Operations
torch.cat
- 설명: 여러 텐서를 주어진 차원(dim)에서 연결(concatenate)합니다.
- 예시:
import torch a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) b = torch.tensor([[5, 6], [7, 8]]) c = torch.cat((a, b), dim=0) # shape: (4, 2) d = torch.cat((a, b), dim=1) # shape: (2, 4)
torch.stack
- 설명: 입력 텐서들을 새로운 차원(dim)을 추가하여 쌓습니다.
- 예시:
import torch a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6]) c = torch.stack((a, b), dim=0) # shape: (2, 3) d = torch.stack((a, b), dim=1) # shape: (3, 2)
torch.cat과 torch.stack의 차이:
torch.cat은 기존 차원 중 하나에서 텐서들을 이어붙입니다.torch.stack은 새로운 차원을 추가하여 텐서들을 쌓습니다.
tensor.expand
- 설명: 텐서를 특정한 크기로 확장하지만, 메모리를 실제로 복사하지 않고, 뷰(view)를 생성합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = a.expand(3, 3) # shape: (3, 3)
tensor.repeat
- 설명: 텐서를 지정된 크기만큼 반복하여 새로운 텐서를 생성합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = a.repeat(3, 1) # shape: (3, 3)
tensor.add
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별(element-wise) 덧셈 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6]) c = a.add(b) # tensor([5, 7, 9])
tensor.add_
- 설명:
add와 동일하지만, in-place 연산으로 결과를 첫 번째 텐서에 저장합니다. - 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6]) a.add_(b) # a는 tensor([5, 7, 9])로 변함
tensor.sub
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별 뺄셈 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6]) c = a.sub(b) # tensor([-3, -3, -3])
tensor.sub_
- 설명:
sub와 동일하지만, in-place 연산으로 결과를 첫 번째 텐서에 저장합니다. - 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6]) a.sub_(b) # a는 tensor([-3, -3, -3])로 변함
tensor.mul
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별 곱셈 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6]) c = a.mul(b) # tensor([4, 10, 18])
tensor.mul_
- 설명:
mul와 동일하지만, in-place 연산으로 결과를 첫 번째 텐서에 저장합니다. - 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6]) a.mul_(b) # a는 tensor([4, 10, 18])로 변함
tensor.div
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별 나눗셈 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([4, 9, 16]) b = torch.tensor([2, 3, 4]) c = a.div(b) # tensor([2, 3, 4])
tensor.div_
- 설명:
div와 동일하지만, in-place 연산으로 결과를 첫 번째 텐서에 저장합니다. - 예시:
a = torch.tensor([4, 9, 16]) b = torch.tensor([2, 3, 4]) a.div_(b) # a는 tensor([2, 3, 4])로 변함
torch.pow
- 설명: 텐서의 각 요소를 주어진 지수(exponent)로 거듭 제곱합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.pow(a, 2) # tensor([1, 4, 9])
torch.pow_
- 설명:
pow와 동일하지만, in-place 연산으로 결과를 첫 번째 텐서에 저장합니다. - 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) a.pow_(2) # a는 tensor([1, 4, 9])로 변함
torch.eq
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별 비교 결과를 반환합니다 (같으면 True, 다르면 False).
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([1, 0, 3]) c = torch.eq(a, b) # tensor([True, False, True])
torch.ne
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별 비교 결과를 반환합니다 (다르면 True, 같으면 False).
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([1, 0, 3]) c = torch.ne(a, b) # tensor([False, True, False])
torch.gt
- 설명: 첫 번째 텐서가 두 번째 텐서보다 큰 요소들을 비교하여 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([1, 0, 3]) c = torch.gt(a, b) # tensor([False, True, False])
torch.ge
- 설명: 첫 번째 텐서가 두 번째 텐서보다 크거나 같은 요소들을 비교하여 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([1, 0, 3]) c = torch.ge(a, b) # tensor([True, True, True])
torch.lt
- 설명: 첫 번째 텐서가 두 번째 텐서보다 작은 요소들을 비교하여 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([1, 0, 3]) c = torch.lt(a, b) # tensor([False, False, False])
torch.le
- 설명: 첫 번째 텐서가 두 번째 텐서보다 작거나 같은 요소들을 비교하여 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([1, 0, 3]) c = torch.le(a, b) # tensor([True, False, True])
torch.logical_and
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별 논리 AND 연산 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([True, False, True]) b = torch.tensor([True, True, False]) c = torch.logical_and(a, b) # tensor([True, False, False])
torch.logical_or
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별 논리 OR 연산 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([True, False, True]) b = torch.tensor([True, True, False]) c = torch.logical_or(a, b) # tensor([True, True, True])
torch.logical_xor
- 설명: 두 텐서의 요소별 논리 XOR 연산 결과를 반환합니다.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([True, False, True]) b = torch.tensor([True, True, False]) c = torch.logical_xor(a, b) # tensor([False, True, True])
Ln Norm (노름)
torch.norm(L1 노름)
- 설명: 텐서의 각 요소 절댓값의 합을 계산함.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, -2, 3]) norm_l1 = torch.norm(a, p=1) # L1 노름: 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
torch.norm(a, p=2)(L2 노름)
- 설명: 텐서의 각 요소 제곱합의 제곱근을 계산함. L2 노름은 유클리드 노름이라고도 불림.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, -2, 3]) norm_l2 = torch.norm(a, p=2) # L2 노름: sqrt(1^2 + (-2)^2 + 3^2) = sqrt(14)
torch.norm(a, p=float('inf'))(Linf 노름)
- 설명: 텐서의 각 요소 절댓값 중 가장 큰 값을 계산함. 무한 노름이라고도 불림.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, -2, 3]) norm_linf = torch.norm(a, p=float('inf')) # Linf 노름: max(1, 2, 3) = 3
torch.norm(a - b, p=1)(맨해튼 거리, 맨해튼 유사도)
- 설명: 두 텐서 사이의 각 요소 차이의 절댓값의 합을 계산함. 맨해튼 거리라고도 불림.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 0, -1]) manhattan_distance = torch.norm(a - b, p=1) # 맨해튼 거리: |1-4| + |2-0| + |3+1| = 9 # 맨해튼 유사도: 1 / (1 + manhattan_distance)
torch.norm(a - b, p=2)(유클리드 거리, 유클리드 유사도)
- 설명: 두 텐서 사이의 각 요소 차이의 제곱합의 제곱근을 계산함. 유클리드 거리라고도 불림.
- 예시:
a = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) b = torch.tensor([4, 0, -1]) euclidean_distance = torch.norm(a - b, p=2) # 유클리드 거리: sqrt((1-4)^2 + (2-0)^2 + (3+1)^2) = sqrt(26) # 유클리드 유사도: 1 / (1 + euclidean_distance)
torch.dot(a, b) / (torch.norm(a, p=2) * torch.norm(b, p=2))(코사인 거리, 코사인 유사도)
- 설명: 두 텐서 사이의 코사인 유사도를 계산함. 두 벡터가 이루는 각의 코사인 값으로, -1에서 1 사이의 값을 가짐.
- 예시:
b = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]) c = torch.tensor([4, 0, -1]) cos_similarity = torch.dot(a, b) / (torch.norm(a, p=2) * torch.norm(b, p=2)) # 코사인 유사도: 1*4 + 2*0 + 3*(-1) / (sqrt(1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2) * sqrt(4^2 + 0^2 + (-1)^2))
a.matmul(b), a.mm(b), a @ b
- 설명: 두 텐서의 행렬 곱셈을 계산함.
matmul,mm,@연산자는 모두 행렬 곱셈을 수행함. - 예시:
a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) b = torch.tensor([[5, 6], [7, 8]]) matmul_result = a.matmul(b) # 행렬 곱셈 결과 mm_result = a.mm(b) # 행렬 곱셈 결과 at_result = a @ b # 행렬 곱셈 결과
- 행렬의 좌우 반전
- 설명: 행렬을 좌우 반전
- 예시:
import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) a_flipped_lr = torch.fliplr(a) # 좌우 대칭 # a_flipped_ud = a @ torch.tensor([[0, 1], [1, 0]]) 도 동일 plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.imshow(a, cmap='gray') plt.title('Original') plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.imshow(a_flipped_lr, cmap='gray') plt.title('Left-Right Flipped') plt.show()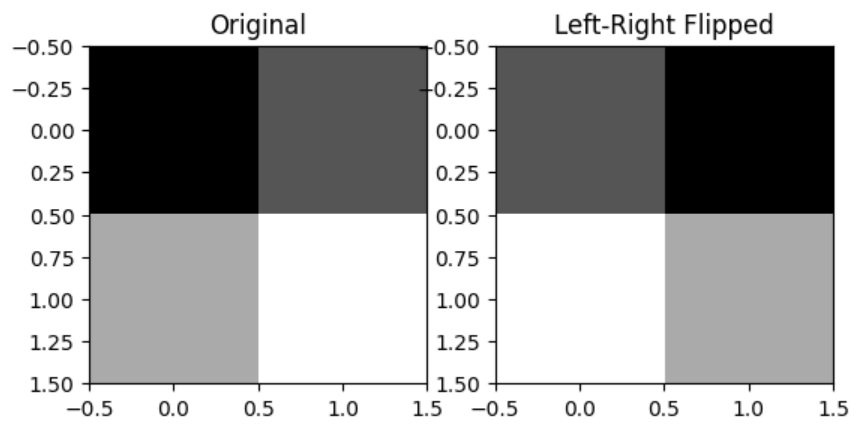
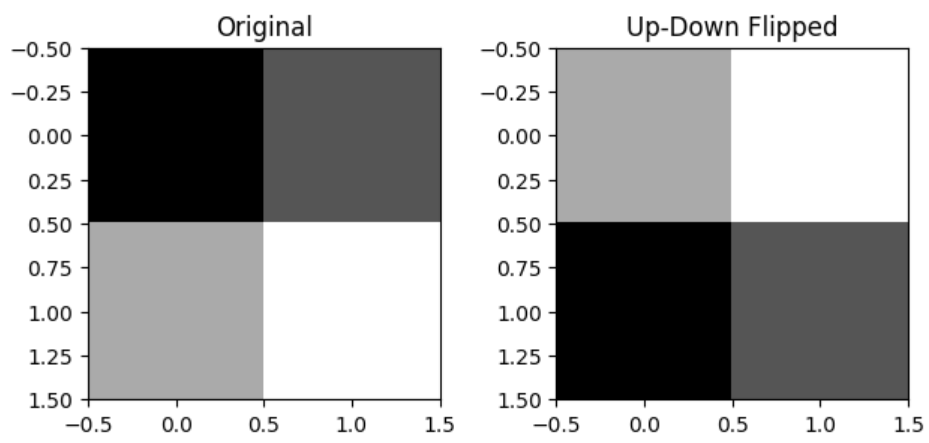
- 행렬의 상하 반전
- 설명: 행렬을 상하 반전
- 예시:
import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) a_flipped_ud = torch.flipud(a) # 상하 대칭 # a_flipped_ud = torch.tensor([[0, 1], [1, 0]]) @ a 도 동일 plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.imshow(a, cmap='gray') plt.title('Original') plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.imshow(a_flipped_ud, cmap='gray') plt.title('Up-Down Flipped') plt.show()