23.08.05 최초 작성
23.11.14 예제 추가
1. Running Process
- Executing new Program : Binary Program을 읽어서 자신을 호출한 프로세스의 메모리 영역에 덮어 씀
- Creating new Program : 자신을 호출한 프로세스를 복사해 새로운 프로세스를 생성함 (Forking)
1.1 Exec Family of Call (Executing new Program)
#include <unistd.h>
execl (const char *path, const char *arg, ... /*(char *) NULL*/); //절대경로
int execlp (const char * file, const char *arg, ... /*(char *) NULL*/);
int execle (const char *path, const char *arg, /*, (char *) NULL, char * const envp[] */);
int execv (const char *path, char *const argv[]); //절대경로
int execvp (const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe (const char *file, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
///
path / file : 실행할 program binary
arg / argv[] : 실행할 program의 인자 (마지막에 NULL을 넣어주어야 함)
envp[] : 프로그램 실행 시 새로 저정할 환경 변수 arg / argv[] : 실행할 program의 인자 (마지막에 NULL을 넣어주어야 함)
Return
(없음 : Sucess, -1 : Error)1.2 Creating a Child Process
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t fork(void); // 자신을 복사해 새로운 프로세스 생성
///
Return
Parent Process : Child Process의 PID
Child Process : 0
-1 : Eror)- 상속되는 정보
- 권한 : RUID, EUID, RGID, EGID, setuid, setgid
- 환경 변수, File Descriptor
- Working Directory, Signal Handling Setup, Resource Limit
- Child Process 고유 정보
- PID, PPID
- tms structure
- 자원 사용 정보 : Resource Statics, Pending Signals, File Locks...
ex) 예제
copy.c:argv[1]에 생성할 child 프로세스 갯수를 입력받아fork()를 통해 프로세스를 생성하는 코드
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int numChildren, j;
pid_t childPid;
//입력받은 인자 갯수가 1개가 아니면 에러 발생
if (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s [num-children]\n", argv[0]);
//argv[1]의 값을 int형으로 변환해 numChildren에 저장
numChildren = (argc > 1) ? getInt(argv[1], GN_GT_0, "num-children") : 1;
setbuf(stdout, NULL); /* Make stdout unbuffered */
//numChildren 만큼 반복하며 프로세스 생성
for (j = 0; j < numChildren; j++) {
switch (childPid = fork()) {
case -1:
errExit("fork");
case 0:
printf("%d child\n", j);
_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
default:
printf("%d parent\n", j);
wait(NULL); /* Wait for child to terminate */
break;
}
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
t_execl.c: 현재 프로세스를printenv()를 수행하는 프로세스로 교체하는 코드
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
printf("Initial value of USER: %s\n", getenv("USER"));
if (putenv("USER=britta") != 0)
errExit("putenv");
/* exec printenv to display the USER and SHELL environment vars */
execl("/usr/bin/printenv", "printenv", "USER", "SHELL", (char *) NULL);
errExit("execl"); /* If we get here, something went wrong */
}#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "curr_time.h" /* Declaration of currTime() */
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int numDead; /* Number of children so far waited for */
pid_t childPid; /* PID of waited for child */
int j;
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s sleep-time...\n", argv[0]);
setbuf(stdout, NULL); /* Disable buffering of stdout */
for (j = 1; j < argc; j++) { /* Create one child for each argument */
switch (fork()) {
case -1:
errExit("fork");
case 0: /* Child sleeps for a while then exits */
printf("[%s] child %d started with PID %ld, sleeping %s "
"seconds\n", currTime("%T"), j, (long) getpid(),
argv[j]);
sleep(getInt(argv[j], GN_NONNEG, "sleep-time"));
_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
default: /* Parent just continues around loop */
break;
}
}
numDead = 0;
for (;;) { /* Parent waits for each child to exit */
childPid = wait(NULL);
if (childPid == -1) {
if (errno == ECHILD) {
printf("No more children - bye!\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else { /* Some other (unexpected) error */
errExit("wait");
}
}
numDead++;
printf("[%s] wait() returned child PID %ld (numDead=%d)\n",
currTime("%T"), (long) childPid, numDead);
}
}2. 프로세스 종료
-
프로세스가 종료 되면 어떻게 종료 되었는지를 exit status에 저장한다.
(0 : 정상 종료) -
종료 과정
- atexit에 등록된 함수들을 등록 역순으로 수행
- Standard IO Stream의 모든 내용을 모두 Flush
- 모든 Temporal File 삭제
- exit() 호출 (이후 kernel이 동작 수행)
- File Descriptor 닫기
- 부모 프로세스에 exit status 전달
- 부모 프로세스에게 SIGCHLD 신호 전달
- 자식 프로세스에게 SIGHUP 신호 전달
- 프로세스가 점유하던 자원들 반납
#include <stdlib.h>
void exit (int status); // status에 종료 상태 저장#include <stdlib.h>
int atexit (void (*function)(void)); //프로세스 종료 시 호출할 함수 등록
///
Return
(0 : Success, 그 이외 : Error)3. 자식 프로세스 동기화
동기화 : 프로세스들이 서로 동작을 맞추고 정보를 공유하는 것 (Race Condition 방지).
Zombie Process : 종료되었지만 아직 삭제되지 않은 프로세스. 부모 프로세스보다 먼저 종료된 경우 zombie state가 되며 부모 프로세스가 exit status를 받아갈 때 까지 지속된다.
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t wait (int *status); //자식 프로세스가 종료할 때까지 대기
///
status : exit status를 저장할 공간
Return : 자식 프로세스의 exit status
(-1 : 실행중인 자식 프로세스가 없음, 여러개의 경우 가장 빨리 종료된 것의 exit status 반환)- status 값 분석
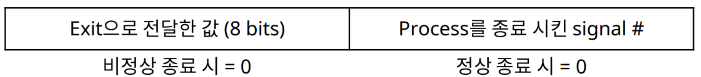
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t waitpid (pid_t pid, int *status, int options);
///
pid : 대상 프로세스의 PID
status : exit status를 저장할 공간
- pid의 종류
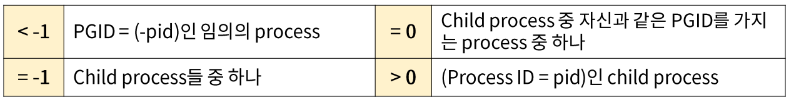
- option의 종류
- WNOHANG : 자식이 종료하기 전이라도 상태 값 바로 반환. 대기하지 않고 수행을 계속 함.
- WNOWAIT : 상태 값을 반환한 자식 프로세스를 대기상태로 유지. 다시 exit status를 요청할 수 있음.