Activity
An activity is the entry point for interacting with the user. It represents a single screen with a user interface.
Activity는 사용자에게 보이는 화면이다.
모바일 환경에서 다양한 어플리케이션이 서로를 호출할 수 있도록 Activity는 설계되었다.
그렇기에 진입점이 main()으로 고정되는 여타 프로그램과 달리, 안드로이드는 Activity가 하나의 진입점이 된다.
Lifecycle
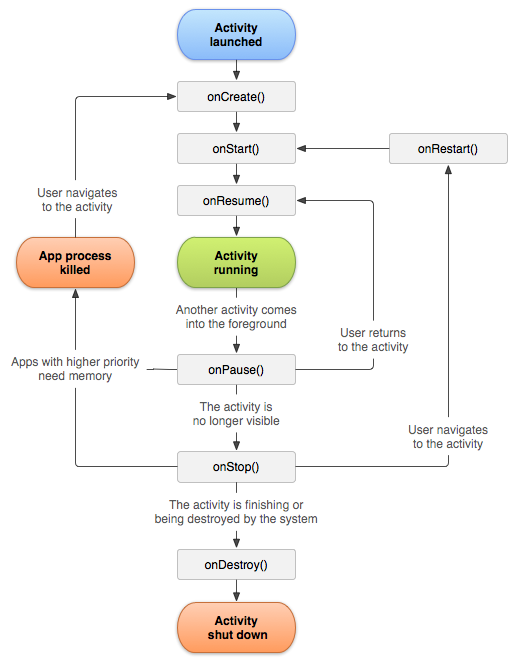
onCreate
On activity creation, the activity enters the
Created state. In theonCreate()method, perform basic application startup logic that happens only once for the entire life of the activity.
Lifecycle을 통틀어 단 한번 실행된다.
- 변수 초기화
- View 생성
아직 사용자에게 화면이 보이지 않는다.
onStart
When the activity enters the
Started state, the system invokesonStart(). This call makes the activity visible to the user as the app prepares for the activity to enter the foreground and become interactive.
사용자에게 화면이 보여진다.
사용자가 화면과 상호작용은 할 수 없다.
onResume
When the activity enters the
Resumed state, it comes to the foreground, and the system invokes theonResume()callback. This is the state in which the app interacts with the user. The app stays in this state until something happens to take focus away from the app.
사용자가 화면과 상호작용할 수 있다.
포커스를 잃기 전까지 이 상태에 머무른다.
onPause
When an interruptive event occurs, the activity enters the
Paused stateand the system invokes theonPause()callback.
포그라운드의 포커스를 잃을 때 호출된다.
- 다른 Activity가 실행
- Dialog가 올라옴
- 홈 버튼을 누름
- 다른 앱이 올라옴
- 화면이 꺼짐
- 멀티 윈도우 모드에서 다른 앱으로 넘어감
상황에 따라 사용자가 화면을 보는 것이 가능할 수 있다.
onStop
When your activity is no longer visible to the user, it enters the Stopped state, and the system invokes the onStop() callback. This can occur when a newly launched activity covers the entire screen. The system also calls onStop() when the activity finishes running and is about to be terminated.
사용자에게 화면이 완전히 보이지 않는다.
onDestroy
onDestroy() is called before the activity is destroyed. The system invokes this callback for one of two reasons:
- The activity is finishing, due to the user completely dismissing the activity or due to finish() being called on the activity.
- The system is temporarily destroying the activity due to a configuration change, such as device rotation or entering multi-window mode.
두 경우 중 어느것인지는 isFinishing() 메소드를 통해 알 수 있다.
There are situations where the system will simply kill the activity's hosting process without calling this method
시스템이 메모리 해제를 위해 프로세스를 종료시킬 때는 onDestroy 호출을 보장하지 않는다.
따라서 중요한 데이터 저장은 onStop에서 이루어지는 것이 안전하다.
Lifecycle Event & State
안드로이드에서는 Activity의 라이프사이클을 이벤트와 상태로 확인할 수 있다.
Lifecycle.Eventpublic enum class Event {
/**
* Constant for onCreate event of the [LifecycleOwner].
*/
ON_CREATE,
/**
* Constant for onStart event of the [LifecycleOwner].
*/
ON_START,
/**
* Constant for onResume event of the [LifecycleOwner].
*/
ON_RESUME,
/**
* Constant for onPause event of the [LifecycleOwner].
*/
ON_PAUSE,
/**
* Constant for onStop event of the [LifecycleOwner].
*/
ON_STOP,
/**
* Constant for onDestroy event of the [LifecycleOwner].
*/
ON_DESTROY,
/**
* An [Event] constant that can be used to match all events.
*/
ON_ANY;
/**
* Returns the new [Lifecycle.State] of a [Lifecycle] that just reported
* this [Lifecycle.Event].
*
* Throws [IllegalArgumentException] if called on [.ON_ANY], as it is a special
* value used by [OnLifecycleEvent] and not a real lifecycle event.
*
* @return the state that will result from this event
*/
public val targetState: State
get() {
when (this) {
ON_CREATE, ON_STOP -> return State.CREATED
ON_START, ON_PAUSE -> return State.STARTED
ON_RESUME -> return State.RESUMED
ON_DESTROY -> return State.DESTROYED
ON_ANY -> {}
}
throw IllegalArgumentException("$this has no target state")
}
public companion object {
/**
* Returns the [Lifecycle.Event] that will be reported by a [Lifecycle]
* leaving the specified [Lifecycle.State] to a lower state, or `null`
* if there is no valid event that can move down from the given state.
*
* @param state the higher state that the returned event will transition down from
* @return the event moving down the lifecycle phases from state
*/
@JvmStatic
public fun downFrom(state: State): Event? {
return when (state) {
State.CREATED -> ON_DESTROY
State.STARTED -> ON_STOP
State.RESUMED -> ON_PAUSE
else -> null
}
}
/**
* Returns the [Lifecycle.Event] that will be reported by a [Lifecycle]
* entering the specified [Lifecycle.State] from a higher state, or `null`
* if there is no valid event that can move down to the given state.
*
* @param state the lower state that the returned event will transition down to
* @return the event moving down the lifecycle phases to state
*/
@JvmStatic
public fun downTo(state: State): Event? {
return when (state) {
State.DESTROYED -> ON_DESTROY
State.CREATED -> ON_STOP
State.STARTED -> ON_PAUSE
else -> null
}
}
/**
* Returns the [Lifecycle.Event] that will be reported by a [Lifecycle]
* leaving the specified [Lifecycle.State] to a higher state, or `null`
* if there is no valid event that can move up from the given state.
*
* @param state the lower state that the returned event will transition up from
* @return the event moving up the lifecycle phases from state
*/
@JvmStatic
public fun upFrom(state: State): Event? {
return when (state) {
State.INITIALIZED -> ON_CREATE
State.CREATED -> ON_START
State.STARTED -> ON_RESUME
else -> null
}
}
/**
* Returns the [Lifecycle.Event] that will be reported by a [Lifecycle]
* entering the specified [Lifecycle.State] from a lower state, or `null`
* if there is no valid event that can move up to the given state.
*
* @param state the higher state that the returned event will transition up to
* @return the event moving up the lifecycle phases to state
*/
@JvmStatic
public fun upTo(state: State): Event? {
return when (state) {
State.CREATED -> ON_CREATE
State.STARTED -> ON_START
State.RESUMED -> ON_RESUME
else -> null
}
}
}
}/**
* Lifecycle states. You can consider the states as the nodes in a graph and
* [Event]s as the edges between these nodes.
*/
public enum class State {
/**
* Destroyed state for a LifecycleOwner. After this event, this Lifecycle will not dispatch
* any more events. For instance, for an [android.app.Activity], this state is reached
* **right before** Activity's [onDestroy][android.app.Activity.onDestroy] call.
*/
DESTROYED,
/**
* Initialized state for a LifecycleOwner. For an [android.app.Activity], this is
* the state when it is constructed but has not received
* [onCreate][android.app.Activity.onCreate] yet.
*/
INITIALIZED,
/**
* Created state for a LifecycleOwner. For an [android.app.Activity], this state
* is reached in two cases:
*
* * after [onCreate][android.app.Activity.onCreate] call;
* * **right before** [onStop][android.app.Activity.onStop] call.
*
*/
CREATED,
/**
* Started state for a LifecycleOwner. For an [android.app.Activity], this state
* is reached in two cases:
*
* * after [onStart][android.app.Activity.onStart] call;
* * **right before** [onPause][android.app.Activity.onPause] call.
*
*/
STARTED,
/**
* Resumed state for a LifecycleOwner. For an [android.app.Activity], this state
* is reached after [onResume][android.app.Activity.onResume] is called.
*/
RESUMED;
/**
* Compares if this State is greater or equal to the given `state`.
*
* @param state State to compare with
* @return true if this State is greater or equal to the given `state`
*/
public fun isAtLeast(state: State): Boolean {
return compareTo(state) >= 0
}
}특이한 점은 Event는 Activity 라이프사이클의 onRestart외에 모든 콜백 이벤트를 가지고 있지만, State는 onPause, onStop에 대응하는 상태를 가지고 있지 않다는 점이다.
class ActivityLifecycleObserver(private val lifecycleOwner: LifecycleOwner) :
LifecycleEventObserver {
private val TAG = "ActivityLifecycleObserver"
init {
lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.addObserver(this)
}
override fun onStateChanged(source: LifecycleOwner, event: Lifecycle.Event) {
when (event) {
Lifecycle.Event.ON_CREATE -> Log.d(TAG, "onCreate : ${lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.currentState}")
Lifecycle.Event.ON_START -> Log.d(TAG, "onStart : ${lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.currentState}")
Lifecycle.Event.ON_RESUME -> Log.d(TAG, "onResume : ${lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.currentState}")
Lifecycle.Event.ON_PAUSE -> Log.d(TAG, "onPause : ${lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.currentState}")
Lifecycle.Event.ON_STOP -> Log.d(TAG, "onStop : ${lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.currentState}")
Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY -> Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy : ${lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.currentState}")
Lifecycle.Event.ON_ANY -> Log.d(TAG, "onAny : ${lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.currentState}")
else -> Log.d(TAG, "onStateChanged: ${lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.currentState}")
}
}
}실행 -> 네비게이션 버튼 -> 재개 -> 홈버튼
onCreate : CREATED
onStart : STARTED
onResume : RESUMED
onPause : STARTED
onStop : CREATED
onStart : STARTED
onResume : RESUMED
onPause : STARTED
onStop : CREATED
onDestroy : DESTROYEDonPause에서도 State는 STARTED이고 onStop에서는 CREATED인 것을 알 수 있다.
또한, onRestart 콜백은 이벤트로 존재하지 않기 때문에, 라이프사이클 옵저버로 재시작인지 체크하기 위한 추가적인 구현을 하거나 Activity에 직접 onRestart를 오버라이딩해야한다.
