
Chapter 14. Secure HTTP
(해석 또는 이해가 잘못된 부분이 있다면 댓글로 편하게 알려주세요.)
✏️ 원문 번역
Digital Signatures
So far, we’ve been talking about various kinds of keyed ciphers, using symmetric and asymmetric keys, to allow us to encrypt and decrypt secret messages.
- 앞서 대칭 키와 비대칭 키를 사용하여 메시지를 암호화하고 복호화하기 위한 다양한 Cipher에 대해 논의하였습니다.
In addition to encrypting and decrypting messages, cryptosystems can be used to sign messages, proving who wrote the message and proving the message hasn’t been tampered with. This technique, called digital signing, is important for Internet security certificates, which we discuss in the next section.
-
Cryptosystem은 메시지 암호화/복호화와 더불어 메시지를 서명하는 데 사용될 수 있습니다.
-
어떤 사람이 메시지를 작성하였는지 증명하고, 해당 메시지가 변조되지 않았음을 보장할 수 있습니다.
-
Digital Signing이라고 하는 이러한 기술은 인터넷 보안 증명에 있어 중요한 개념입니다.
-
다음 섹션에서 Digital Signing에 대해 상세히 다룹니다.
Signatures Are Cryptographic Checksums
Digital signatures are special cryptographic checksums attached to a message. They have two benefits:
-
Digital Signature는 메시지에 첨부되는 특수한 Cryptographic Checksum입니다.
-
서명이 가지는 두 가지 효과는 다음과 같습니다.
• Signatures prove the author wrote the message. Because only the author has the author’s top-secret private key,* only the author can compute these checksums. The checksum acts as a personal “signature” from the author.
-
서명은 메시지를 작성한 저자가 누구인지 증명합니다.
-
오직 메시지 작성자만이 알려지지 않은 비공개 키를 가지고 있기 때문에 checksum을 계산할 수 있는 사람은 작성자뿐입니다.
-
즉 checksum이 작성자의 고유한 "서명"으로써 사용됩니다.
• Signatures prevent message tampering. If a malicious assailant modified the message in-flight, the checksum would no longer match. And because the checksum involves the author’s secret, private key, the intruder will not be able to fabricate a correct checksum for the tampered-with message.
-
서명은 메시지 변조를 방지할 수 있습니다.
-
악의적인 공격자가 전송중인 메시지를 변조하는 경우 checksum이 더 이상 일치하지 않습니다.
-
checksum은 저자의 비공개 키를 포함하고 있기 때문에 변조된 메시지에 대해 올바른 checksum을 조작하는 것이 불가능합니다.
Digital signatures often are generated using asymmetric, public-key technology. The author’s private key is used as a kind of “thumbprint,” because the private key is known only by the owner.
-
Digital Signature는 주로 비대칭 공개 키 기술을 사용하여 생성됩니다.
-
저자의 Private Key는 오직 저자만이 알고 있기 때문에 일종의 "지문" 역할을 수행하게 됩니다.
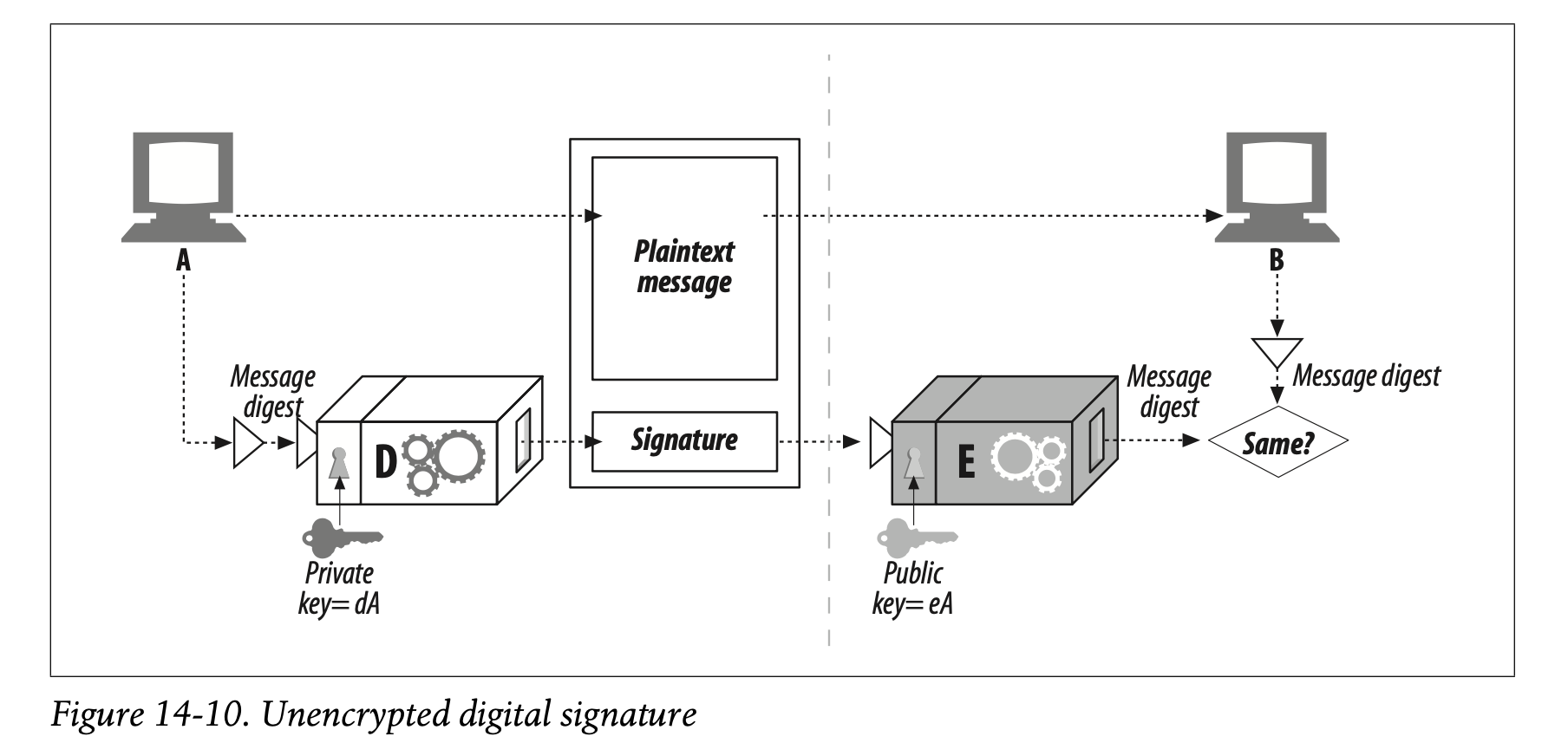
Figure 14-10 shows an example of how node A can send a message to node B and sign it:
• Node A distills the variable-length message into a fixed-sized digest.
• Node A applies a “signature” function to the digest that uses the user’s private key as a parameter. Because only the user knows the private key, a correct signature function shows the signer is the owner. In Figure 14-10, we use the decoder function D as the signature function, because it involves the user’s private key.
• Once the signature is computed, node A appends it to the end of the message and sends both the message and the signature to node B.
• On receipt, if node B wants to make sure that node A really wrote the message, and that the message hasn’t been tampered with, node B can check the signature. Node B takes the private-key scrambled signature and applies the inverse function using the public key. If the unpacked digest doesn’t match node B’s own version of the digest, either the message was tampered with in-flight, or the sender did not have node A’s private key (and therefore was not node A).
-
Figure 14-10에서는 노드 A가 노드 B에 메시지를 전송하고 서명하는 과정을 나타내고 있습니다.
-
노드 A가 가변 길이의 메시지를 고정된 길이의 digest로 변환합니다.
-
노드 A는 digest에 사용자의 Private Key를 파라미터로 한 "서명" 함수를 적용합니다. Private Key는 사용자만 알고 있기 때문에 올바른 서명 함수는 서명인이 송신자라는 사실을 나타냅니다. Figure 14-10에서는 디코딩 함수 D를 서명 함수로 사용합니다. 디코딩 함수가 사용자의 Private Key를 포함하고 있기 때문입니다.
-
서명이 계산되고 나면 노드 A는 메시지의 끝에 서명을 추가하여 노드 B로 전송합니다. 즉 메시지와 서명이 모두 B에 전달됩니다.
-
노드 B는 수신된 메시지가 정말 노드 A로부터 온 것인지, 메시지가 중간에 변조되지는 않았는지 확인하고 싶다면, 노드 B는 서명을 확인할 수 있습니다. Private Key로 처리된 서명에 Public Key를 사용한 역함수를 적용하면 됩니다. 만약 unpacked digest가 노드 B가 가진 digest 버전과 일치하지 않는다면, 중간에 메시지가 변조되었거나 송신자가 A의 Private Key를 가지고 있지 않은 것입니다(즉 송신자가 A가 아닌 상황).
✏️ 요약
Digital Signatures
: 송신자가 자기 자신임을 증명할 수 있는 서명
- 송신자의 Private Key로 암호화된 digest -> 어떤 사람이 메시지를 전송하였는지 증명할 수 있다
- 메시지 변조가 발생하는 경우 수신자가 Public Key로 복호화한 digest와 실제 digest가 불일치 -> 변조 발생 여부를 알 수 있다
✏️ 감상
서명이 있어도 100% 안전하지 않다
Digital Signature는 Private Key로 digest를 암호화하여 전송자의 신원을 보증하고 메시지 변조를 방지하는 역할을 한다. 하지만 정말 전송자가 본인이 맞는지에 대해서는 증명할 수 없다. 누군가가 A의 Private Key로 digest를 암호화한 것을 전송했는데, 이 '누군가'가 A가 아닐 수도 있다는 뜻이다. 공격자가 A를 가장하여 MITM 공격을 시도하는 경우에는 Digital Signature만으로 대처하기 어렵다.
때문에 네트워크 환경 자체의 신뢰도를 보장하기 위한 Public Key Infrastruecutre(PKI)의 개념이 등장했다. 메시지의 출처와 무결성을 보장하기 위해 공신력이 있는 기관(CA, Certificate Authority)을 통해 Registration과 Verification 과정을 거치는 방식이다. 이때 Registration은 송신자가 자신의 신원을 증명할 수 있는 서명을 CA에 등록하는 것이고, Verification은 수신자가 CA의 Public Key를 사용하여 송신자의 서명을 확인하는 것이다. CA의 Public Key로 서명을 확인할 수 있다는 것은 해당 서명이 공신력 있는 인증 기관이 인증서를 발급하였음을 의미한다. 보통 TLS에서는 PKI를 통한 인증 과정을 거친 후에 암호화된 채널을 형성한다.
