이 글은 이 영상들을 토대로 작성되었다.
삽입
규칙
- 노드 x가 새로 삽입된다고 할 때,
- x.color = RED. 새로 삽입되는 노드는 빨간색
- 4가지 경우로 나누어서 조정
-
x = t -> root인 경우:
x.color = black으로 변경. -
x -> parent -> color = black인 경우:
문제가 발생하지 않으므로 아무것도 안 함. -
x -> parent -> color = red인 경우:
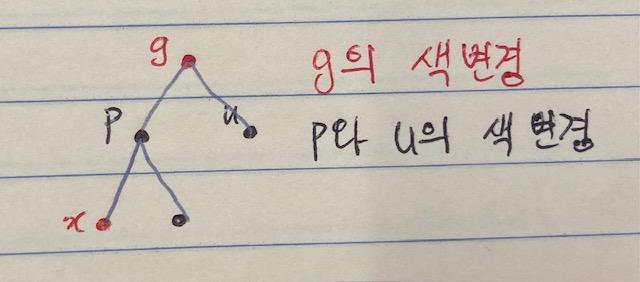
- x -> uncle -> color = red인 경우:
조부모(g)의 색을 변경한 후 부모(p)와 삼촌(u)의 색을 변경
-
x -> parent -> color = black인 경우:
-x, p, g 가 linear한 경우: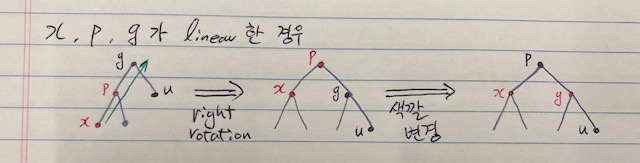
-x, p, g 가 triangle인 경우:
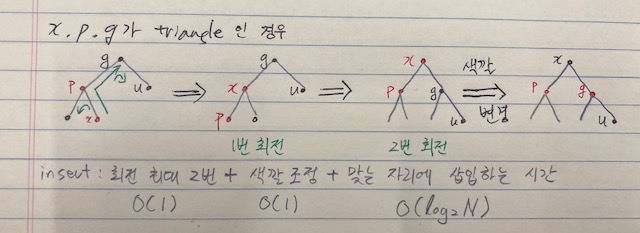
실제 코드
void rbtree_insert_fixup(rbtree *t, node_t *z) {
node_t *y;
//삽입된 노드의 부모가 black일 경우 아무 문제 없다.
while (z -> parent ->color ==RBTREE_RED) {
//z의 부모가 조부모의 왼쪽 서브트리인 경우
if (z -> parent == z -> parent -> parent -> left) {
//y는 z의 uncle 노드
y = z -> parent -> parent -> right;
//case.1 삽입된 노드 z의 삼촌 y가 red 인 경우 (parent 도 red, uncle도 red)
if (y -> color == RBTREE_RED) {
z -> parent -> color = RBTREE_BLACK; //부모의 색을 black으로
y -> color = RBTREE_BLACK; //uncle의 색도 black으로
z -> parent -> parent -> color = RBTREE_RED; //조부모의 색을 red로 변경
z = z -> parent -> parent;
}
//case.2 삽입된 노드 z의 삼촌 y가 black이며 z가 오른쪽 자식인 경우 (triangle 모양)
else {
if (z == z -> parent -> right) {
z = z -> parent;
left_rotation(t, z);
} //triangle 모양일때는 left rotation과 (아래에서)right rotation 을 실시한다.(2회전)
//case.3 삽입된 노드 z의 삼촌 y가 black이며 z가 왼쪽 자식인 경우 (linear 모양)
z -> parent -> color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z -> parent -> parent -> color = RBTREE_RED;
right_rotation(t, z -> parent -> parent);
//linear 모양일때는 right_rotation만 실시한다. (1회전)
}
} else { //z의 부모가 조부모의 오른쪽 서브 트리일 경우
y = z -> parent -> parent ->left; //삼촌은 왼쪽에 있다.
//case.4 삽입된 노드 z의 삼촌 y가 red인 경우 (parent 도 red, uncle도 red)
if (y->color == RBTREE_RED) {
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
y->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
z = z->parent->parent;
}
//case.5 z의 삼촌 y가 black이며 z가 왼쪽 자식인 경우 (triangle 모양)
else {
if (z == z -> parent -> left) {
z = z -> parent;
right_rotation(t, z);
}
//case.6: z의 삼촌 y가 black이며 z가 오른쪽 자식인 경우 (linear 모양)
z -> parent -> color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z -> parent -> parent -> color = RBTREE_RED;
left_rotation(t, z -> parent -> parent);
}
}
}
t -> root -> color = RBTREE_BLACK; //root는 black
}
node_t *rbtree_insert(rbtree *t, const key_t key) {
node_t *y = t -> nil;
node_t *x = t -> root;
node_t *z = (node_t*) malloc(sizeof(node_t)); //z를 동적할당
z -> key = key; //z에 key 대입
while (x != t -> nil) {
y = x;
if (z -> key < x -> key) { //z의 key가 x의 key 보다 작다면
x = x -> left; //왼쪽으로
} else { // 작지 않으면(같은 경우 포함)
x = x -> right; //오른쪽으로
}
}
z -> parent = y;
if (y == t -> nil) { //z의 부모가 없다면 z가 root다.
t->root = z;
} else if (z -> key < y -> key) {
y -> left = z;
} else {
y -> right = z;
}
z -> left = t -> nil;
z -> right = t -> nil; //z의 자식들이 모두 NIL (z는 가장 아래)
z -> color = RBTREE_RED;
rbtree_insert_fixup(t, z);
return t -> root;
}회전
pseudo-code

스도코드를 처음 접했을 때, 코드만으로는 잘 이해가 안 되서 직접 손으로 그려보았다. 개발자는 컴퓨터를 통해 일을 하는 직업이지만 나는 어째 아날로그 도구인 펜과 노트가 있어야 머리에 들어온다.
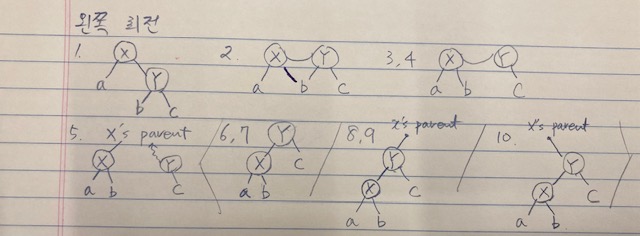
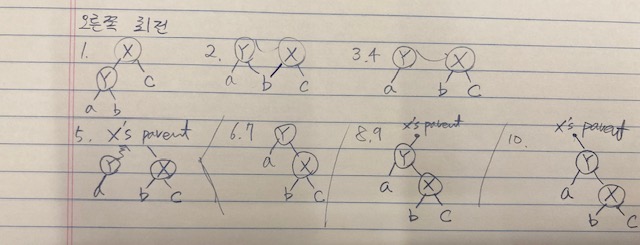
void right_rotation(rbtree *t, node_t *x) {
//1. target의 left로 y를 선언
node_t *y = x -> left;
//2. y의 오른쪽 서브트리를 target의 왼쪽 서브트리로 옮김
x -> left = y -> right;
//3. y의 오른쪽 노드가 NIL이 아니라면, y의 오른쪽 노드의 부모를 target으로 변경
if (y -> right != t -> nil) {
y -> right -> parent = x;
}
//4. y의 부모 노드를 target의 부모 노드로 설정
y -> parent = x -> parent;
//5. target의 부모 노드가 NIL 이라면 (target이 root인 경우) t 구조체의 root를 y로 설정 (target의 자리를 y가 차지)
if (x -> parent == t -> nil) {
t -> root = y;
//6. target이 target 부모 노드의 왼쪽이면, target 부모의 왼쪽을 y로 설정 (target의 자리를 y가 차지)
} else if (x == x -> parent -> left) {
x -> parent -> left = y;
//7. target이 target 부모 노드의 오른쪽이면, target 부모의 오른쪽을 y로 설정 (target의 자리를 y가 차지)
} else {
x -> parent -> right =y;
}
//8. target을 y의 오른쪽으로 설정
y -> right = x;
//9. target의 부모를 y로 설정
x -> parent = y;
}
void left_rotation(rbtree *t, node_t *x) { //right rotation의 반대
node_t *y = x->right;
x->right = y->left;
if (y->left != t->nil) {
y->left->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == t->nil) {
t->root = y;
} else if (x == x->parent->left) {
x->parent->left = y;
} else {
x->parent->right = y;
}
y -> left = x;
x -> parent = y;
}