Collection Framework
다수의 데이터를 쉽고 효과적으로 처리할 수 있는 Framework 을 사용하여 데이터를 주입해보겠다.
자바의 Framework란 JAVA-Framework 포스트를 참고하면 좋겠다.
보통 Spring에서 데이터를 주입하고 넘겨줄 때 Setter Injection을 사용하여 넘겨주는데, Framework도 비슷하다.
xml bean property에 Collection Framework 사용하기
값을 저장하는 저장소, Person 클래스 전체코드
package com.gdu.app1.xml06;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
// Collection Framework(List, Set, Map)에 주입
public class Person {
// field
private List<String> hobbies;
private Set<String> contacts;
private Map<String, String> friends;
// method + getter + setter
public List<String> getHobbies() {
return hobbies;
}
public void setHobbies(List<String> hobbies) {
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
public Set<String> getContacts() {
return contacts;
}
public void setContacts(Set<String> contacts) {
this.contacts = contacts;
}
public Map<String, String> getFriends() {
return friends;
}
public void setFriends(Map<String, String> friends) {
this.friends = friends;
}
// info() 메소드
public void info() {
// List
for(int i = 0; i <hobbies.size(); i++) {
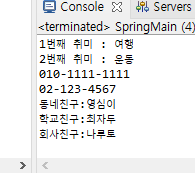
System.out.println((i + 1) + "번째 취미 : " + hobbies.get(i));
}
// Set (인덱스 없음 : 향상 for문만 가능)
for(String contact : contacts) {
System.out.println(contact);
}
// Map (Key + Value ==> Entry)
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : friends.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
field
1) Class를 만들어 field를 선언해준다.
// field
private List<String> hobbies;
private Set<String> contacts;
private Map<String, String> friends;getter/setter
그리고, source - generate getters and setters ... 에서 getter / setter를 만들어준다.**
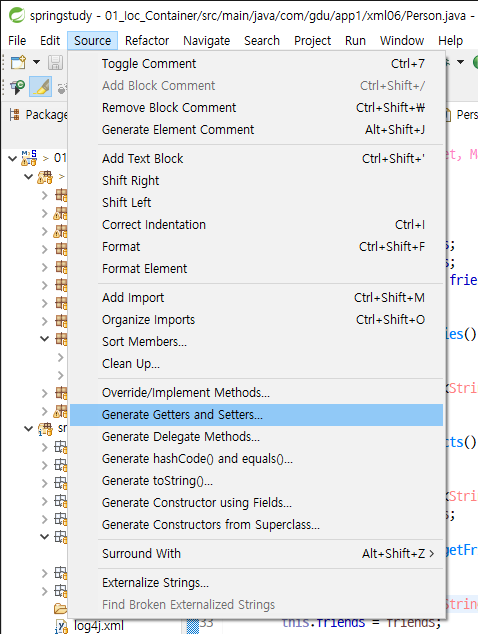
getter/setter
public List<String> getHobbies() {
return hobbies;
}
public void setHobbies(List<String> hobbies) {
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
public Set<String> getContacts() {
return contacts;
}
public void setContacts(Set<String> contacts) {
this.contacts = contacts;
}
public Map<String, String> getFriends() {
return friends;
}
public void setFriends(Map<String, String> friends) {
this.friends = friends;
}info() method
각 List와 Set, Map에 값을 넣기위한 메소드를 만들어 준다.
public void info() {
// List
for(int i = 0; i <hobbies.size(); i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + "번째 취미 : " + hobbies.get(i));
}
// Set (인덱스 없음 : 향상 for문만 가능)
for(String contact : contacts) {
System.out.println(contact);
}
// Map (Key + Value ==> Entry)
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : friends.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}값을 지정해주는 appCtx.xml, Spring Bean Configuration File
전체코드
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="human" class="com.gdu.app1.xml06.Person">
<!-- Property 태그는 Setter를 이용해서 데이터를 주입합니다. Setter가 없으면 안된다. (Setter Injection) -->
<!-- List -->
<!-- List속성은 <list>태그를 사용하면 된다. -->
<property name="hobbies">
<list>
<value>여행</value>
<value>운동</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- Set -->
<!-- Set 속성은 <set> 태그를 사용하면 된다. -->
<property name="contacts">
<set>
<value>010-1111-1111</value>
<value>010-1111-1111</value>
<value>010-1111-1111</value> <!-- 인덱스는 없으나, 중복데이터 저장 x -->
<value>02-123-4567</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- Map -->
<!-- Map 속성은 <map> 태그와 <entry>태그를 사용하며, key와 value값을 속성으로 준다.-->
<property name="friends">
<map>
<entry key="동네친구" value="영심이"/>
<entry key="학교친구" value="최자두"/>
<entry key="회사친구" value="나루토"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
- List는
<List>태그를 이용하여, value에 값을 넣어준다. - Set은
<Set>태그를 이용하여, value에 값을 넣어준다. - Map은
<Map>태그를 이용하여, value에 값을 넣어준다. - xml을 이용한 스프링 설정 파일에서는 컨테이너가 생성할 객체를 지정하기 위해
<bean>태그를 사용한다. (일반 JAVA 객체와 동일)
실행시키는 Main Class
package com.gdu.app1.xml06;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("xml06/appCtx.xml");
Person p = ctx.getBean("human", Person.class);
p.info();
ctx.close();
}
}
getBean()메소드에는 bean의 id값을 넣어주면 된다.AbstractApplicationContext: 컨테이너 종료(close)와 같은 기능을 제공해 주는 객체.ex] ctx.close()GenericXmlApplicationContext클래스는 xml파일(Spring Bean Configuration File)에 정의된 설정 정보를 읽어와서 객체를 생성하고, 각각의 객체를 연결한 뒤에 내부적으로 보관한다.
결과