23.08.04 최초 작성
1. Process
실행을 위해 시스템(커널)에 등록된 작업. 시스템 성능 향상을 위해 커널이 관리한다.
1.1 Process ID
프로세스에 부여된 식별번호
- Parent Process : Child Process를 생성한 프로세스(fork()). 최상위 프로세스는 kernel이다. 부모 프로세스의 ID를 Parent Process ID (PPID)라고 한다.
1.2 Getting PID / PPID
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t getpid (void); //자신의 pid
pid_t getppid (void); //부모의 pid1.3 Process Group
관련된 프로세스의 모임으로 하나의 작업 수행을 목적으로 함. Process Group에 전달 된 신호는 그룹 내 모든 프로세스에 전달된다.
- Process Group Leader : Process Group의 프로세스들 중 하나
- Process Group ID (PGID) : Process Group에 부여 된 고유 번호. Process Group Leader의 PID가 PGID가 된다.
#include <unistd.h>
int setpgid (pit_t pid, pit_t pgid);
// pid를 가진 프로세스를 pgid를 가진 Group으로 이동시킴
// pid = 0 : 최근 프로세스
// pgid = 0 : 자신을 pgid로 설정1.4 Session
사용자가 로그인해 작업하고 있는 터미널 단위로 프로세스 그룹을 묶은 것. (Process Group의 묶음)
사용자 로그인 시 새로운 Session이 생성되며 하나의 Foreground Process Group과 0개 이상의 Background Process Group을 가진다.
-
Foreground Process Group : 사용자의 입력을 받는 Process Group으로 터미널을 통해 전달되는 신호를 전달 받는다.
-
Background Process Group : Foreground Process Group이외의 Process Group으로 결과는 터미널에 출력된다.
-
Session Leader : Login Shell Process
-
Session ID : Session Leader의 PID
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t getsid (pid_t pid); //pid를 가지는 프로세스의 세션 ID 가져옴
pid_t setsid (void); // 현재 프로세스를 Session Leader로 설정함2. Process Running Time
- Process Running Time = System Running Time + User Running Time
- System Running Time : Kernel Code를 수행한 시간 (System Call에 소요된 시간)
- User Running Time : 사용자 모드에서 수행한 시간 (사용자 작성 코드를 실행하는데 걸린 시간)
#include <sys/times.h>
clock_t times (struct tms *buf);
///
buf : Running Time 정보를 저장함
Return : 특정 시점부터 경과한 시간 (Clock Tick 단위)
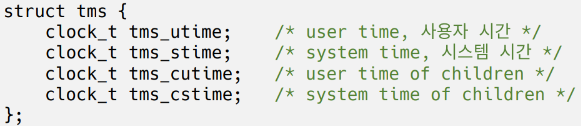
(-1 : Error)- tms 구조체
3. 환경 변수
Process 실행환경에 정의되어 있는 변수. 관례적으로 대문자를 사용한다.
3.1 환경 변수 가져오기
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
extern char **environ; // 어디선가 설정된 전역변수를 가져와 활용#include <stdio.h>
int main (int argc, char **argv, char **envp)
{} // main의 인자로 전달하는 방법#include <stdlib.h>
char *getenv(const char *name);
///
name : 검색할 환경 변수 이름
Return : 환경 변수가 있는지 결과값을 저장하고 주소를 반환함
(NULL : Fail)3.2 환경 변수 설정
#include <stdlib.h>
int putenv (char *string);
int setenv (const char *name, const char *value, int overwrite);
///
string : 선언할 환경 변수와 값으로 구성한 문자열 ('환경 변수' = '값')
Return
(0 : Success)
name : 환경변수 이름
value : 값
overwrite : overwrite할 건지 확인 (0 : 덮어쓰기, 그 이외 : 덮어쓰지 않음)3.3 환경 변수 해제
#include <stdlib.h>
int unsetenv (const char *name);
///
name : 삭제할 환경 변수 이름
Return
(0 : Sucess, -1 : Error)