
연결리스트(Linked List)
연결 리스트는 일련의 원소를 배열처럼 차례대로 저장하지만, 원소들이 메모리상에 연속적으로 위치하지 않는다는 점이 다르다.
- 연속되는 항목들이 포인터로 연결된다.
- 마지막 항목은 Null을 가리킨다.
- 프로그램이 수행되는 동안 크기가 커지거나 작아질 수 있다.
- (시스템 메모리가 허용하는 한) 필요한 만큼 길어질 수 있다.
- 메모리 공간을 낭비하지 않는다.
- 배열에 비해 데이터의 추가/삽입 및 삭제가 용이하다.
- 순차적으로 탐색하지 않으면 특정 위치의 요소에 접근할 수 없어 일반적으로 탐색 속도가 떨어진다.
즉, 탐색 또는 정렬을 자주 하면 배열을, 추가/삭제가 많으면 연결 리스트를 사용하는 것이 유리하다.
노드(Node)
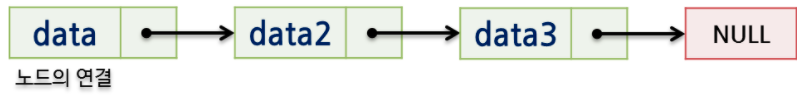
연결 리스트에서 각 원소는 원소 자신과 다음 원소를 가리키는 포인터가 포함된 노드로 구성된다.

위 그림에서 보이듯이 '데이터를 저장할 장소'와 '다른 변수를 가리키기 위한 장소'가 구분되어있다.
그래서 둘 이상의 Node가 연결된 상황은 이와 같다.
연결 리스트의 종류
- 단일 연결 리스트(Single Linked List)
단일 연결 리스트는 각 노드에 자료 공간과 한 개의 포인터 공간이 있고, 각 노드의 포인터는 다음 노드를 가리킨다. - 이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List)
이중 연결 리스트의 구조는 단일 연결 리스트와 비슷하지만, 포인터 공간이 두 개가 있고 각각의 포인터는 앞의 노드와 뒤의 노드를 가리킨다. - 원형(환형) 연결 리스트(Circular Linked List)
원형 연결 리스트는 일반적인 연결 리스트에 마지막 노드와 처음 노드를 연결시켜 원형으로 만든 구조이다. - 이중 원형(환형) 연결 리스트(Doubly Circular Linked List)
이중 원형 연결 리스트는 이중 연결 리스트의 마지막 노드와 처음 노드를 연결시켜 원형으로 만든 구조이다.
연결 리스트 구현
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this._size = 0;
}
// 주어진 값을 연결 리스트의 끝에 추가
addToTail(value) {
// 해당 함수가 실행 될 때마다 value값을 가지는 Node의 인스턴스 생성
let node = new Node(value);
// 최초 데이터를 생성 할 경우
if(!this.head) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
this._size++;
// 데이터가 1개 이상 존재할 경우
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
this._size++;
}
}
// 주어진 값을 찾아서 연결을 삭제
// 찾은 후 링크를 다시 연결
remove(value) {
// 값이 없을 경우
if(!this.head) {
return undefined;
}
// 삭제할 value가 head일 경우
if(this.head.value === value) {
this.head = this.head.next;
this._size--;
}
let previousNode = this.head;
let currentNode = this.head.next;
while(currentNode) {
if(currentNode.value === value) {
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
this._size--;
break;
} else {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
}
// 주어진 인덱스의 노드를 찾아서 반환
// 값이 아니라 노드를 반환해야함
// 해당 인텍스에 노드가 없다면 undefined 반환
getNodeAt(index) {
let currentNode = this.head;
if(this._size < index) {
return undefined;
} else {
for(let i = 0; i < this._size; i++) {
if(i === index) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
}
// 연결리스트에 주어진 값을 가지는 노드의 존재 여부 반환
contains(value) {
let currentNode = this.head;
while(currentNode) {
if(currentNode.value === value) {
return true;
}
currentNode =currentNode.next;
}
return false;
}
// 주어진 값의 인덱스 반환, 없을 경우 -1 반환
indexOf(value) {
let count = 0;
// 현재 인스턴스의 head
let currentNode = this.head;
// 현재 인스턴스 부터 next에 저장되어 있는 node를
// 모두 순회하면서 각 node의 value값이 파라미터와 같은지 확인
while(currentNode) {
if(currentNode.value === value) {
return count;
}
count++;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return -1;
}
size() {
return this._size;
}
}