1. Replay method의 처리 개요
- 저장된 transition 수 확인
1. 저장된 transition 수가 미니배치 크기보다 작으면 처리 중단 - 미니 배치 생성
2. memory 객체에서 랜덤으로 미니배치 크기와 같은 개수의 transition 추출
3. 각 상태 변수 미니 배치와 맞도록 변형
4. Neural Network를.eval()모드로 설정 - 정답신호로 사용할 계산
5. Neural Network의 output 값 계산
6. 계산. 이 때 존재 여부에 주의
7. Q-learning 수식으로 예측하는 계산 - weight 값 update
8. Neural Network를.train()모드로 설정
9. loss 함수로 loss 값 계산
10. weight 값 update
2. Replay method 상세 처리
- 저장된 transition 수 < mini batch 크기: 처리 중단
- 미니 배치 생성
random적으로 mini batch 크기만큼의transition을 꺼내서 이를transitions변수에 저장 (하나의transition은 한 step의 data).- 각 변수(state 및 action)를 mini batch에 해당하는 형태로 변환.
(state, action, state_next, reward) * BATCH_SIZE를(state*BATCH_SIZE, action*BATCH_SIZE, state_next*BATCH_SIZE, reward*BATCH_SIZE)형태로 변환. state는 1 x 4인torch.FloatTensor가BATCH_SIZE개 만큼 늘어선 형태로 돼 있음. 이를BATCH_SIZEx 4인torch.FloatTensor하나로 변환.- 다음 state()가 존재하는지 혹은 종료 상태인지에 따라 Q-learning 수정식이 달라짐. 이 시점에서
non_final_next_states라는 이름으로 다음 state()가 존재하는 state만을 모아놓은 미니배치를 따로 만듬.
- 정답신호(Neural Network의 output)로 사용할 계산
1. NN의 를 구하기 위해 NN을.eval()로 바꿔서 output 값 계산.
2. state에 해당하는 미니배치 변수인state_batch를 NN에 입력하고 이렇게 구한 output을gather를 사용해 실제 취했던 행동에 대한action_batch와 대응시킴.
3. 를 구함. 다음 state의 존재 여부에 주의. 다음 상태가 존재하지 않으면 이 값을 0으로.
이를 위해 이 존재하는 state의 index를 마스킹한non_final_mask만들기. 다음 상태가 존재하는 index만 계산
4. reward의 미니배치 변수(reward_batch)에 시간할인율GAMMA를 곱한 를 더하고 NN의 정답 신호인 계산.> Fixed Target Q-Network를 미니배치 학습으로 대체. - weight 값 update
- weight 값을 update하기 위해 NN을
.train()으로 변경 Huber함수(F.smooth_l1_loss)로 3.에서 구했던 와 현재 정답신호의 의 Error를 구한다.- 이 Error을 역전파시켜 각 weight의 미분을 구한 다음, 앞서 설정해 둔 optimizer(
Adam)으로 update한다.
- weight 값을 update하기 위해 NN을
detach()는 정답 신호를 계산할 때 NN의 출력값을 꺼내오는 역할. 이 method는 pytorch에서 변수가 갖고 있던 지금까지의 계산 이력을 잃어버리고, 오차 역전파를 할 때도 미분 계산되지 않음. 정답신호는 weight training에서 고정된 값이어야 한다.반면 NN이 실제 예측을 통해 출력된 는 미분 가능하도록
detach()를 호출하지 않고 이 값이 정답신호()에 가까워지도록 미분을 구하고 NN의 weight를 update하도록 한다.
3. 코드 구현
3.1 라이브러리 포함하기
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import gym
# key-value 쌍 형태로 값을 저장 가능
# key를 field명으로 값에 접근할 수 있어 편리
from collections import namedtuple
import random
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch import optim
import torch.nn.functional as F참고1.
namedTuple사용예시# 사용예시 Tr = namedtuple('tr', ('name_a', 'value_b')) Tr_object = Tr('이름A', 100) print(Tr_object) # tr(name_a='이름A', value_b=100) print(Tr_object.name_a) #이름
3.2 상태변수 값
Transition = namedtuple('Transition', ('state', 'action', 'next_state', 'reward'))3.3 상수 정의
ENV = 'CartPole-v1' # task
GAMMA = 0.99 # 시간할인율
MAX_STEPS = 200 # 한 episode당 최대 step 수
NUM_EPISODES = 500 # 최대 episode 수
BATCH_SIZE = 32
CAPACITY = 100003.4 ReplayMemory 구현
class ReplayMemory:
def __init__(self, CAPACITY):
self.capacity = CAPACITY # Memeory에 최대 저장 건수
self.memory = [] # 실제 transition을 저장할 Memory
self.index = 0 # 저장 위치를 가리킬 index
def push(self, state, action, state_next, reward):
'''transition = (state, action, state_next, reward) Memory에 저장'''
# 1. 메모리가 가득 차지 않은 경우
if len(self.memory) < self.capacity:
self.memory.append(None)
# 2. Transition 키-값 쌍의 형태로 값 저장
self.memory[self.index] = Transition(state, action, state_next, reward)
# push 했으니깐 다음 칸으로 index 옮기기.
self.index = (self.index + 1) % self.capacity
def sample(self, batch_size):
'''Memory에서 batch_size만큼 sampleing 하기'''
return random.sample(self.memory, batch_size)
def __len__(self):
'''len 함수로 현재 저장된 transition 개수 return'''
return len(self.memory)3.5 DQN 알고리즘 구현
# DQN 실제 수행
# Q함수를 딥러닝 신경망 형태로 정의
class Brain:
def __init__(self, num_states, num_actions):
self.num_actions = num_actions # 행동 수(왼쪽, 오른쪽)를 구함
# transition을 기억하기 위한 Memory 객체 10000개 생성
self.memory = ReplayMemory(CAPACITY)
# Linear(4,32) -> ReLU() -> Linear(32,32) -> ReLU() -> Linear(32,2)
self.model = nn.Sequential()
self.model.add_module('fc1', nn.Linear(num_states,32))
self.model.add_module('relu1', nn.ReLU())
self.model.add_module('fc2', nn.Linear(32,32))
self.model.add_module('relu2', nn.ReLU())
self.model.add_module('fc3', nn.Linear(32, num_actions))
# print(self.model) # 신경망 구조 출력
# 최적화 기법 선택
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.model.parameters(), lr= 0.0001)
def replay(self):
'''Experience Replay로 신경망의 weight 학습'''
# ------------------------
# 1. 저장된 transition의 수가 미니배치보다 작으면 아무것도 하지 않기
if len(self.memory) < BATCH_SIZE:
return
# ------------------------
# 2. 미니 배치 생성
# 2.1 ReplayMemory 객체의 sample 메소드로 미니 배치를 추출
transitions = self.memory.sample(BATCH_SIZE)
# 2.2 transition를 미니 배치에 맞는 형태로 변형
# transitions는 각 step 별로 (state, action, state_next, reward) 형태가 BATCH_SIZE만큼 저장됨.
# (state, action, state_next, reward) * BATCH_SIZE --->
# (state*BATCH_SIZE, action*BATCH_SIZE, state_next*BATCH_SIZE, reward*BATCH_SIZE) 형태로 변환
# 예시 zip(*[(1,'hello'),(1,2)]) -> [(1,1),('hello',2)]
batch = Transition(*zip(*transitions))
# 2.3 state의 요소들을 미니 배치에 맞게 변형 후 신경망으로 다룰 수 있는 변수로 변형.
# state를 예로 들면, [torch.FloatTensor of size 1*4] 형태의 요소가 BATCH_SIZE 개수만큼 있는 형태
# 이를 torch.FloatTensor of size BATCH_SIZE*4 형태로 변형
# state, action, reward, 최종이 아닌 state로 된 미니배치를 나타내는 변수 생성
state_batch = torch.cat(batch.state) # [BATCH_SIZE * 4]
action_batch = torch.cat(batch.action) # [BATCH_SIZE * 1]
reward_batch = torch.cat(batch.reward) # [BATCH_SIZE]
non_final_next_states = torch.cat([s for s in batch.next_state
if s is not None])
# ------------------------
# 3. 정답 신호로 사용할 Q(s_t, a_t) 계산
# 3.1 신경망 추론 모드로 전환
self.model.eval()
# 3.2 신경망으로 Q(s_t, a_t) 계산
# self.model(state_batch)은 각 action에 대한 Q 값 출력
# [BATCH_SIZE * 2] 형태. type은 FloatTensor
# 여기서부터 실행한 행동 a_t에 대한 Q 값을 계산하므로 action_batch에서 취한 행동
# action_batch에서 a_t가 0,1인지 index를 state별로 모아서 model의 output 값을 모으기.
# axis=1 방향
state_action_values = self.model(state_batch).gather(1, action_batch) # [BATCH_SIZE * 1]
# self.model(state.batch)를 통과한 output 값을, action_batch의 action index에 맞춰서 선택함.
# 3.3 max{(Q(s_t+1,a) 값 계산
# 다음 state 존재 확인 필요. None 상태가 아니고 next_state 존재 확인하는 index 마스크 만들기
# batch.next_state에 None에 따라서 tuple(map()) -> (False, False, False, True, False, ...)
# (False, False, False, True, False, ...) dtype=torch.bool
non_final_mask = torch.tensor(list(map(lambda s: s is not None, batch.next_state)), dtype=torch.bool) # [BATCH_SIZE * 1]
# 정답 신호 계산에 쓰일 next_state
# 먼저 전체를 0으로 초기화
next_state_values= torch.zeros(BATCH_SIZE) # [BATCH_SIZE]
# state_next가 있는 index에 대한 최대 Q 값 구하기
# model 출력 값에서 col 방향 최댓값(max(axis=1))이 되는 [value, index]를 구한다
# 그리고 Q 값(index=0)을 출력한 다음
# detach 메서드로 값 꺼내오기(학습과 독립적으로)
#print("특이점",self.model(non_final_next_states).max(1)[0].detach())
next_state_values[non_final_mask] = self.model(
non_final_next_states).max(1)[0].detach()
# 3.4 정답 신호로 사용할 Q(s_t, a_t) 값을 Q러닝 식으로 계산
expected_state_action_values = reward_batch + GAMMA * next_state_values # [BATCH_SIZE]
# 4. weight 수정
# 4.1 신경망 학습모드
self.model.train()
# 4.2 손실함수를 계산(smooth_l1_loss는 Huber))
# expected_state_action_values는 size가 [minibatch] -> unsqueez해서 [minibatch * 1]
loss = F.smooth_l1_loss(state_action_values,
expected_state_action_values.unsqueeze(1)) # axis=1에 새로운 차원 추가
# 4.3 model 가중치 수정 (model(state_batch).gather)
self.optimizer.zero_grad() # 경사 초기화
loss.backward() # 역전파 계산
self.optimizer.step() # 결합 가중치 수정
# 2024
def decide_action(self, state, episode):
'''현재 state에 따라 actioon 결정'''
# e-greedy 알고리즘에서 서서히 최적 행동의 비중을 늘림
epsilon = 0.5*(1/(episode+1))
if epsilon <= np.random.uniform(0,1):
self.model.eval() #신경망 추론 모드
with torch.no_grad():
action = self.model(state).max(1)[1].view(1,1)
else:
# 행동 무작위로 반환(0,1)
action=torch.LongTensor(
[[random.randrange(self.num_actions)]]) # 0 또는 1 중 행동을 무작위로 반환
# action은 [1*1] 형태 torch.LongTensor
return action
참고2.
.zip()사용법(1,'hello'),(2,'bye') -> [(1, 2), ('hello', 'bye')]a=zip(*[(1,'hello'),(2,'bye')]) print(list(a))
참고3.
namedtuple()과*zip(*)사용법from collections import namedtuple import random Transition = namedtuple('Transition', ('state', 'action','next_state','reward')) memory=[Transition(1,1,2,0), Transition(2,2,3,0), Transition(3,3,4,0), Transition(4,4,5,0)] transitions = random.sample(memory, 4) batch = Transition(*zip(*transitions)) torch.tensor(batch.state) #state_batch = torch.cat(list(batch.state))tensor([4, 1, 3, 2])
참고4.
.gather()사용법import torch tensor = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.2], [0.4, 0.5], [0.7, 0.8]]) action_batch = torch.tensor([1, 0, 0]) result = tensor.gather(1, action_batch.view(1,-1)) result.shape # torch.Size([1, 3])
참고5.
next_state_values[non_final_mask] = self.model(non_final_next_states).max(1)[0].detach()해석
.max(1)함수는 axis=1 으로 최댓값의 value tensor, indices tensor로 저장함.next_state = [1,2,3,4, None, 5, None] non_final_mask = torch.tensor(list(map(lambda s: s is not None, next_state)), dtype=torch.bool) # tensor([ True, True, True, True, False, True, False]) next_state_values = torch.zeros(7) non_final_output = torch.tensor([[0.25,0.75], [0.4,0.6], [0.7,0.3], [0.2,0.8], [0.55, 0.45]]) non_final_output.max(1)[0].detach() # tensor([0.7500, 0.6000, 0.7000, 0.8000, 0.5500]) next_state_values[non_final_mask] = non_final_output.max(1)[0].detach() next_state_values #tensor([0.7500, 0.6000, 0.7000, 0.8000, 0.0000, 0.5500, 0.0000])
3.6 Agent 정의
class Agent:
def __init__(self, num_states, num_actions):
'''task의 state 및 action 수를 설정'''
self.brain = Brain(num_states, num_actions) # Agent의 action을 결정할 Brain 객체 생성
def update_q_function(self):
'''Q 함수를 수정'''
self.brain.replay()
def get_action(self, state, episode):
'''action 결정'''
action = self.brain.decide_action(state, episode)
return action
def memorize(self, state, action, state_next, reward):
''' memory 객체에 state, action, state_next, reward 내용 저장'''
self.brain.memory.push(state, action, state_next, reward) 3.7 Environment 정의
# CartPole을 실행헐 환경 정의
class Environment:
def __init__(self):
self.env = gym.make(ENV, render_mode='human') # task 설정
num_states = self.env.observation_space.shape[0] # task 상태 변수 수 4
num_actions = self.env.action_space.n # task action 수 2
self.agent = Agent(num_states, num_actions) # agent 객체 생성
def run(self):
'''실행'''
episode_10_list = np.zeros(10) # 최근 10 episode 동안 버틴 단계 수를 저장
# (평균 step 수 출력)
complete_episodes = 0 # 현재까지 195단계를 버틴 episode 수
episode_final = False # 마지막 episode 여부
for episode in range(NUM_EPISODES):
observation = self.env.reset()[0] # 환경 초기화
state = observation # 관측을 변환 없이 그대로 state s로 사용\
state = torch.from_numpy(state).type(torch.FloatTensor) # NumPy 변수 - Pytorch Tensor로 변환
state = torch.unsqueeze(state, 0) # size 4를 size 1*4로 변환
for step in range(MAX_STEPS): # 1 episode
action = self.agent.get_action(state, episode) # 다음 행동 결정
# 행동 a_t를 실행해 다음상태 s_{t+1}과 done 플래그 값 결정
# action에 .item()을 호출해 행동 내용을 구함
observation_next, _, done, _, _ = self.env.step(action.item()) # reward와 info는 사용하지 않음
# 보상을 부여하고 episode의 종료 판정 및 state_next를 설정
if done: # step > 200, 봉이 일정 각도 이상 기울면
state_next = None
# 최근 10 episdoe에서 버틴 step 수를 list에 저장
episode_10_list = np.hstack( (episode_10_list[1:], step+1) )
if step < 195:
reward = torch.FloatTensor([-1.0])
complete_episodes = 0
else:
reward = torch.FloatTensor([1.0])
complete_episodes = complete_episodes+1
else:
reward = torch.FloatTensor([0.0])
state_next = observation_next
state_next = torch.from_numpy(state_next).type(torch.FloatTensor)
state_next = torch.unsqueeze(state_next, 0)
# memory에 경험 저장
self.agent.memorize(state, action, state_next, reward)
# Experience Replay로 Q 함수 수정
self.agent.update_q_function()
# 관측 결과를 update
state = state_next
# episdoe 종료 처리
if done:
print('%d Episode: Finished after %d steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = %.1lf' % (episode, step+1, episode_10_list.mean()))
break
if episode_final is True:
# anmiation 생성 및 저장
break
# 10 episode 연속으로 200단계 버티면 task 성공
if complete_episodes >=10:
print('10 episode 연속 성공')
episode_final = True # 종료 생성
3.8 Entry 실행
cartpole_env = Environment()
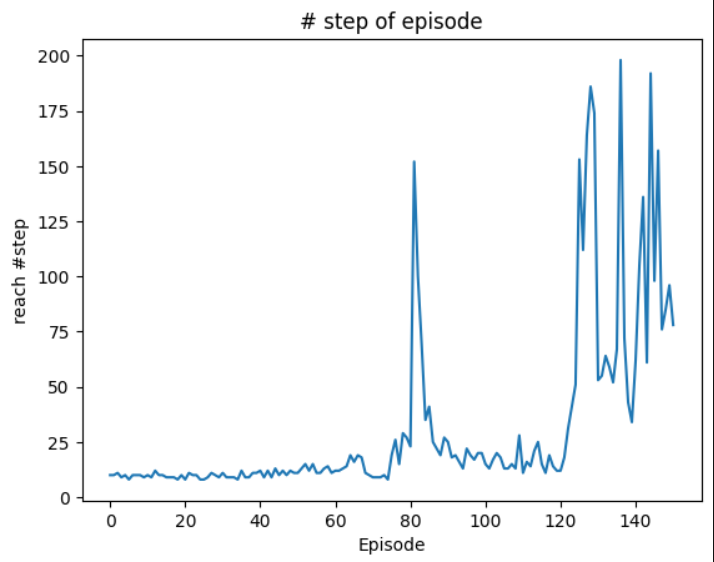
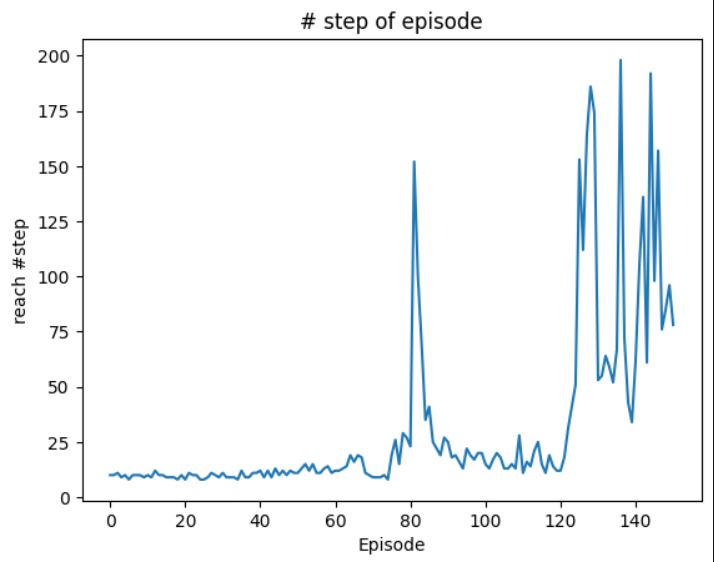
cartpole_env.run()4 학습결과
0 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 1.0
1 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 2.0
2 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 3.1
3 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 4.0
4 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 5.0
5 Episode: Finished after 8 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 5.8
6 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 6.8
7 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 7.8
8 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 8.8
9 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.7
10 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.7
11 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.6
12 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.7
13 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.8
14 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.8
15 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.9
16 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.8
17 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.7
18 Episode: Finished after 8 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.5
19 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.6
20 Episode: Finished after 8 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.4
21 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.6
22 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.4
23 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.4
24 Episode: Finished after 8 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.2
25 Episode: Finished after 8 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.1
26 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.1
27 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.3
28 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.5
29 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.4
30 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.7
31 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.5
32 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.4
33 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.3
34 Episode: Finished after 8 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.3
35 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.7
36 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.7
37 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.5
38 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.6
39 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.8
40 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.9
41 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 9.9
42 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 10.2
43 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 10.2
44 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 10.7
45 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 10.5
46 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 10.8
47 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 10.9
48 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 11.0
49 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 11.0
50 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 10.9
51 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 11.3
52 Episode: Finished after 15 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 11.6
53 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 11.9
54 Episode: Finished after 15 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.1
55 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.2
56 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.1
57 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.4
58 Episode: Finished after 14 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.6
59 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.6
60 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.7
61 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.6
62 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.4
63 Episode: Finished after 14 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.6
64 Episode: Finished after 19 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 13.0
65 Episode: Finished after 16 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 13.5
66 Episode: Finished after 19 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 14.3
67 Episode: Finished after 18 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 14.8
68 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 14.5
69 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 14.4
70 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 14.1
71 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 13.8
72 Episode: Finished after 9 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 13.4
73 Episode: Finished after 10 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 13.0
74 Episode: Finished after 8 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 11.9
75 Episode: Finished after 19 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.2
76 Episode: Finished after 26 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.9
77 Episode: Finished after 15 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 12.6
78 Episode: Finished after 29 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 14.4
79 Episode: Finished after 27 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.1
80 Episode: Finished after 23 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.5
81 Episode: Finished after 152 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 31.8
83 Episode: Finished after 100 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 40.9
84 Episode: Finished after 69 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 46.8
85 Episode: Finished after 35 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 49.5
86 Episode: Finished after 41 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 51.7
87 Episode: Finished after 25 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 51.6
88 Episode: Finished after 22 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 52.3
89 Episode: Finished after 19 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 51.3
90 Episode: Finished after 27 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 51.3
91 Episode: Finished after 25 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 51.5
92 Episode: Finished after 18 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 38.1
93 Episode: Finished after 19 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 30.0
94 Episode: Finished after 16 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 24.7
95 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 22.5
96 Episode: Finished after 22 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 20.6
97 Episode: Finished after 19 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 20.0
98 Episode: Finished after 17 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 19.5
99 Episode: Finished after 20 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 19.6
100 Episode: Finished after 20 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 18.9
101 Episode: Finished after 15 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.9
102 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.4
103 Episode: Finished after 17 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.2
104 Episode: Finished after 20 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.6
105 Episode: Finished after 18 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 18.1
106 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.2
107 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.6
108 Episode: Finished after 15 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.4
109 Episode: Finished after 13 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 15.7
110 Episode: Finished after 28 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.5
111 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.1
112 Episode: Finished after 16 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.4
113 Episode: Finished after 14 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.1
114 Episode: Finished after 21 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.2
115 Episode: Finished after 25 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.9
116 Episode: Finished after 15 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.1
117 Episode: Finished after 11 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.9
118 Episode: Finished after 19 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.3
119 Episode: Finished after 14 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.4
120 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 15.8
121 Episode: Finished after 12 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 15.9
122 Episode: Finished after 18 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 16.1
123 Episode: Finished after 31 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 17.8
124 Episode: Finished after 41 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 19.8
125 Episode: Finished after 51 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 22.4
126 Episode: Finished after 153 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 36.2
127 Episode: Finished after 112 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 46.3
128 Episode: Finished after 164 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 60.8
129 Episode: Finished after 186 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 78.0
130 Episode: Finished after 174 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 94.2
131 Episode: Finished after 53 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 98.3
132 Episode: Finished after 55 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 102.0
133 Episode: Finished after 64 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 105.3
134 Episode: Finished after 59 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 107.1
135 Episode: Finished after 52 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 107.2
136 Episode: Finished after 67 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 98.6
137 Episode: Finished after 198 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 107.2
138 Episode: Finished after 72 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 98.0
139 Episode: Finished after 43 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 83.7
140 Episode: Finished after 34 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 69.7
141 Episode: Finished after 62 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 70.6
142 Episode: Finished after 105 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 75.6
143 Episode: Finished after 136 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 82.8
144 Episode: Finished after 61 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 83.0
146 Episode: Finished after 192 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 97.0
147 Episode: Finished after 98 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 100.1
148 Episode: Finished after 157 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 96.0
149 Episode: Finished after 76 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 96.4
150 Episode: Finished after 85 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 100.6
151 Episode: Finished after 96 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 106.8
152 Episode: Finished after 78 steps: 최근 10 Episode의 평균 단계 수 = 108.4결과 그래프