23.08.03 최초 작성
1. High Level File I/O
- C Standard Library를 사용해 파일 입출력 수행
- File Pointer 사용
- 버퍼(Block)단위로 디스크에 입출력
1.1 Standard I/O
플랫폼에 독립적인 user-buffering solution
- File Pointer(FILE *) : File Operation을 관리하는 구조체를 가리키는 포인터로 내부적으로 File Descriptor와 매핑 됨
- Stream : 프로그램과 파일을 연결한 통로
2. File Open/Close
2.1 File Open
#include <stdio.h>
FILE *fopen(const char *path, const char *mode);
///
path : 열려는 파일 경로
mode : 파일 열기 모드
Return : File Pointer
(NULL : fail to open)- 파일 열기 모드
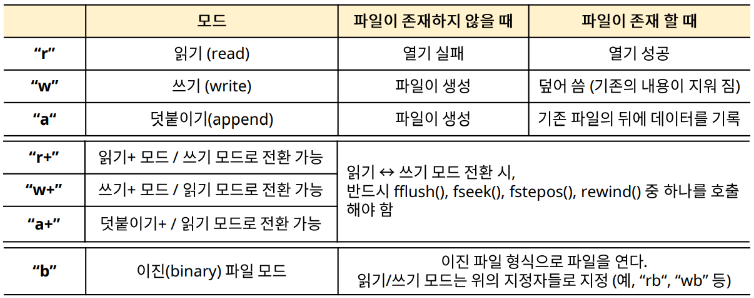
2.2 File Close
#include <stdio.h>
int fclose(FILE *stream);
//
stream : 닫으려는 파일의 File Pointer
Return
(0 : Success, -1(EOF) : Error)3. File Read/Write
3.1 Character-based R/W
/*Reading*/
#include <stdio.h>
int fgetc (FILE * stream);
int getc (FILE * stream); // MACRO 형태로 구현(실행이 빠름), 인자에 수식 X
int getchar (void); // = getc(stdin) 키보드로부터의 입력
///
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
Return : 읽은 / 기록한 문자
(EOF(-1) : Error)/*Writing*/
#include <stdio.h>
int fputc (int c, FILE * stream);
int putc (int c, FILE * stream);
int putchar (void);
///
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
c : 쓰려는 문자
Return : 읽은 / 기록한 문자
(EOF(-1) : Error)3.2 String-based R/W
/*Reading*/
#include <stdio.h>
int fgets (char *s, int n, FILE *stream); // Stream에서 (n-1)개의 문자를 읽어 s에 저장 & \n, EOF를 만나면 해당 지점까지 읽음
int gets (char *s); // get from stdin
///
s : 읽은 문자열을 저장할 buffer
n : buffer의 크기
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
Return : Buffer의 시작 주소
(NULL : 읽을 내용이 없음)/*Writing*/
#include <stdio.h>
int fputs (const char *s, FILE * stream);
int puts (const char *s);
///
s : 기록할 문자열을 저장한 buffer
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
Return : 읽은 / 기록한 문자
(양수 : Success, 음수 : Error)3.3 Binary R/W
#include <stdio.h>
FILE *fopen(const char *name, const char *mode);
size_t fread (void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
size_t fwrite (const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t memb, FILE *stream);
///
ptr : buffer의 포인터
size :항목의 자료형 크기
nmemb : 읽거나 쓸 항목의 갯수
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
Return : Read/Write한 항목 수
(EOF : 파일의 끝)- fopen의 mode
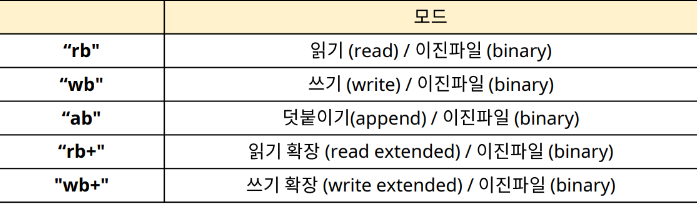
3.4 Formatted R/W
#include <stdio.h>
int scanf (const char *format, ...);
int fscanf (FILE *stream, const char *format, ...);
int printf (const char *format, ...);
int fprintf (FILE *stream, const char *format, ...);
///
format : 입출력 형식
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
Return : 입출력한 문자 수
(음수 : Error)3.5 Synchronizing with Disk
#include <stdio.h>
int fflush (FILE *stream);
///
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
Return
(0 : Success, EOF(-1) : Error)4. Controlling Buffering
#include <stdio.h>
int setvbuf (FILE *stream, char *buf, int mode, size_t size);| mode | 의미 | 기능 |
|---|---|---|
| _IONBF | Unbuffered | 버퍼를 사용하지 않음 |
| _IOLBF | Line-Buffered | \n이 나올 때 내용을 내보냄 |
| _IOFBF | Block-Buffered | Block 단위마다 버퍼링 됨(Default) |
5. File Offset(High Level)
파일 포인터를 통해 File Offset을 조작하는 함수들
#include <stdio.h>
int fseek (FILE *stream, long offset, int whence);
long ftell (FILE *stream);
void rewind (FILE *stream);
int fsetpos (FILE *stream, const fpost_t *pos);
int fgetpos (FILE *stream, fpos_t *pos);
///
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
offset : 이동시킬 byte 수
whence : 기준 위치
pos : offset을 저장하거나 저장하고 있는 fpos_t 주소| 함수 | 기능 | Return |
|---|---|---|
| fseek | 파일 오프셋 이동 | 0 : Success, EOF : Error |
| ftell | 현재 파일 오프셋 | 파일 시작에서 현재 위치까지의 byte 수, EOF : Error |
| rewind | 함수 오프셋을 시작위치로 변경 | - |
| fgetpos | pos가 가리키는 영역에 파일 오프셋 저장 | 0 : Success, 다른 모든 값 : Error |
| fsetpos | pos가 가리키는 값으로 파일 오프셋 설정 | 0 : Success, 다른 모든 값 : Error |
6. File Pointer, File Descriptor 변환
#include <stdio.h>
FILE* fdopen (int fd, const char *mode);
///
fd : File Descriptor
mode : 파일 열기 모드 (fd와 같아야 함)
Return : File Pointer
(NULL : Fail)int fileno (FILE *stream);
///
stream : File Operation을 수행 할 파일의 File Pointer
Return : File Descriptor
(-1 : Error)7. Temporal File
#include <stdio.h>
char *tmpnam (char *s); // 중복 되지 않는 임시 파일 이름 생성
char *Tempnam (const char *dir, const char *pfx); // 중복 되지 않는 임시 파일 이름 생성, 직접 열어야 함
FILE * tmpfile (); // w+ 모드로 열린 임시 파일 포인터 생성