[백준] 7562번. 나이트의 이동
1. 문제
체스판 위에 한 나이트가 놓여져 있다. 나이트가 한 번에 이동할 수 있는 칸은 아래 그림에 나와있다. 나이트가 이동하려고 하는 칸이 주어진다. 나이트는 몇 번 움직이면 이 칸으로 이동할 수 있을까?
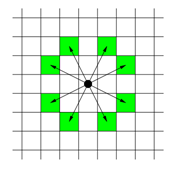
2. 입력
입력의 첫째 줄에는 테스트 케이스의 개수가 주어진다.
각 테스트 케이스는 세 줄로 이루어져 있다. 첫째 줄에는 체스판의 한 변의 길이 l(4 ≤ l ≤ 300)이 주어진다. 체스판의 크기는 l × l이다. 체스판의 각 칸은 두 수의 쌍 {0, ..., l-1} × {0, ..., l-1}로 나타낼 수 있다. 둘째 줄과 셋째 줄에는 나이트가 현재 있는 칸, 나이트가 이동하려고 하는 칸이 주어진다.
3. 출력
각 테스트 케이스마다 나이트가 최소 몇 번만에 이동할 수 있는지 출력한다.
4. 풀이
BFS를 하였다.- 시작점부터
BFS를 하였고 도착점의 값을 출력하였다.
5. 처음 코드와 달라진 점
while의 조건을 나중에 써야지 하고 안 썼다.ㅎ
6. 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int map[300][300];
int dx[] = { 1,2,1,2,-1,-2,-1,-2 };
int dy[] = { 2,1,-2,-1,2,1,-2,-1 };
int bfs(int n, int x, int y, int target_x, int target_y) {
map[x][y] = 0;
bool visited[300][300] = { 0, };
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({ x, y });
visited[x][y] = true;
while (!q.empty()){
int current_x = q.front().first;
int current_y = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
int nx = current_x + dx[i];
int ny = current_y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= n) continue;
if (!visited[nx][ny]) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
map[nx][ny] = map[current_x][current_y] + 1;
q.push({ nx, ny });
}
}
}
return map[target_x][target_y];
}
int main() {
cin.tie(NULL);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
int T;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++){
int n;
cin >> n;
int current_x, current_y;
cin >> current_x >> current_y;
int target_x, target_y;
cin >> target_x >> target_y;
cout << bfs(n, current_x, current_y, target_x, target_y)<<"\n";
}
}