https://www.tutorialspoint.com/rust/rust_generic_types.htm
제네릭은 형식이 다른 여러 컨텍스트에 대한 코드를 작성하는 기능
Rust에서 제네릭은 데이터 형식 및 특성의 매개변수화를 나타냄
Generics를 사용하면 코드 중복을 줄이고 형식 안전성을 제공하여 보다 간결하고 깨끗한 코드를 작성할 수 있음
Generics의 개념은 메서드, 함수, 구조체, 열거형, 컬렉션 및 trait에 적용될 수 있음
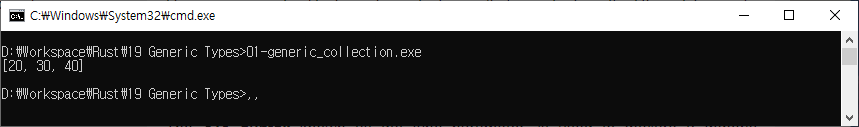
Generic Collection
fn main(){
let mut vector_integer: Vec<i32> = vec![20,30];
vector_integer.push(40);
println!("{:?}",vector_integer);
}
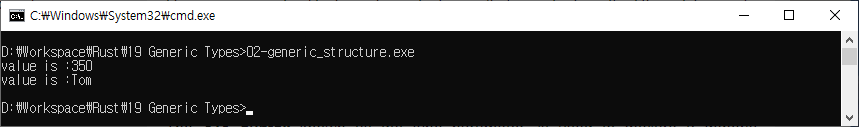
Generic Structure
struct Data<T> {
value:T,
}
fn main() {
//generic type of i32
let t:Data<i32> = Data{value:350};
println!("value is :{} ",t.value);
//generic type of String
let t2:Data<String> = Data{value:"Tom".to_string()};
println!("value is :{} ",t2.value);
}
Traits
trait을 사용하여 여러 구조체에서 표준 동작(메서드) 집합을 구현할 수 있음
trait은 객체 지향 프로그래밍의 인터페이스와 같음
trait 선언
trait some_trait {
//abstract or method which is empty
fn method1(&self);
// this is already implemented , this is free
fn method2(&self){
//some contents of method2
}
}trait에는 구체적인 메서드(본문이 있는 메서드) 또는 추상 메서드(본문이 없는 메서드)가 포함될 수 있음
trait에 구현된 구체적인 메서드는 공유된 모든 구조체에서 사용 가능
trait에 명시된 추상 메서드는 재정의 할 수 있음
trait 구현
impl some_trait for structure_name {
// implement method1() there..
fn method1(&self ){
}
}fn main(){
//create an instance of the structure
let b1 = Book {
id:1001,
name:"Rust in Action"
};
b1.print();
}
//declare a structure
struct Book {
name:&'static str,
id:u32
}
//declare a trait
trait Printable {
fn print(&self);
}
//implement the trait
impl Printable for Book {
fn print(&self){
println!("Printing book with id:{} and name {}",self.id,self.name)
}
}
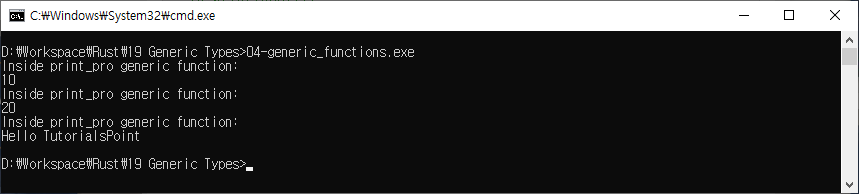
Generic Functions
use std::fmt::Display;
fn main(){
print_pro(10 as u8);
print_pro(20 as u16);
print_pro("Hello TutorialsPoint");
}
fn print_pro<T:Display>(t:T){
println!("Inside print_pro generic function:");
println!("{}",t);
}