터치 이벤트 처리하기
레이아웃 XML 파일 코드
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<View
android:id="@+id/view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#C53E3E" />
<View
android:id="@+id/view2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#2196F3" />
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@color/white">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>다른 색상의 view 두개와 Text를 출력하는 스크롤 뷰를 세로로 배치하였다.
JAVA 파일 코드
package org.techtown.sampleevent;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = findViewById(R.id.textView);
View view = findViewById(R.id.view);
view.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
int action = event.getAction();
float curX = event.getX();
float curY = event.getY();
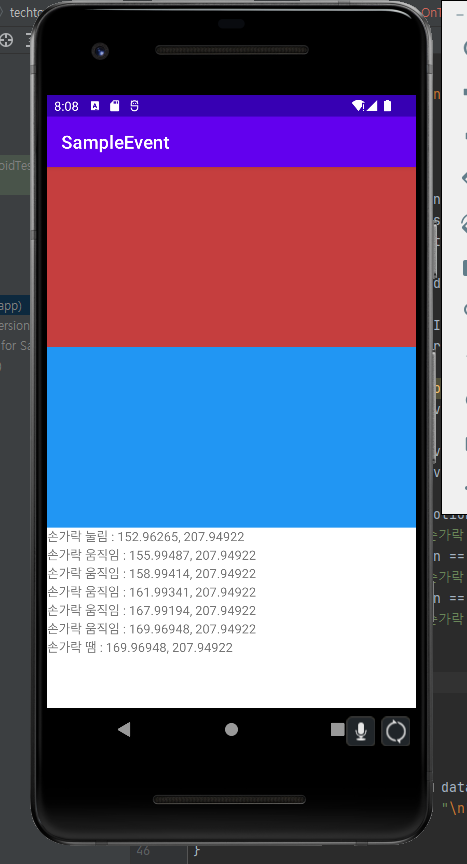
if(action == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN){
println("손가락 눌림 : " + curX + ", " + curY);
}else if(action == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE){
println("손가락 움직임 : " + curX + ", " + curY);
}else if(action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP){
println("손가락 땜 : " + curX + ", " + curY);
}
return true;
}
});
}
public void println(String data){
textView.append(data + "\n");
}
}첫 번째 view에 setOnTouchListener 메소드를 호출하여 리스너를 등록한다.
이 메소드의 파라메터로 전달하는 리스너 객체를 new 연산자를 이용해 OnTouchListener 객체를 생성하면서 전달한다. 뷰가 터치되었을 때 이 리스너 객체의 onTouch 메서드가 자동으로 호출된다.
View view = findViewById(R.id.view);
view.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
}
});onTouch 메소드로 MotionEvent 객체가 파라미터로 전달된다. 이 객체에는 액션 정보나 터치한 곳의 좌표 등이 들어있다.
액션 정보를 .getAction() 메소드로 확인하고, .getX()와 .getY() 메소드로 좌표를 확인한다.
int action = event.getAction();
float curX = event.getX();
float curY = event.getY();.getAction() 메소드로 받은 값은 정수 자료형이다. 이를 MotionEvent 클래스에 정의된 상수 값과 비교하면서 액션 정보를 확인한다.
액션 정보에 따라서 textview에 출력되는 문구를 다르게 설정했다.
if(action == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN){
println("손가락 눌림 : " + curX + ", " + curY);
}else if(action == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE){
println("손가락 움직임 : " + curX + ", " + curY);
}else if(action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP){
println("손가락 땜 : " + curX + ", " + curY);
} public void println(String data){
textView.append(data + "\n");
}
제스처 이벤트 처리하기
제스처 이벤트는 터치 이벤트 중에서 스크롤 등을 구별한 후 알려주는 이벤트이다.
제스처 이벤트를 처리해주는 클래스는 GestureDetector이며, GestureDetector 객체를 만들고 터치 이벤트를 전달하면 이 객체에서 각 상황에 맞는 메소드를 호출한다.
위에서 만든 화면에서 파란색 뷰를 터치했을 때 제스처 이벤트를 처리하도록 코드를 추가한다.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView textView;
GestureDetector detector;
...
detector = new GestureDetector(this, new GestureDetector.OnGestureListener() {
@Override
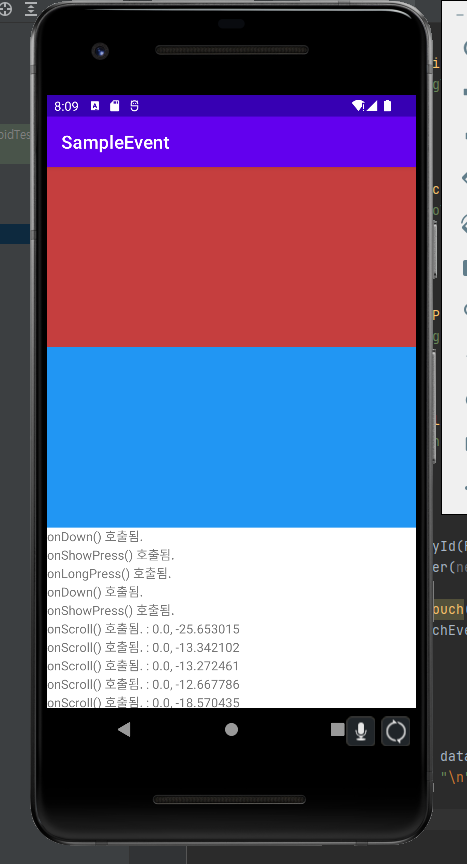
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
println("onDown() 호출됨.");
return true;
}
@Override
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
println("onShowPress() 호출됨.");
}
@Override
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
println("onSingleTapUp() 호출됨.");
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY) {
println("onScroll() 호출됨. : " + distanceX + ", " + distanceY);
return true;
}
@Override
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
println("onLongPress() 호출됨.");
}
@Override
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY) {
println("onFling() 호출됨. : " + velocityX + ", " + velocityY);
return true;
}
});
View view2 = findViewById(R.id.view2);
view2.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
detector.onTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
});
}
...두번째 view도 첫번째 view와 똑같이 setOnTouchListener 객체를 설정한다.
두번째 view의 onTouch 메소드 안에는 GestureDetector 객체의 onTouchEvent 메서드를 호출하면서 MotionEvent 객체를 전달한다. 이렇게 함으로서 GesterDetector 객체가 터치 이벤트를 처리한 후 GestureDetector 객체에 정의된 메소드를 호출한다.
키 이벤트 처리하기
키 입력은 onKeyDown 메소드를 재정의하여 처리할 수 있다.
onKeyDown 메소드로 전달되는 파라메터로는 KeyCode와 KeyEvent로 두가지가 있고,
KeyCode는 어떤 키가 사용되는지 구별할 때 사용되고, KeyEvent는 키 입력 이벤트에 대한 정보를 알고 싶을 때 사용된다.
MainActivity 클래스에 우클릭->Generete->Override Methods를 선택해 onKeyDown 메소드를 선택한다.
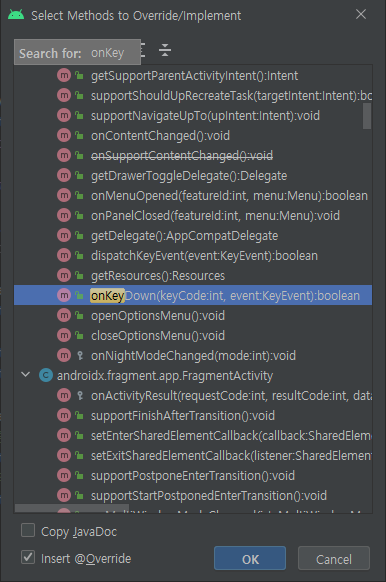
다음과 같은 코드가 추가된다.
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
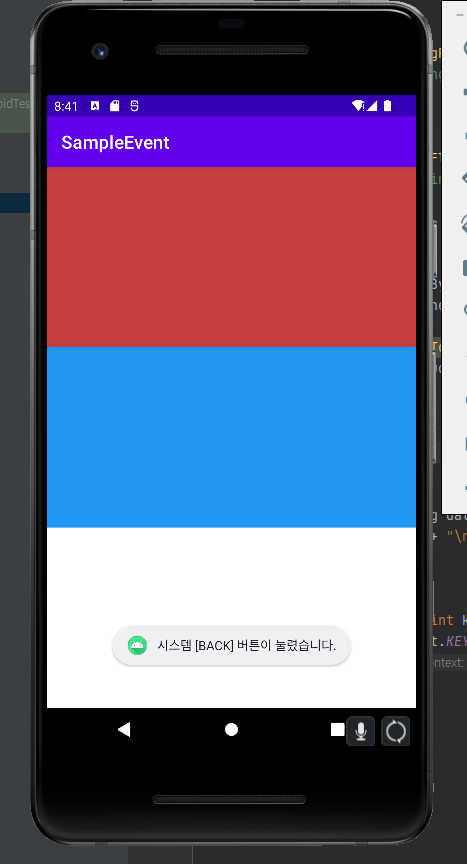
}'BACK' 버튼을 누르면 Toast 메세지가 표시되도록 코드를 추가한다.
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if(keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK){
Toast.makeText(this, "시스템 [BACK] 버튼이 눌렸습니다.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return true;
}
return false;
}