https://www.tutorialspoint.com/rust/rust_input_output.htm
표준 입력(키보드)에서 값을 받아들이고 표준 출력(콘솔)에 값을 표시하는 방법에 대한 설명
명령줄 인수 전달에 대해서도 설명
Reader and Writer Types
입력 및 출력에 대한 Rust의 표준 라이브러리 기능은 두 가지 특성을 중심으로 구성
| Sr.No. | Trait | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Read | Read를 구현하는 유형에는 바이트 지향 입력을 위한 메소드, Reader라고 지칭 | Stdin, File |
| 2 | Write | Write를 구현하는 유형은 바이트 지향 및 UTF-8 텍스트 출력을 모두 지원 | Stdout, File |
Read Trait
Reader는 프로그램에서 바이트를 읽을 수 있는 구성 요소
예로 read_line()이 있음
| Sr.No. | Trait | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Read | read_line(&mut line)->Result | 텍스트 줄을 읽고 문자열인 줄에 추가, 반환 값은 읽은 바이트 수인 io::Result |
fn main(){
let mut line = String::new();
println!("Enter your name :");
let b1 = std::io::stdin().read_line(&mut line).unwrap();
println!("Hello , {}", line);
println!("no of bytes read , {}", b1);
}
Write Trait
Writer는 프로그램이 바이트를 쓸 수 있는 구성 요소
표준 출력 스트림에 데이터를 쓰는 데 사용 가능
| Sr.No. | Trait | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Write | write(&buf)->Result | 텍스트 줄을 읽고 문자열인 줄에 추가, 반환 값은 읽은 바이트 수인 io::Result |
use std::io::Write;
fn main() {
let b1 = std::io::stdout().write("Tutorials ".as_bytes()).unwrap();
let b2 = std::io::stdout().write(String::from("Point").as_bytes()).unwrap();
std::io::stdout().write(format!("\nbytes written {}",(b1+b2)).as_bytes()).unwrap();
}
CommandLine Arguments
CommandLine 인수는 프로그램을 실행하기 전에 프로그램에 전달
함수에 전달되는 매개변수와 같음
CommandLine 매개변수를 사용하여 main() 함수에 값을 전달할 수 있음
std::env::args()는 명령줄 인수를 반환
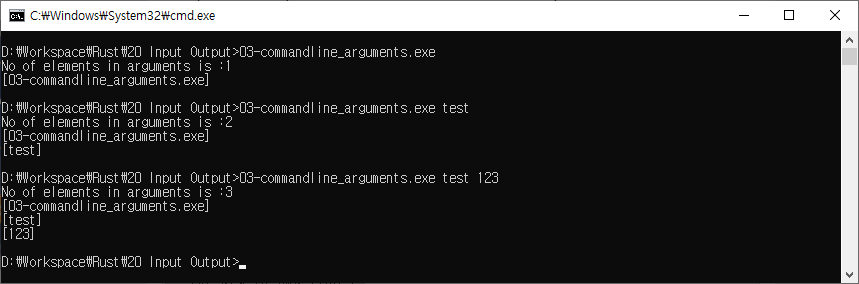
//main.rs
fn main(){
let cmd_line = std::env::args();
println!("No of elements in arguments is :{}",cmd_line.len());
//print total number of values passed
for arg in cmd_line {
println!("[{}]",arg); //print all values passed as commandline arguments
}
}
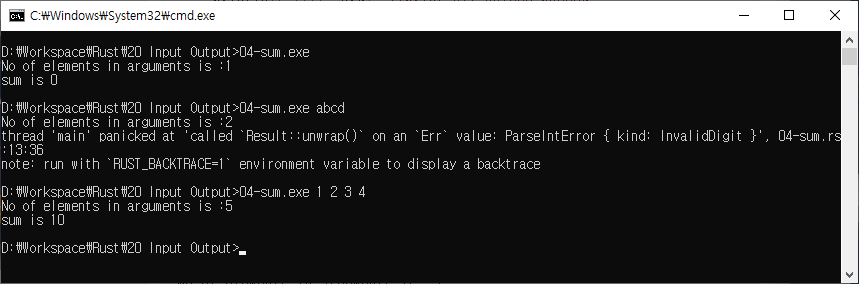
fn main(){
let cmd_line = std::env::args();
println!("No of elements in arguments is :{}",cmd_line.len());
// total number of elements passed
let mut sum = 0;
let mut has_read_first_arg = false;
//iterate through all the arguments and calculate their sum
for arg in cmd_line {
if has_read_first_arg { //skip the first argument since it is the exe file name
sum += arg.parse::<i32>().unwrap();
}
has_read_first_arg = true;
// set the flag to true to calculate sum for the subsequent arguments.
}
println!("sum is {}",sum);
}