23.08.03 최초 작성
23.11.14 예제 추가
1. File
관련 있는 데이터의 집합으로 보조 기억 장치에 일정한 형태로 저장됨. OS는 파일 조작을 위한 시스템 콜을 제공한다.
| 파일 종류 | 특징 |
|---|---|
| 일반 파일 | 텍스트 바이너리 형태의 데이터를 저장하는 파일 |
| 특수 파일 | 데이터 전송, 장치 접근 시 사용 |
| Directory | Unix/Linux 에서는 파일 형태로 존재 |
2. Low Level File I/O
- 시스템 콜을 이용해 파일 입출력 수행
- File Descriptor 사용
- Byte 단위로 디스크에 입출력
- 특수 파일에 대한 입출력
2.1 File Open
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int open (const char *pathname, int flags [, mode_t mode]);
///
pathname : 열려고 하는 파일의 경로
flags : 파일을 여는 방법
mode : 접근 권한, 파일을 새로 생성할 때만 유효
Return : File Descriptor-
주요 flags 옵션( '|' 연산자로 여러 옵션 지정 가능)
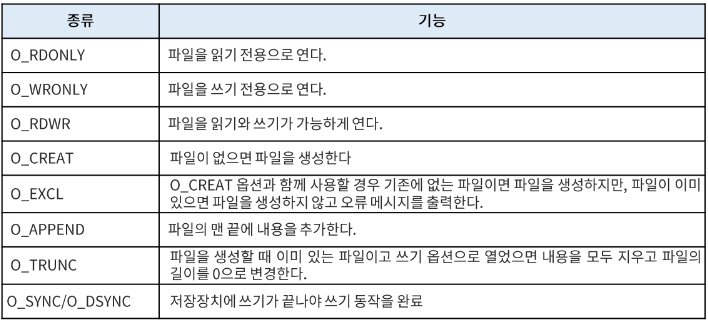
-
주요 mode 옵션( '|' 연산자로 여러 옵션 지정 가능)
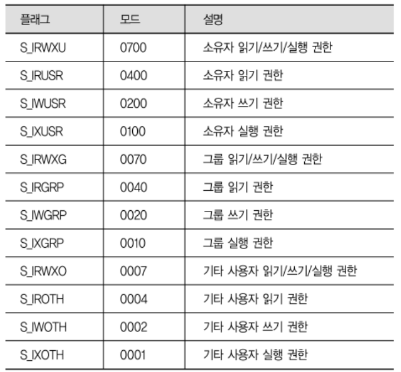
2.1.1 File Descriptor
프로세스가 열고 있는 파일을 구분하는 정수 값. 파일을 열 때 순차적으로 할당 됨
0 : stdin
1 : stdout
2 : stderr
File Descriptor 복사
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
///
oldfd : 복사하려는 File Descriptor
newfd : 새로운 fd 지정
(dup()의 경우 할당 가능한 fd 중 가장 작은 값 할당)
Return : oldfd를 복사한 새로운 fd 번호
(-1 : error)File Descriptor 조작
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl (int fd, int cmd, /* arg */ ...);
///
fd : 대상 File Descriptor
cmd : 수행할 명령
arg : cmd에 필요한 인자들
Return : cmd에 따라 다름2.1.2 File Table
열린 파일을 관리하는 표로 File Descriptor가 가르키는 정보를 담고 있다. 커널이 프로세스 별로 유지하며 열린 파일에 대한 각종 정보를 관리한다.
2.2 File Close
#include <unistd.h>
int close(int fd);
///
fd : 닫으려고 하는 File Descriptor
Return 0(Success) or -1(Error)2.3 Read
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t read (int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
///
fd : 읽으려는 파일의 File Descriptor
buf (buffer) : 읽을 내용을 저장할 buffer의 시작 주소
count : 읽을 byte 수
Return : 실제로 읽을 byte의 수
(0 : 파일의 끝에 도달, -1 : 에러)2.4 Write
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t write (int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
///
fd : 기록하려는 파일의 File Descriptor
buf (buffer) : 기록할 내용을 저장할 buffer의 시작 주소
count : 기록할 byte 수
Return : 실제로 기록한 byte의 수
(-1 : 에러)2.5 Fsync
Page Write-Back을 바로 실행해 줌
#include <unistd.h>
int fsync (int fd);
///
fd : File Descriptor
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)3. File Offset(Low Level)
-
File operation(read/write)을 적용 할 위치를 나타내며 시작점부터 현재 위치까지의 byte 수. Read/Write 시 count 수 만큼 이동 함.
-
file offset 이동
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
off_t lseek (int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
///
fd : 대상 File Descriptor
offset : 이동 시킬 byte 수
whence : 기준 위치
Return : 이동 후 File Offset
(-1 : 에러)| whence 옵션 | |
|---|---|
| SEEK_SET | 파일의 시작점 |
| SEEK_CUR | 현재 위치 기준 |
| SEEK_END | 파일의 끝 기준 |
4. 예제
4.1 파일을 복사
argv[1]에 입력된 파일을argv[2]에 입력된 파일에 복사하는 코드
/*************************************************************************\
* Copyright (C) Michael Kerrisk, 2022. *
* *
* This program is free software. You may use, modify, and redistribute it *
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the *
* Free Software Foundation, either version 3 or (at your option) any *
* later version. This program is distributed without any warranty. See *
* the file COPYING.gpl-v3 for details. *
\*************************************************************************/
/* Listing 4-1 */
/* copy.c
Copy the file named argv[1] to a new file named in argv[2].
*/
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
#ifndef BUF_SIZE /* Allow "cc -D" to override definition */
#define BUF_SIZE 1024
#endif
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int inputFd, outputFd, openFlags;
mode_t filePerms;
ssize_t numRead;
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
if (argc != 3 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s old-file new-file\n", argv[0]);
/* Open input and output files */
inputFd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (inputFd == -1)
errExit("opening file %s", argv[1]);
openFlags = O_CREAT | O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC;
filePerms = S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP |
S_IROTH | S_IWOTH; /* rw-rw-rw- */
outputFd = open(argv[2], openFlags, filePerms);
if (outputFd == -1)
errExit("opening file %s", argv[2]);
/* Transfer data until we encounter end of input or an error */
while ((numRead = read(inputFd, buf, BUF_SIZE)) > 0)
if (write(outputFd, buf, numRead) != numRead)
fatal("write() returned error or partial write occurred");
if (numRead == -1)
errExit("read");
if (close(inputFd) == -1)
errExit("close input");
if (close(outputFd) == -1)
errExit("close output");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}