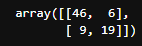
혼돈 행렬(Confusion Matrix)
- 분류 모델의 성능을 평가하는 데 사용하는 표
- 예측값과 실제값을 비교하여 모델이 얼마나 정확하게 분류했는지 확인 할 수 있음
| 실제 값 \ 예측 값 | Positive (P) | Negative (N) | 설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (P) | TP (True Positive) | FN (False Negative) | 실제 Positive를 올바르게 예측 |
| Negative (N) | FP (False Positive) | TN (True Negative) | 실제 Negative를 올바르게 예측 |
-
정확도(Accuracy)
전체 데이터 중에서 올바르게 예측한 비율을 의미 -
정밀도(Precision)
모델이 Positive라고 예측한 것 중에서 실제로 Positive인 비율을 의미 -
재현율(Recall)
실제 Positive 중에서 모델이 Positive라고 예측한 비율을 의미 -
F1-스코어(F1-Score)
Precision과 Recall의 조화 평균으로, 두 값이 균형을 이루도록 함
classification_report()
- Scikit-learn의 metrics 모듈에서 제공하는 분류 모델의 평가 지표를 출력해주는 함수
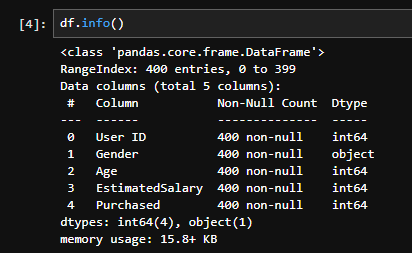
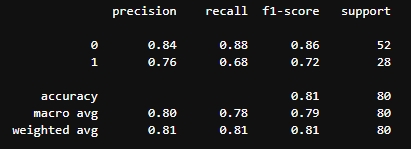
classification_report()를 통해 정확도, 정밀도, 재현율, F1-스코어, Support의 값을 확인 할 수 있음
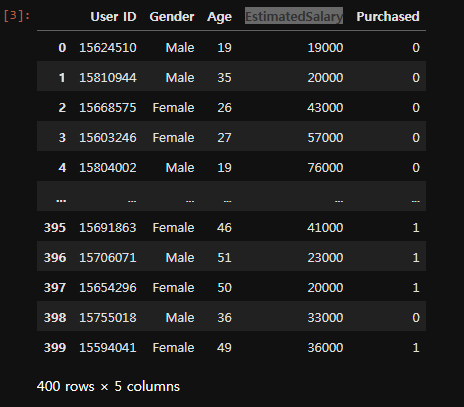
사용 cvs 정보
이상치 해결
- traindata에서 Age와 EstimatedSalary의 값 차이가 크기 때문에 이상치를 해결해야함
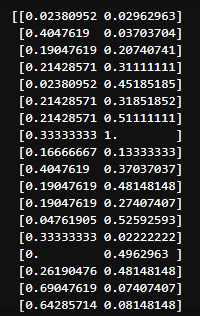
- MinMaxScaler
minmax_scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X = minmax_scaler.fit_transform(X)
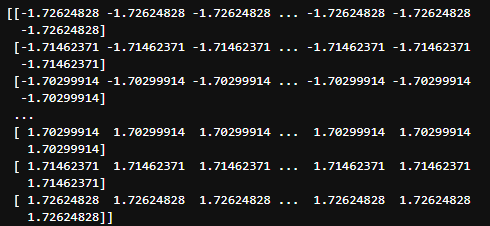
print(X)- StandardScaler
X2 = df.loc[:, 'Age':'EstimatedSalary']
stand_scaler = StandardScaler()
X2 = stand_scaler.fit_transform(X2)train, test 데이터 분류및 모델 학습
X = df.loc[:, 'Age':'EstimatedSalary'] # train_data
y = df['Purchased'] #target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size= 0.2)
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}")confusion_matrix, classification_report
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test ,y_pred)
print(cm)
cr = classification_report(y_test ,y_pred)
print(cr)ROC Curve와 AUC
ROC Curve
-
이진 분류 모델의 성능을 평가하는 그래프
-
TPR(True Positive Rate)는 Positive로 예측된 것들 중 진짜 Positive인 것의 비율을 나타냅니다.
-
TNR(True Negative Rate)는 Negative로 예측된 것들 중 진짜 Negative인 것의 비율을 나타냅니다.
-
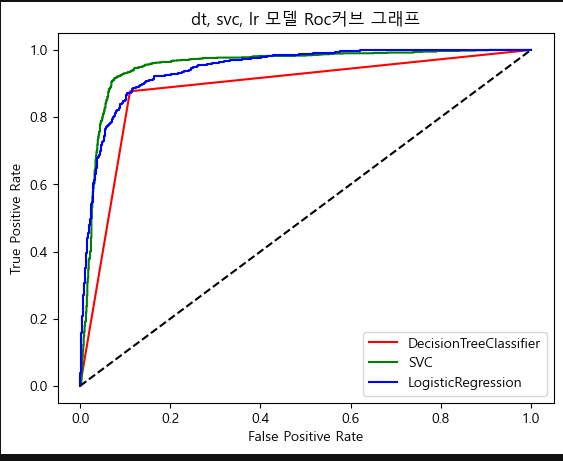
ROC를 이용하여 DecisionTreeClassifier, LogisticRegression, SVC 평가
# 데이터 발생 (데이터 열기)
X, y = make_classification(n_samples = 10000, n_classes = 2, random_state = 42) # random_state = 42로 많이 설정(약속)
tate = 42)
# 데이터 분리
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2)
# 모델 생성 및 학습
# 데이터 생성, 데이터 훈련 테스트 분리, 모델생성/ 모델fit()/predict(x_test)
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier()
lr = LogisticRegression()
svc = SVC(probability=True)
dt.fit(X_train,y_train)
svc.fit(X_train,y_train)
lr.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_pred_dt = dt.predict_proba(X_test) # 예측보다는 성능의 비교, 입계 = 경계 threshold
y_pred_svc = svc.predict_proba(X_test)
y_pred_lr = lr.predict_proba(X_test)
fpr_dt, tpr_dt, z = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred_dt[:, 1])
fpr_svc, tpr_svc, z = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred_svc[:, 1])
fpr_lr, tpr_lr, z = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred_lr[:, 1])
plt.plot(fpr_dt, tpr_dt, color='r', label = 'DecisionTreeClassifier')
plt.plot(fpr_svc, tpr_svc, color='g', label = 'SVC')
plt.plot(fpr_lr, tpr_lr, color='b', label = 'LogisticRegression')
plt.plot([0,1], [0,1], 'k--')
plt.title('dt, svc, lr 모델 Roc커브 그래프')
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.legend()
plt.show()AUC
- ROC 곡선 아래 면적
- 분류 모델의 성능을 평가하는 지표
- 1에 가까울수록 모델이 좋은 성능을 보임
- 0.8이상이면 좋은 모델
AUC 값 범위: 0 ~ 1
AUC = 1 → 완벽한 모델 (100% 정확한 분류)
AUC = 0.5 → 랜덤 예측과 동일한 성능 (무의미한 모델)
AUC < 0.5 → 성능이 최악 (반대로 예측하는 경우)
# 5. AUC Area Under Curve -
# roc_auc_score, roc_curve
auc_dt = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_dt[:, 1])
auc_dt
auc_svc = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_svc[:, 1])
auc_svc
auc_lr = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_lr[:, 1])
auc_lr
- auc_dt
0.8830377893604171- auc_svc
0.9526812965266749- auc_lr
0.9438979803272917