라우팅 테이블을 변경하는데 인증 메커니즘이 없기 때문에스니핑 공격의 방법으로 사용된다. 공격자는 타깃에게 패킷을 자신에게 전달하도록 만든 라우팅 경로를 ICMP 메시지로 만들어 전달한다. 글 출처
type 에서는 30번까지 종류가 있는데, 중요한 것들 추려보면
-
ping
0– Echo Reply: Echo reply (used to ping)
8– Echo Request: Echo request (used to ping) -
오류
- 목적지까지 도달 X (경로 상 문제)
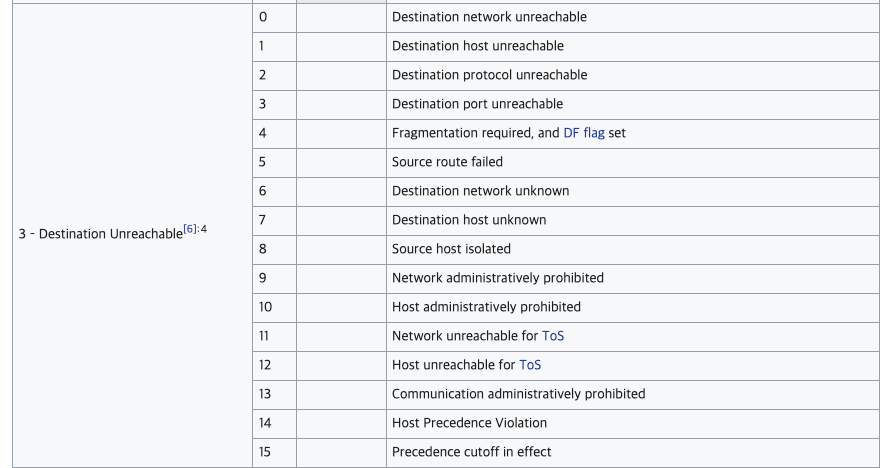
- 목적지까지 가긴 했는데, 응답 못받은 경우 (상대방에게 문제 ex. 방화벽을 쳐놓은 경우)

- 보안 (원격지에 있는 라우팅 테이블을 ICMP가 수정할 때 사용, 요즘은 잘 안 사용함)
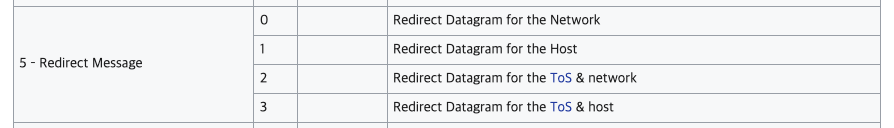
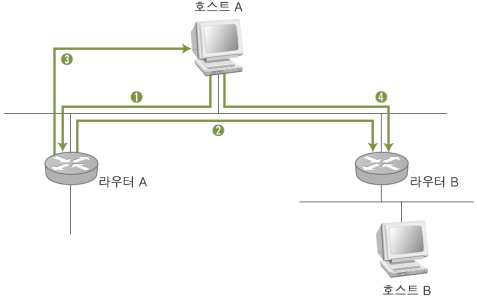
ICMP Redirect 작동 원리
① 호스트 A 에 라우터 A 가 기본으로 설정되어 있기 때문에, 호스트 A 가 원격의 호스트 B 로 데이터를 보낼 때 패킷을 라우터 A 로 보낸다.
② 라우터 A 는 호스트 B 로 보내는 패킷을 수신한다. 그리고 라우팅 테이블을 검색하여 호스트 A 에게 자신을 이용하는 것보다 라우터 B를 이용하는 것이 더 효율적이라고 판단하여 해당 패킷을 라우터 B 로 보낸다.
③ 라우터 A 는 호스트 B 로 향하는 패킷을 호스트 A 가 자신에게 다시 전달하지 않도록, 호스트 A 에 ICMP Redirect 패킷을 보내서 호스트 A 가 호스트 B 로 보내는 패킷이 라우터 B로 바로 향하도록 한다.
④ 호스트 A 는 라우팅 테이블에 호스트 B 에 대한 값을 추가하고, 호스트 B 로 보내는 패킷은 라우터 B로 전달한다.
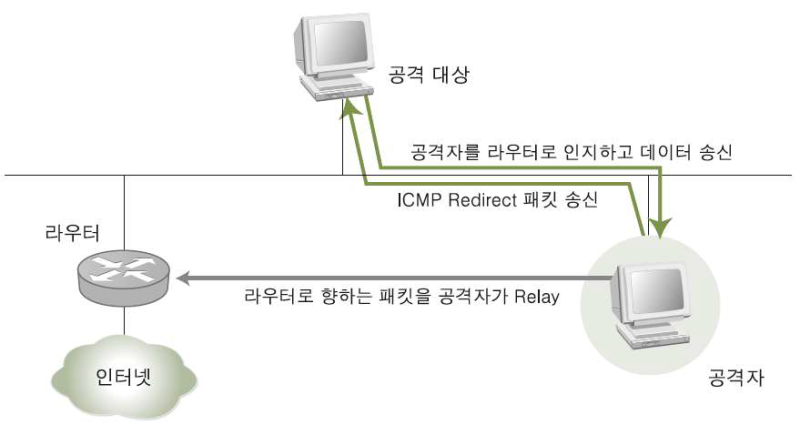
ICMP Redirect 공격 방법
공격자는 공격 대상에게 패킷을 자신에게 전달하도록 만든 라우팅 경로를 ICMP 메시지로 만들어 보내 공격 대상의 라우팅 테이블을 변경한다. 공격 대상이 공격자를 라우터로 인지하고 송신한 패킷을 라우터에 릴레이 시켜주면 공격 대상의 모든 패킷을 스니핑 할 수 있다.
ICMP Redirect 공격 방어
출처
ICMP Redirect 패킷을 허용하지 않도록 설정한다.
- Linux : /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/*/accept_redirects 를 0 으로 설정한다.
- Windows : 방화벽 Option 중에서 ICMP 의 "방향 전환 허용" 체크를 해제한다.
ICMP는 통신을 확인하는 역할, IPv4는 멀리 찾아가기 위한 역할, Ethernet은 가까운 곳을 찾아가기 위한 역할
P 프로토콜이 전달하고 ICMP 프로토콜이 테스트하는 식
ip 스푸핑
스니핑? 스누핑? 스푸핑?
해당 글 틀 출처: https://saladdaily.tistory.com/13
- 스니핑(Sniffing) :
도청
냄새를 킁킁거리다
패킷 가로채기 공격은 네트워크 상에 떠돌아다니는 패킷이나 데이터 등을 훔쳐보는 것을 뜻한다.
300바이트 정도만 가로챌 수 있어도 계정의 id, pwd를 훔칠 수 있기에 보안에 큰 타격을 줄 수 있다.
대표적인 스니핑 공격으로 ICMP 리다이렉트 이용 및 스위치재밍 등이 있다.
스니핑을 방어하기 위해 SSL 등 데이터 암호화 기법이 쓰이고 있다. 데이터를 도둑맞아도 내용을 볼 수 없으므로 안전해진다.
- 스누핑(Snooping) :
도청해서 내용 획득
기웃거리다, 염탐하다
네트워크 상의 정보를 염탐하여 불법적으로 얻는 것을 의미한다.
소프트웨어 프로그램(스누퍼)을 이용하여 원격으로 다른 컴퓨터의 정보를 엿볼 수 있어,
개인적인 메신저 내용, 로그인 정보, 전자 우편 등의 정보를 몰래 획득한다. 반면, 네트워크 트래픽을 분석하기 위해 사용되기도 한다 (스니핑은 슬쩍 보기만 하는데 스누핑은 내용까지 획득함)
- 스푸핑(Spoofing):
신분 위조
더 보면 좋을 문서: IP(Internet Protocol) 스푸핑
https://m.blog.naver.com/PostView.naver?isHttpsRedirect=true&blogId=brickbot&logNo=220441375126
속이다, 사기치다
네트워크 트래픽 흐름을 임의로 변경하기, 시스템 권한 탈취하기 등의 공격을 일컬으며, 그 대상은 MAC 주소, IP 주소, 포트 등 여러 가지가 될 수 있다.
승인받은 사용자인 것처럼 시스템에 접근하거나 네트워크상에서 허가된 주소로 가장하여 접근 제어를 우회하는 공격 행위.
스푸핑은 의도적인 행위를 위해 타인의 신분으로 위장하는 것으로 매체 접근 제어(MAC) 주소, 인터넷 프로토콜(IP) 주소, 포트(port), 전자우편(이메일) 주소 등을 이용한다.
예를 들어, 임의로 웹 사이트를 구성해 일반 사용자들의 방문을 유도하고, 인터넷 프로토콜인 TCP/IP의 구조적 결함을 이용해 사용자의 시스템 권한을 획득한 뒤 정보를 빼 가거나 허가받은 IP을 도용해 로그인을 한다.
또한 소비자들이 믿을 수 있는 이메일로 착각하여 가짜 웹 사이트로 유도하여 사용자가 암호와 기타 정보를 입력하도록 속이기도 한다.
<스푸핑 종류> 출처
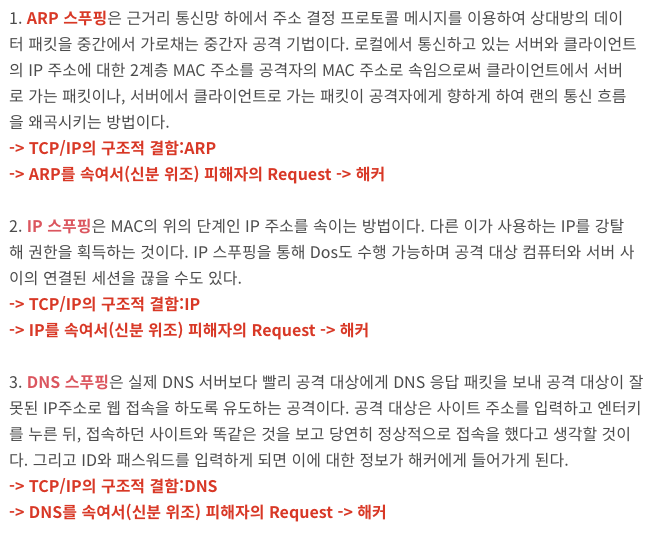
스푸핑에 피해를 입은 시스템은 공격자가 주입한 잘못된 정보를 믿게 되어 스스로 악성 사이트에 접근하거나 공격자에게 정보를 헌납하게 되는데 이 상태에서 피싱과 연계되거나 백도어를 뚫는 수단으로 활용 될 경우 더 큰 2차 피해가 발생하기 쉽다.
특히 피싱은 단순히 누군가가 속아서 접속하기를 기다리는 수준을 넘어서 아예 면전에다 피싱 수단을 들이밀 수 있게 되기에 더 악질적이다.
라우팅 테이블
netstat -r 명령어로 확인 가능! (Mac)
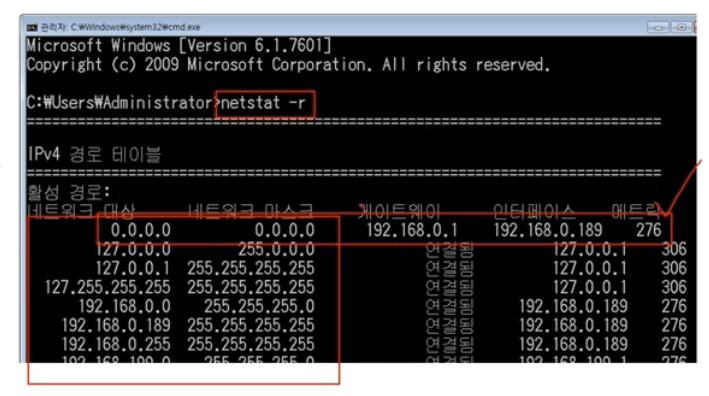
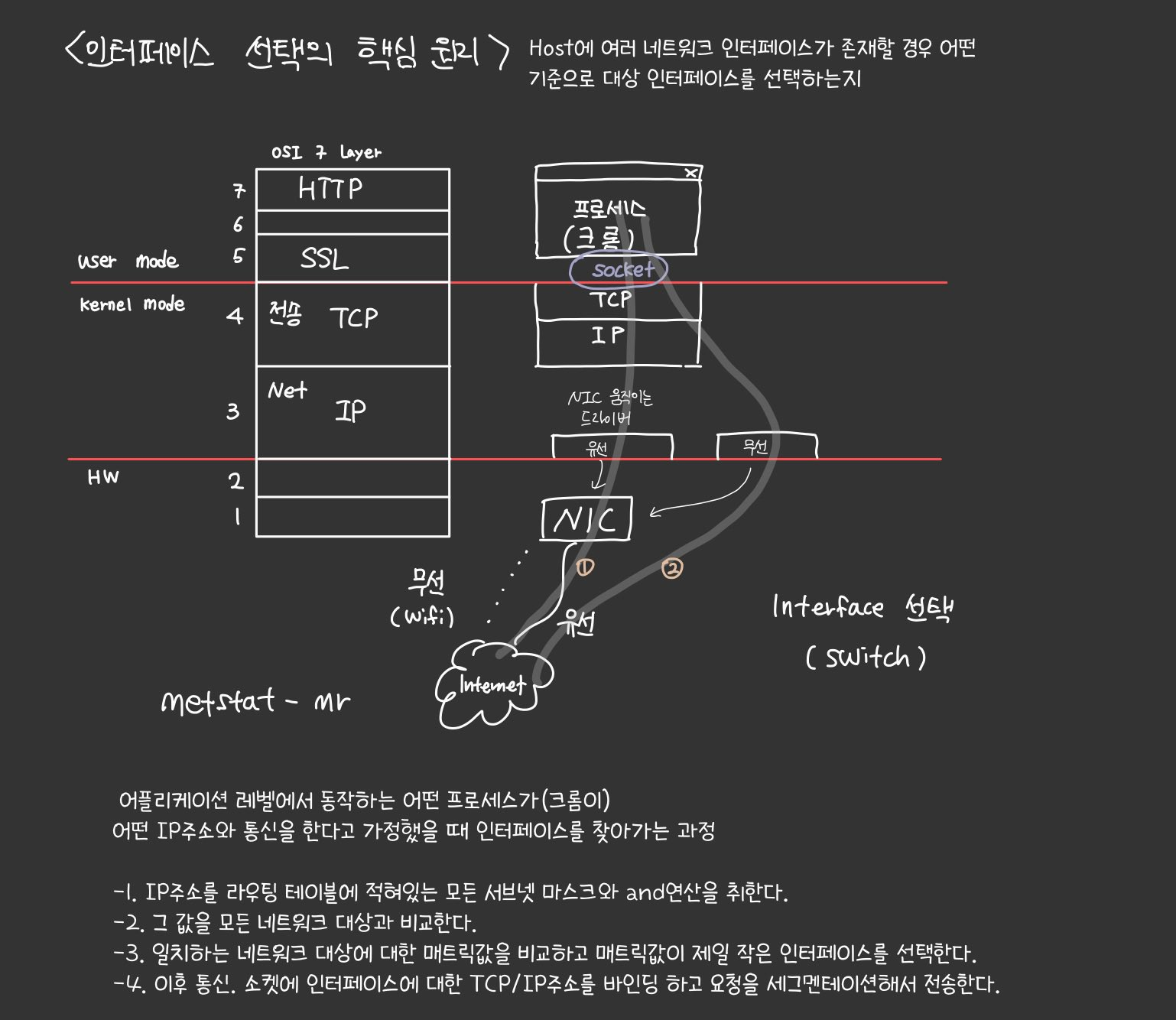
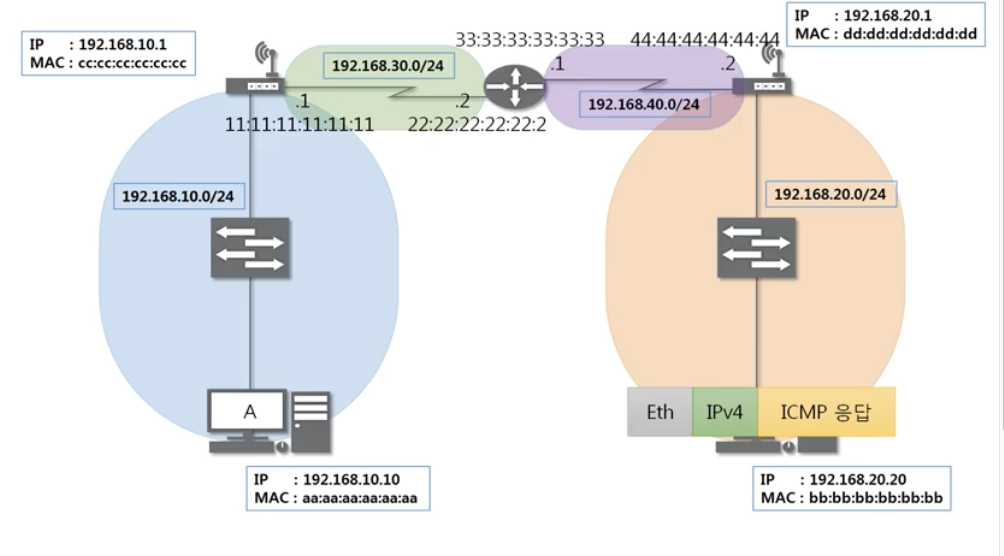
LAN 정의: ARP 프로토콜 (recall: IP 주소를 입력하면 상대방의 MAC 주소를 알아오는 프로토콜)
=> 정리 https://aws-hyoh.tistory.com/70